5.0.0-31,latest4.5.0-51,4.4.2-46
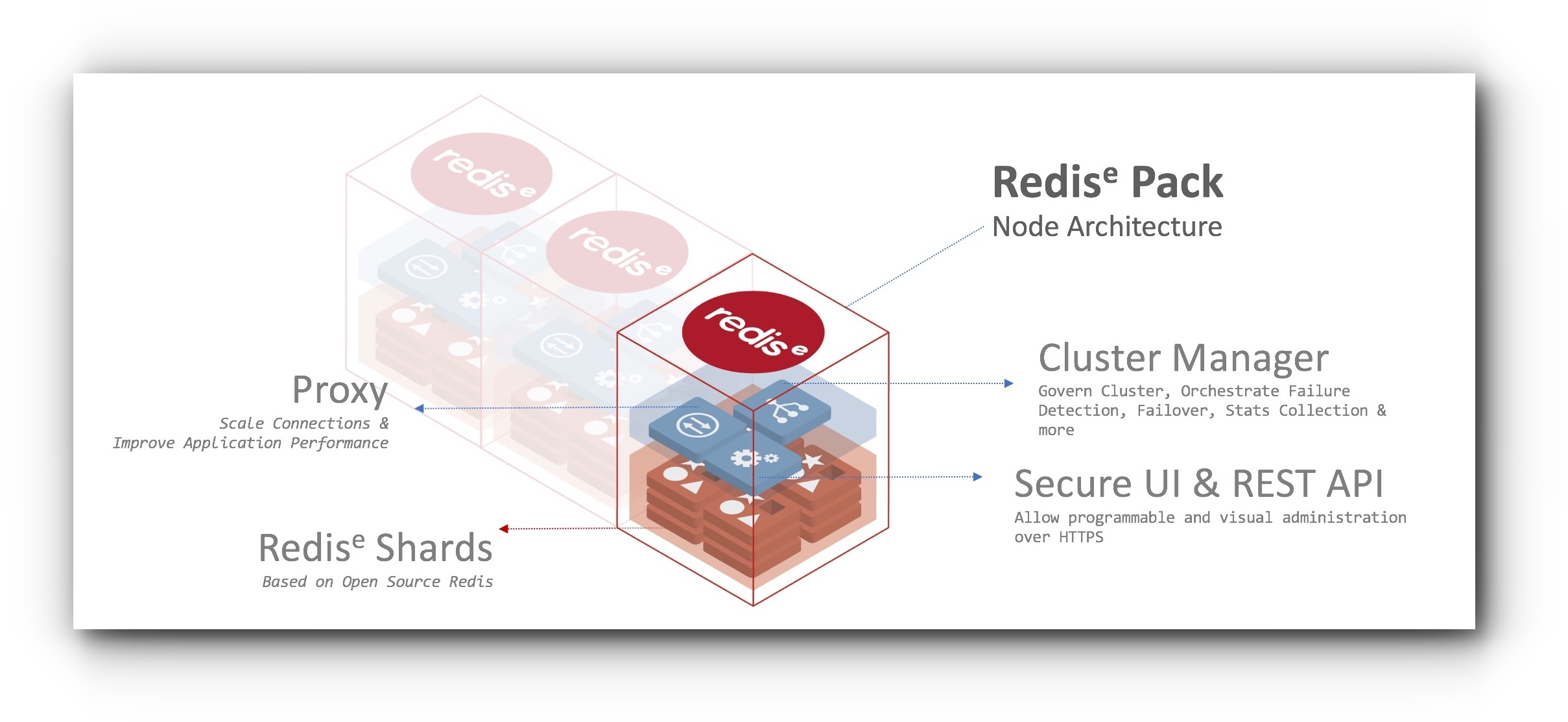
Redis Enterprise Software is enterprise grade, distributed, in-memory NoSQL database server, fully compatible with open source Redis by Redis Labs. Redis Enterprise Software extends open source Redis and delivers stable high performance, zero-downtime linear scaling and high availability, with significant operational savings.
