Difficulty: 🟡 Medium
You are given two linked lists: list1 and list2 of sizes n and m respectively.
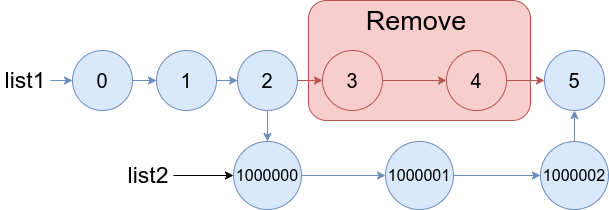
Remove list1's nodes from the ath node to the bth node, and put list2 in their place.
The blue edges and nodes in the following figure indicate the result:
Build the result list and return its head.
Example 1:
Input: list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5], a = 3, b = 4, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002]
Output: [0,1,2,1000000,1000001,1000002,5]
Explanation: We remove the nodes 3 and 4 and put the entire list2 in their place. The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
Example 2:
Input: list1 = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6], a = 2, b = 5, list2 = [1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004]
Output: [0,1,1000000,1000001,1000002,1000003,1000004,6]
Explanation: The blue edges and nodes in the above figure indicate the result.
3 <= list1.length <= 1041 <= a <= b < list1.length - 11 <= list2.length <= 104
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeInBetween(self, list1: ListNode, a: int, b: int, list2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
node = list1
for _ in range(a-1):
node = node.next
temp = node
for _ in range(a, b+1):
node = node.next
temp.next = list2
while temp.next:
temp = temp.next
temp.next = node.next
return list1The given solution uses a two-step approach to perform the required node replacement in list1.
The algorithm works as follows:
- Traverse
list1until the node before theath node, i.e.,a-1iterations. Set the current node astemp. - Traverse
list1from theath node to thebth node, i.e.,b-a+1iterations. Set the current node asnode. - Update
temp.nextto point tolist2. Traverselist2until the last node and settempas the last node. - Update
temp.nextto point to the node after thebth node. - Finally, return
list1with the replaced nodes.
The time complexity of this algorithm is O(n + m), where n is the length of list1 and m is the length of list2. The algorithm performs two traversals: one to reach the a-1th node in list1 and another to traverse list2 to reach its last node. Both traversals take O(n) and O(m) time, respectively.
The space complexity of the algorithm is O(1) since it only uses a constant amount of extra space for the temp and node pointers.
The given solution replaces a portion of nodes in list1 with list2 by traversing the linked lists and updating the necessary pointers. It has a time complexity of O(n + m) and a space complexity of O(1), making it an efficient solution for the problem at hand.
NB: If you want to get community points please suggest solutions in other languages as merge requests.