This is a C library that brings up the libcanard, platform-specific drivers and serialization together to build a minimal DroneCAN application.
A minimal application includes the following protocol-features:
| № | type | message |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | broadcast | uavcan.protocol.NodeStatus |
| 2 | RPC-service | uavcan.protocol.GetNodeInfo |
| 3 | RPC-service | uavcan.protocol.param.* |
| 4 | RPC-service | uavcan.protocol.RestartNode |
| 5 | RPC-service | uavcan.protocol.GetTransportStats |
The following auxiliary features should be provided as well:
- actuator
- airspeed
- baro
- circuit status
- fuel tank
- esc
- ice
- indication
- power
- rangefinder
- gnss
- mag
- etc
The library should support the following platforms:
- Ubuntu: socketcan
- stm32f103: BXCAN based on platform specific
- stm32g0: FDCAN based on STM32 HAL
- stm32f103: DroneCAN/Serial based on STM32 HAL
- libparams v0.8.4 library.
- dronecan/libcanard
Add the following lines into CMakeLists.txt of your project:
# 1. Specify the CAN_PLATFORM. Options: bxcan, fdcan or socketcan.
set(CAN_PLATFORM socketcan)
# 2. Specify path to libparams and platform. Options: stm32f103, stm32g0b1, ubuntu.
set(LIBPARAMS_PATH ../../build/libparams)
set(LIBPARAMS_PLATFORM ubuntu)
# 3. Include the CMakeLists.txt
include(../../CMakeLists.txt)
# 4. Add DroneCAN related source files and headers to you target.
add_executable(${EXECUTABLE}
...
${DRONECAN_SOURCES}
...
)
target_include_directories(${EXECUTABLE} PRIVATE
...
${DRONECAN_HEADERS}
...
)1. Initialize
Include dronecan.h header and call uavcanInitApplication in the beginning of the application. Call uavcanSpinOnce periodically.
// Include dronecan.h header file
#include "dronecan.h"
// Initialize the library somewhere
const uint8_t node_id = 42;
auto init_res = uavcanInitApplication(node_id);
if (init_res < 0) {
// handle error here
}
// Spin it periodically:
while (true) {
...
uavcanSpinOnce();
...
}2. Add publisher
Adding a publisher is very easy. Include publisher.hpp header, create an instance of the required publisher and just call publish when you need. Here is a BatteryInfo publisher example:
#include "dronecan.h"
#include "publisher.hpp"
// Create an instance of the publisher
DronecanPublisher<BatteryInfo_t> battery_info_pub;
// Modify the message
battery_info_pub.msg.voltage = 10.0f;
// Publish the message
battery_info_pub.publish();Alternatively, you can create a periodic publisher:
const auto PUBLISH_RATE_HZ = 1.0f;
DronecanPeriodicPublisher<BatteryInfo_t> battery_info_pub(PUBLISH_RATE_HZ);
while (true) {
...
battery_info_pub.spinOnce();
...
}3. Add subscriber
Adding a subscriber is easy as well. Let's consider a RawCommand subscriber example. Include subscriber.hpp header, create a callback for your application and instance of the required subscriber, then initilize it.
// Include necessary header files
#include "dronecan.h"
#include "subscriber.hpp"
// Add a callback handler function
void rc_callback(const RawCommand_t& msg) {
std::cout << "Get RawCommand with " << (int)msg.size << " commands." << std::endl;
}
// Add the subscription:
DronecanSubscriber<RawCommand_t> raw_command_sub;
if (raw_command_sub.init(&rc_callback) < 0) {
// handle error
}Sometimes for subscriber you want to specify a filter. For example, you may want to subscribe on a specific command channel or sensor ID. Let's consider an ArrayCommand example with filter that will only pass the messages with actuator ID = 0.
