Given a circular integer array nums of length n, return the maximum possible sum of a non-empty subarray of nums.
A circular array means the end of the array connects to the beginning of the array. Formally, the next element of nums[i] is nums[(i + 1) % n] and the previous element of nums[i] is nums[(i - 1 + n) % n].
A subarray may only include each element of the fixed buffer nums at most once. Formally, for a subarray nums[i], nums[i + 1], ..., nums[j], there does not exist i <= k1, k2 <= j with k1 % n == k2 % n.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,-2,3,-2] Output: 3 Explanation: Subarray [3] has maximum sum 3
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,-3,5] Output: 10 Explanation: Subarray [5,5] has maximum sum 5 + 5 = 10
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,-1,2,-1] Output: 4 Explanation: Subarray [2,-1,3] has maximum sum 2 + (-1) + 3 = 4
Example 4:
Input: nums = [3,-2,2,-3] Output: 3 Explanation: Subarray [3] and [3,-2,2] both have maximum sum 3
Example 5:
Input: nums = [-2,-3,-1] Output: -1 Explanation: Subarray [-1] has maximum sum -1
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 3 * 104-3 * 104 <= nums[i] <= 3 * 104
[Queue] [Array] [Divide and Conquer] [Dynamic Programming] [Monotonic Queue]
Hint 1
For those of you who are familiar with the Kadane's algorithm, think in terms of that. For the newbies, Kadane's algorithm is used to finding the maximum sum subarray from a given array. This problem is a twist on that idea and it is advisable to read up on that algorithm first before starting this problem. Unless you already have a great algorithm brewing up in your mind in which case, go right ahead!Hint 2
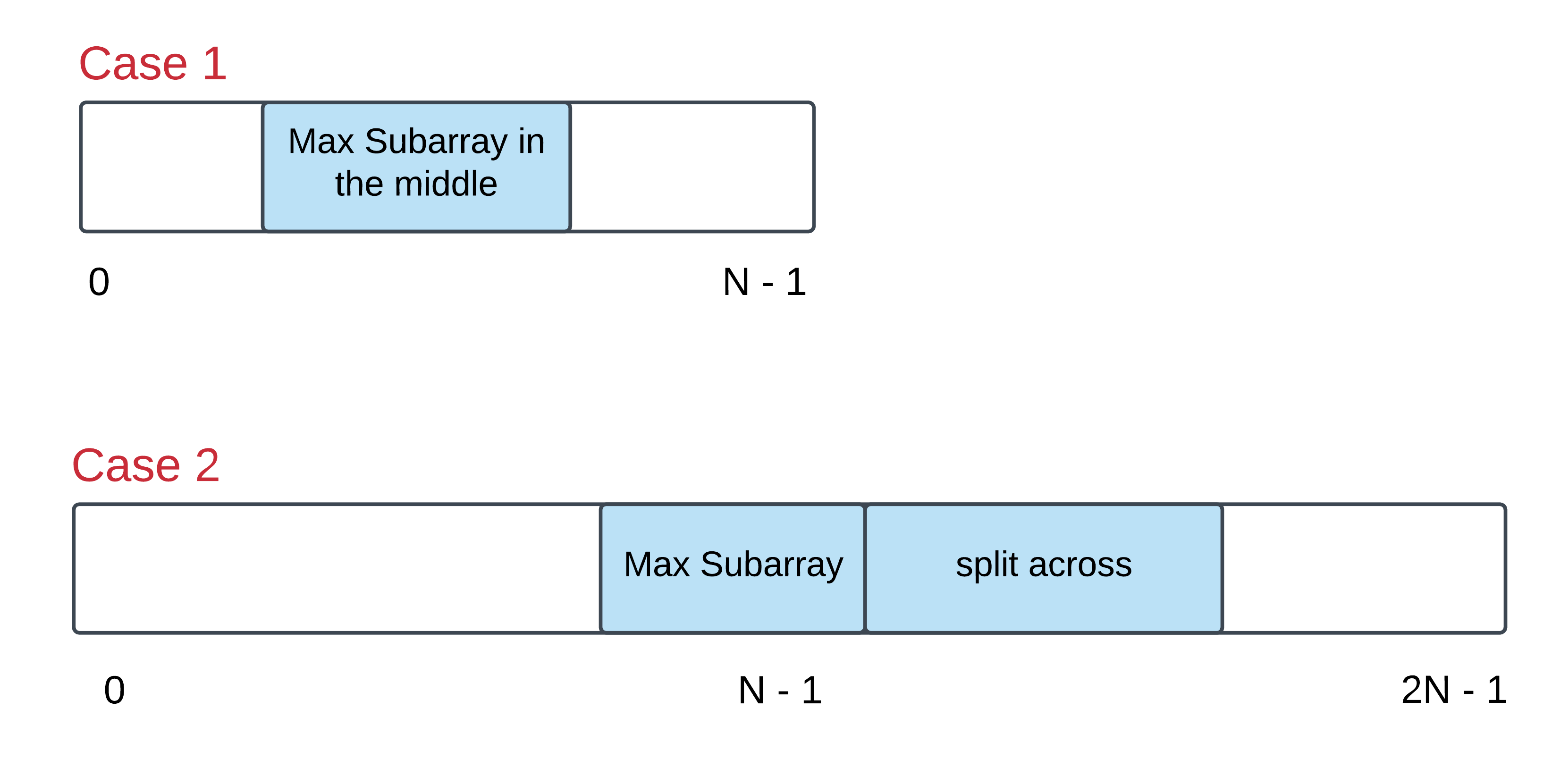
What is an alternate way of representing a circular array so that it appears to be a straight array? Essentially, there are two cases of this problem that we need to take care of. Let's look at the figure below to understand those two cases: