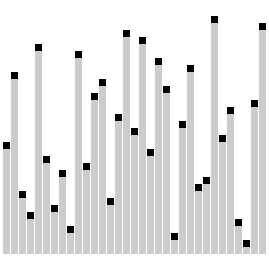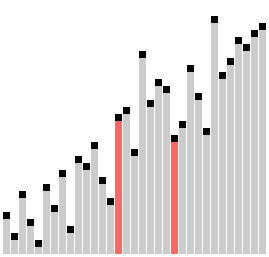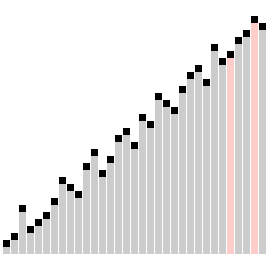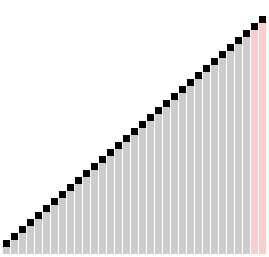
A common issue for Bubble Sort is when small values are located near the end of an array. This problem severely slows down Bubble Sort, as it must move the small value -- or turtle -- through nearly the entire array. Bubble Sort works by checking the current index of an array against the next index, and when those two values are unsorted, they are swapped into place. As a result, the values bubble into their rightful place within the array.
Comb Sort improves upon Bubble Sort by dealing with these turtles near the end of the array. The value of the current index of the array is compared against one a set distance away. This removes a worst-case scenario of Bubble Sort, and greatly improves on the time complexity of Bubble Sort.
A step-by-step example of how Comb Sort works, and differs from Bubble Sort, can be seen here.
Here is a visual to see Comb Sort in effect:
Similar to Bubble Sort, two values within an array are compared. When the lower index value is larger than the higher index value, and thus out of place within the array, they are swapped. Unlike Bubble Sort, the value being compared against is a set distance away. This value -- the gap -- is slowly decreased through iterations.
Here is a Swift implementation of Comb Sort:
func combSort (input: [Int]) -> [Int] {
var copy: [Int] = input
var gap = copy.count
let shrink = 1.3
while gap > 1 {
gap = (Int)(Double(gap) / shrink)
if gap < 1 {
gap = 1
}
var index = 0
while !(index + gap >= copy.count) {
if copy[index] > copy[index + gap] {
swap(©[index], ©[index + gap])
}
index += 1
}
}
return copy
}This code can be tested in a playground by calling this method with a paramaterized array to sort:
combSort(example_array_of_values)This will sort the values of the array into ascending order -- increasing in value.
Comb Sort was created to improve upon the worst case time complexity of Bubble Sort. With Comb Sort, the worst case scenario for performance is polynomial -- O(n^2). At best though, Comb Sort performs at O(n logn) time complexity -- loglinear. This creates a drastic improvement over Bubble Sort's performance.
Similar to Bubble Sort, the space complexity for Comb Sort is constant -- O(1). This is extremely space efficient as it sorts the array in place.
Written for the Swift Algorithm Club by Stephen Rutstein