- Redis Enterprise Software can use both RAM and Flash drives such as SSDs for data processing. See Redis on Flash) for details.
- Redis Enterprise Software can also support active-active geo-distributed applications with Redis CRDTs
- Redis Enterprise Software supports Redis Modules. See details at RediSearch, ReJSON and ReBloom
- Run the Redis Enterprise container
docker run -d --cap-add sys_resource --name rp -p 8443:8443 -p 9443:9443 -p 12000:12000 redislabs/redis
- Configure Redis Enterprise cluster using the
"rladmin"tool and"create cluster"command
docker exec -d --privileged rp "/opt/redislabs/bin/rladmin" cluster create name cluster.local username cihan@redislabs.com password redislabs123
- Create a database on Redis Enterprise cluster
curl -k -u "cihan@redislabs.com:redislabs123" --request POST --url "https://localhost:9443/v1/bdbs" --header 'content-type: application/json' --data '{"name":"db1","type":"redis","memory_size":102400,"port":12000}'
Note: Redis Enterprise may take a few seconds to start depending on your HW. if you receive the following message: "503 Service Unavailable", wait a few more seconds and repeat step-2 and step3 again.
- Connect to Redis database in Redis Enterprise cluster using
"redis-cli"
docker exec -it rp bash
# sudo /opt/redislabs/bin/redis-cli -p 12000
# 127.0.0.1:16653> set key1 123
# OK
# 127.0.0.1:16653> get key1
# "123"
#
You can run the Redis Enterprise Software linux based container on MacOS, various Linux and Windows based machines with Docker. Each Redis Enterprise Software container runs a cluster node. To get started, you can simply set up a one node cluster, create a database and connect your application to the database.
Note: Redis Enterprise Software Docker image works best when you provide a minimum of 2 cores and 6GB ram per container. You can find additional minimum hardware and software requirements for Redis Enterprise Software in the product documentation
- Run Redis Enterprise Software container
Port 8443 is used for the administration UI and port 12000 is reserved for the Redis database that will be created in Step #5 below.
docker run -d --cap-add sys_resource --name rp -p 8443:8443 -p 12000:12000 redislabs/redis
- Setup Redis Enterprise Software by visiting
https://localhost:8443on the host machine to see the RS Web Console
Note: You may see a certificate error with your browser. Simply choose "continue to the website" to get to the setup screen.
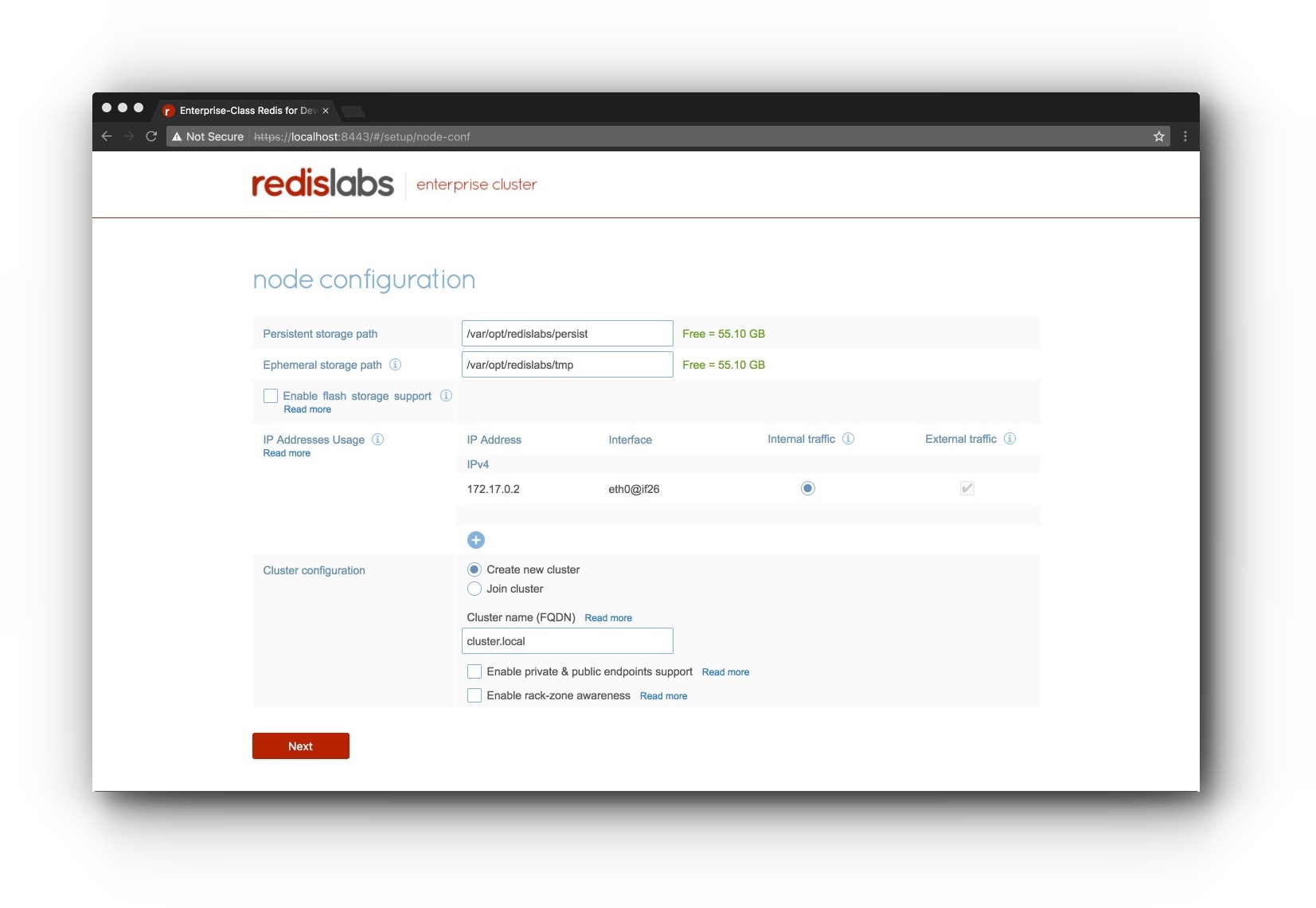
- Go with default settings and provide a cluster FQDN:
"cluster.local"
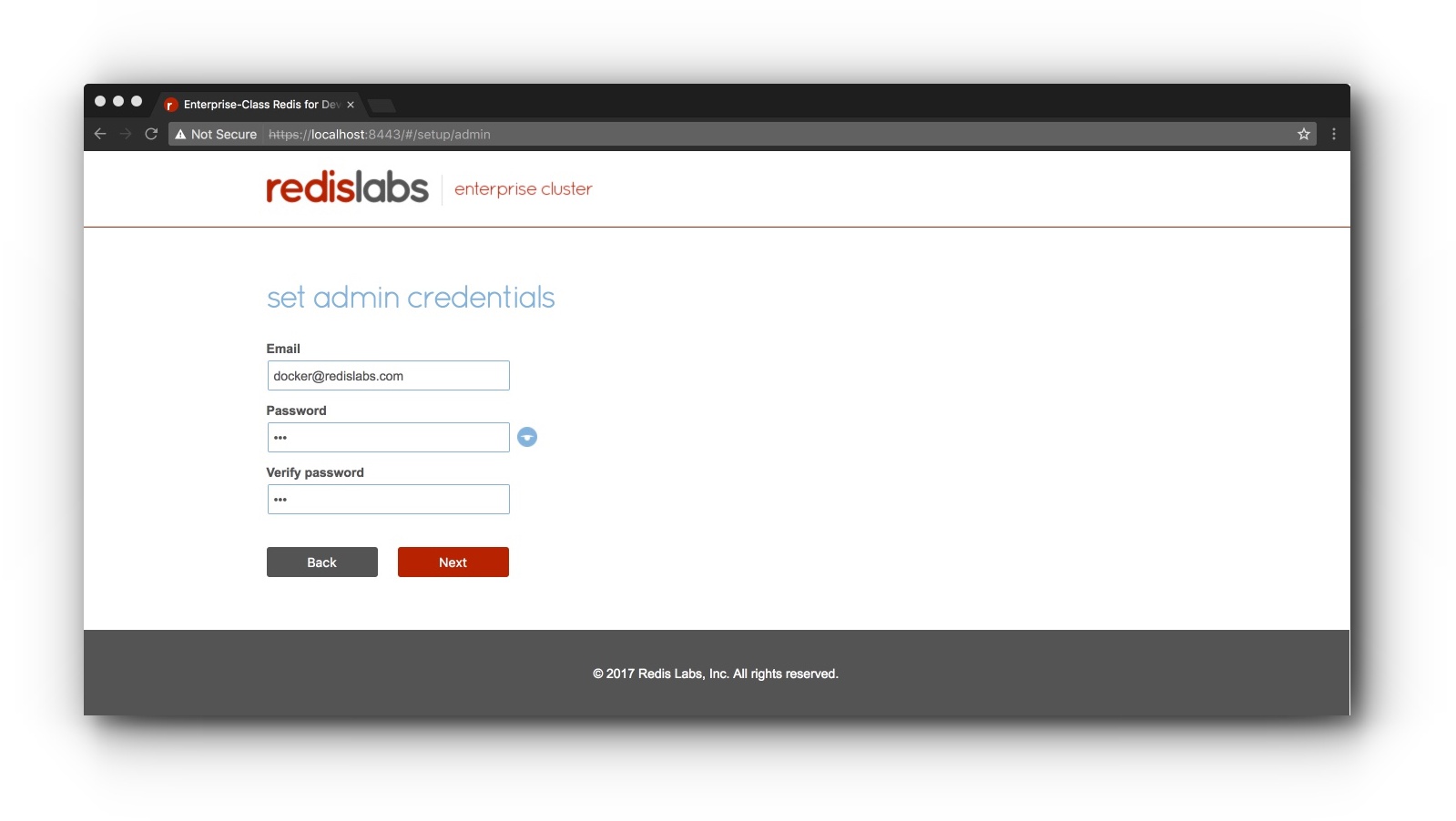
- Configure free trial & set up cluster admin account
If you don't have a license key, click "Next" to skip the license key screen to try the free version of the product. On the next screen, set up a cluster admin email and password.
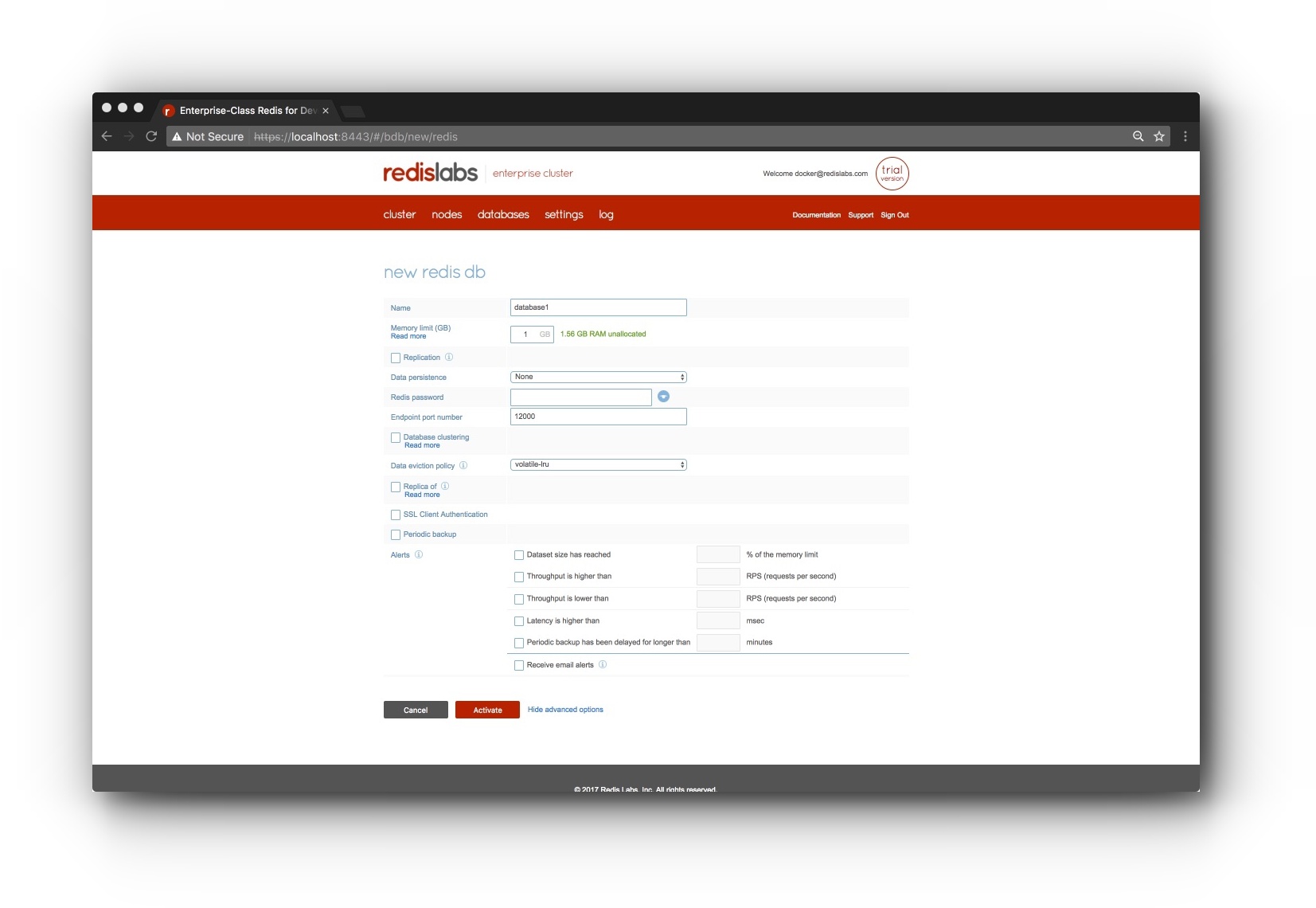
- Choose the new redis db option
In the new redis db screen, click the "show advanced option" link and provide a database name "database1", endpoint port number of "12000" and click "Activate" to create your database.
You now have a Redis database!
With the Redis database created, you are ready to connect to your database to store data. You can use redis-cli or your favorite language with Redis client driver to talk to the new database. There is a python based example below.
- Connect using
redis-cli:
redis-cli is a simple commandline tool to interact with a Redis instance. Use the following script to connect to the Redis Enterprise Software container, run redis-cli connecting to port 12000 and store and retrieve a key.
docker exec -it rp bash
# sudo /opt/redislabs/bin/redis-cli -p 12000
# 127.0.0.1:16653> set key1 123
# OK
# 127.0.0.1:16653> get key1
# "123"
#
- Connect using a Simple Python App:
If you don't have python or redis-py (python library for connecting to Redis) on the host, you can run the redis-py container.
Following section assumes you already have python and redis-py configured on the host machine running the container.
You can find the instructions to install redis-py on the github page for redis-py.
Paste the following into a file named "redis_test.py"
import redis
r = redis.StrictRedis(host='localhost', port=12000, db=0)
print ("set key1 123")
print (r.set('key1', '123'))
print ("get key1")
print(r.get('key1'))
Run redis_test.py application to connect to the database and store and retrieve a key.
python redis_test.py
The output should look like the following screen if the connection is successful.
# set key1 123
# True
# get key1
# b'123'
Supported Docker Versions:
Docker version 17.x or greater.
Getting Started
- Working with Redis Enterprise Software and Docker
- Getting Started with Redis Enterprise Software and Docker on Windows,
- Getting Started with Redis Enterprise Software and Docker on Mac OSx,
- Getting Started with Redis Enterprise Software and Docker on Linux
- Getting Started with Redis on Flash Databases
- Getting Started with Redis CRDTs
Detailed Documentation