static const uint8_t FILTER_ACTUATOR_ID = 0;
void ac_callback(const ArrayCommand_t& msg) {
std::cout << "Get ArrayCommand_t with " << msg.size << "commands." << std::endl;
}
bool ac_filter(const ArrayCommand_t& msg) {
for (size_t idx = 0; idx < msg.size; idx++) {
if (msg.commads[idx].actuator_id == FILTER_ACTUATOR_ID) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
DronecanSubscriber<ArrayCommand_t> array_command_sub;
array_command_sub.init(&ac_callback, &ac_filter);Run example
You can run a provided example in SITL mode. Just run:
git clone git@github.com:PonomarevDA/dronecan_application.git --recursive
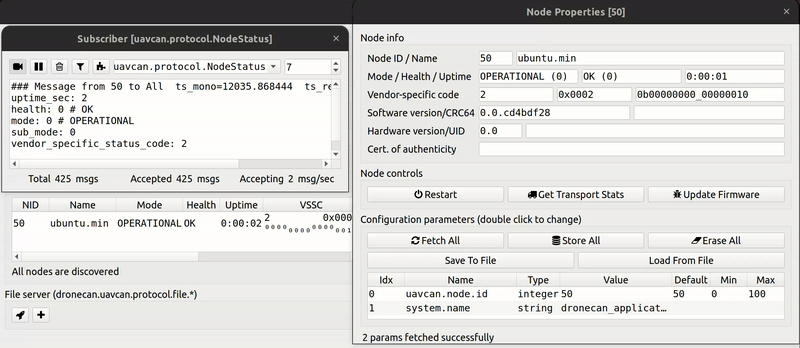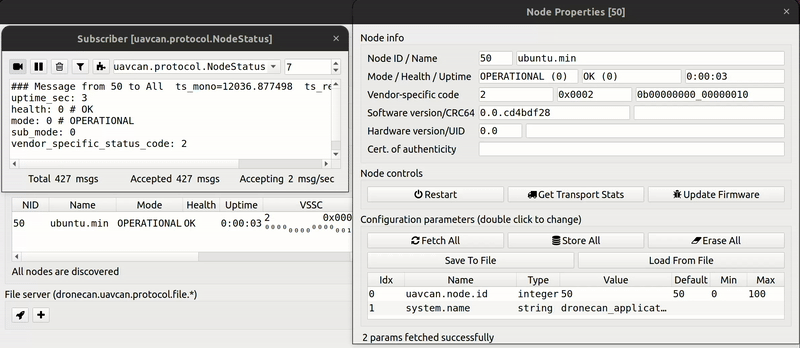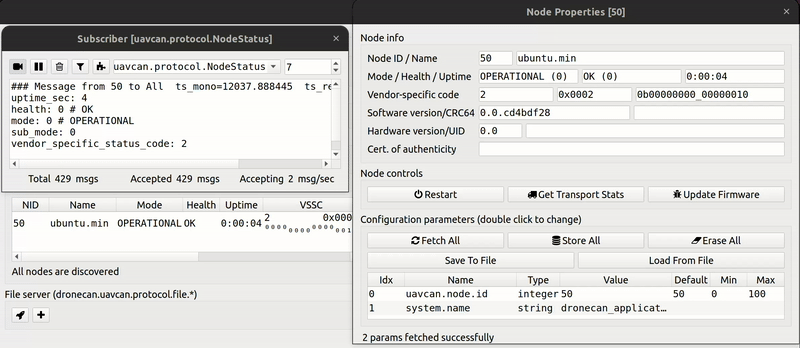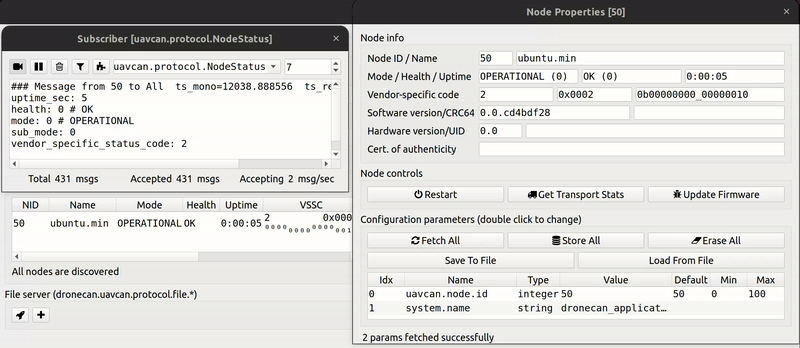
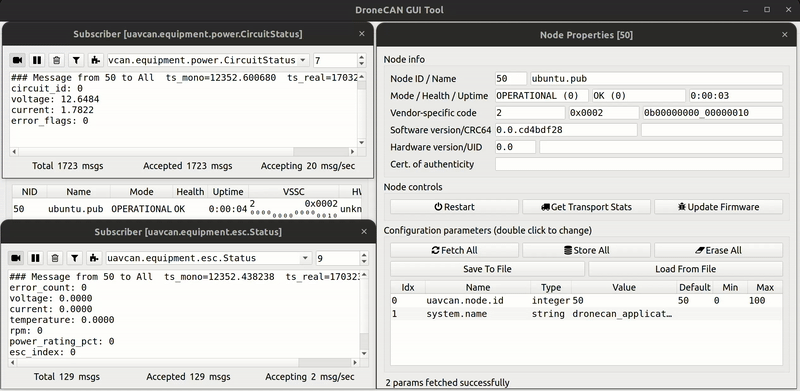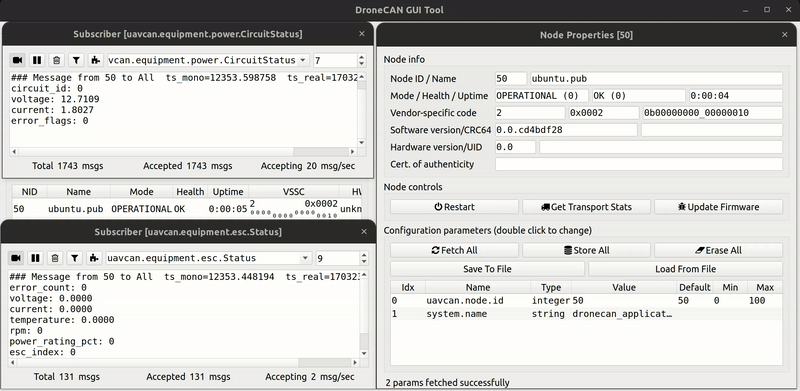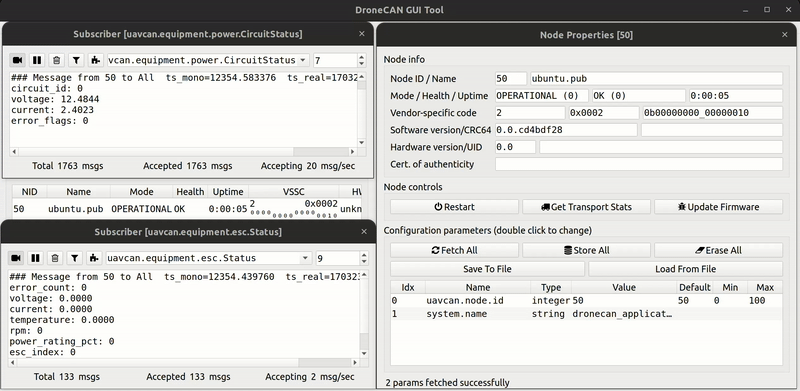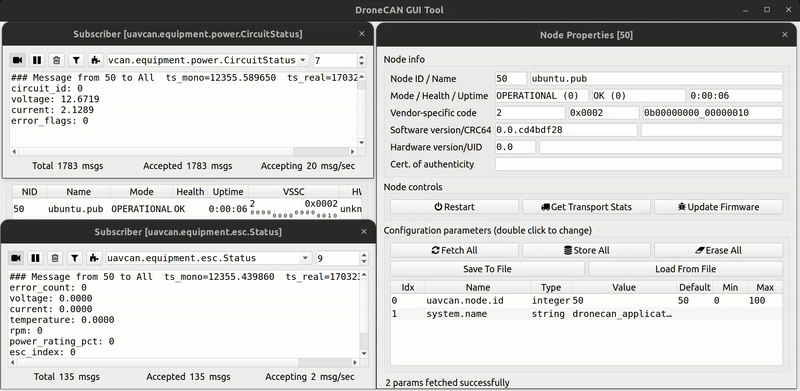
make ubuntuIn gui_tool you will see:
You can find the provided SITL application in examples/ubuntu folder.
There are a few functions that require an implementation. They are declared in include/application/dronecan_application_internal.h.
A user must provide the following function implementation:
/**
* @return the time in milliseconds since the application started.
* @note This function must be provided by a user!
*/
uint32_t platformSpecificGetTimeMs();A user may also provide the implementation of the optional functions. These function have a week implementation in src/weak.c.
/**
* @return whether the request will be processed
* True - the application will be restarted soon.
* False - the restarted is not supported or can't be handled at the moment.
* @note Implementation is recommended, but optional.
*/
bool platformSpecificRequestRestart();
/**
* @param[out] out_id - hardware Unique ID
* @note Implementation is recommended, but optional.
*/
void platformSpecificReadUniqueID(uint8_t out_uid[16]);The software is distributed under term of MPL v2.0 license.