数据的校验的重要性就不用说了,即使在前端对数据进行校验的情况下,我们还是要对传入后端的数据再进行一遍校验,避免用户绕过浏览器直接通过一些 HTTP 工具直接向后端请求一些违法数据。
本文结合自己在项目中的实际使用经验,可以说文章介绍的内容很实用,不了解的朋友可以学习一下,后面可以立马实践到项目上去。
下面我会通过实例程序演示如何在 Java 程序中尤其是 Spring 程序中优雅地的进行参数验证。
如果开发普通 Java 程序的的话,你需要可能需要像下面这样依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.0.9.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.el</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.el-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfish.web</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.el</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6</version>
</dependency>使用 Spring Boot 程序的话只需要spring-boot-starter-web 就够了,它的子依赖包含了我们所需要的东西。除了这个依赖,下面的演示还用到了 lombok ,所以不要忘记添加上相关依赖。
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>下面这个是示例用到的实体类。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Person {
@NotNull(message = "classId 不能为空")
private String classId;
@Size(max = 33)
@NotNull(message = "name 不能为空")
private String name;
@Pattern(regexp = "((^Man$|^Woman$|^UGM$))", message = "sex 值不在可选范围")
@NotNull(message = "sex 不能为空")
private String sex;
@Email(message = "email 格式不正确")
@NotNull(message = "email 不能为空")
private String email;
}正则表达式说明:
- ^string : 匹配以 string 开头的字符串 - string$ :匹配以 string 结尾的字符串 - ^string$ :精确匹配 string 字符串 - ((^Man$|^Woman$|^UGM$)) : 值只能在 Man,Woman,UGM 这三个值中选择
下面这部分校验注解说明内容参考自:https://www.cnkirito.moe/spring-validation/ ,感谢@徐靖峰。
JSR提供的校验注解:
@Null被注释的元素必须为 null@NotNull被注释的元素必须不为 null@AssertTrue被注释的元素必须为 true@AssertFalse被注释的元素必须为 false@Min(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值@Max(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值@DecimalMin(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值@DecimalMax(value)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值@Size(max=, min=)被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内@Digits (integer, fraction)被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内@Past被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期@Future被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期@Pattern(regex=,flag=)被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式
Hibernate Validator提供的校验注解:
@NotBlank(message =)验证字符串非null,且长度必须大于0@Email被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址@Length(min=,max=)被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内@NotEmpty被注释的字符串的必须非空@Range(min=,max=,message=)被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内
Controller:
我们在需要验证的参数上加上了@Valid注解,如果验证失败,它将抛出MethodArgumentNotValidException。默认情况下,Spring会将此异常转换为HTTP Status 400(错误请求)。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class PersonController {
@PostMapping("/person")
public ResponseEntity<Person> getPerson(@RequestBody @Valid Person person) {
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(person);
}
}ExceptionHandler:
自定义异常处理器可以帮助我们捕获异常,并进行一些简单的处理。如果对于下面的处理异常的代码不太理解的话,可以查看这篇文章 《SpringBoot 处理异常的几种常见姿势》。
@ControllerAdvice(assignableTypes = {PersonController.class})
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> handleValidationExceptions(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
Map<String, String> errors = new HashMap<>();
ex.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().forEach((error) -> {
String fieldName = ((FieldError) error).getField();
String errorMessage = error.getDefaultMessage();
errors.put(fieldName, errorMessage);
});
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).body(errors);
}
}通过测试验证:
下面我通过 MockMvc 模拟请求 Controller 的方式来验证是否生效,当然你也可以通过 Postman 这种工具来验证。
我们试一下所有参数输入正确的情况。
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class PersonControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Test
public void should_get_person_correctly() throws Exception {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("SnailClimb");
person.setSex("Man");
person.setClassId("82938390");
person.setEmail("Snailclimb@qq.com");
mockMvc.perform(post("/api/person")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person)))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("name").value("SnailClimb"))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("classId").value("82938390"))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("sex").value("Man"))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("email").value("Snailclimb@qq.com"));
}
}验证出现参数不合法的情况抛出异常并且可以正确被捕获。
@Test
public void should_check_person_value() throws Exception {
Person person = new Person();
person.setSex("Man22");
person.setClassId("82938390");
person.setEmail("SnailClimb");
mockMvc.perform(post("/api/person")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(person)))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("sex").value("sex 值不在可选范围"))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("name").value("name 不能为空"))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("email").value("email 格式不正确"));
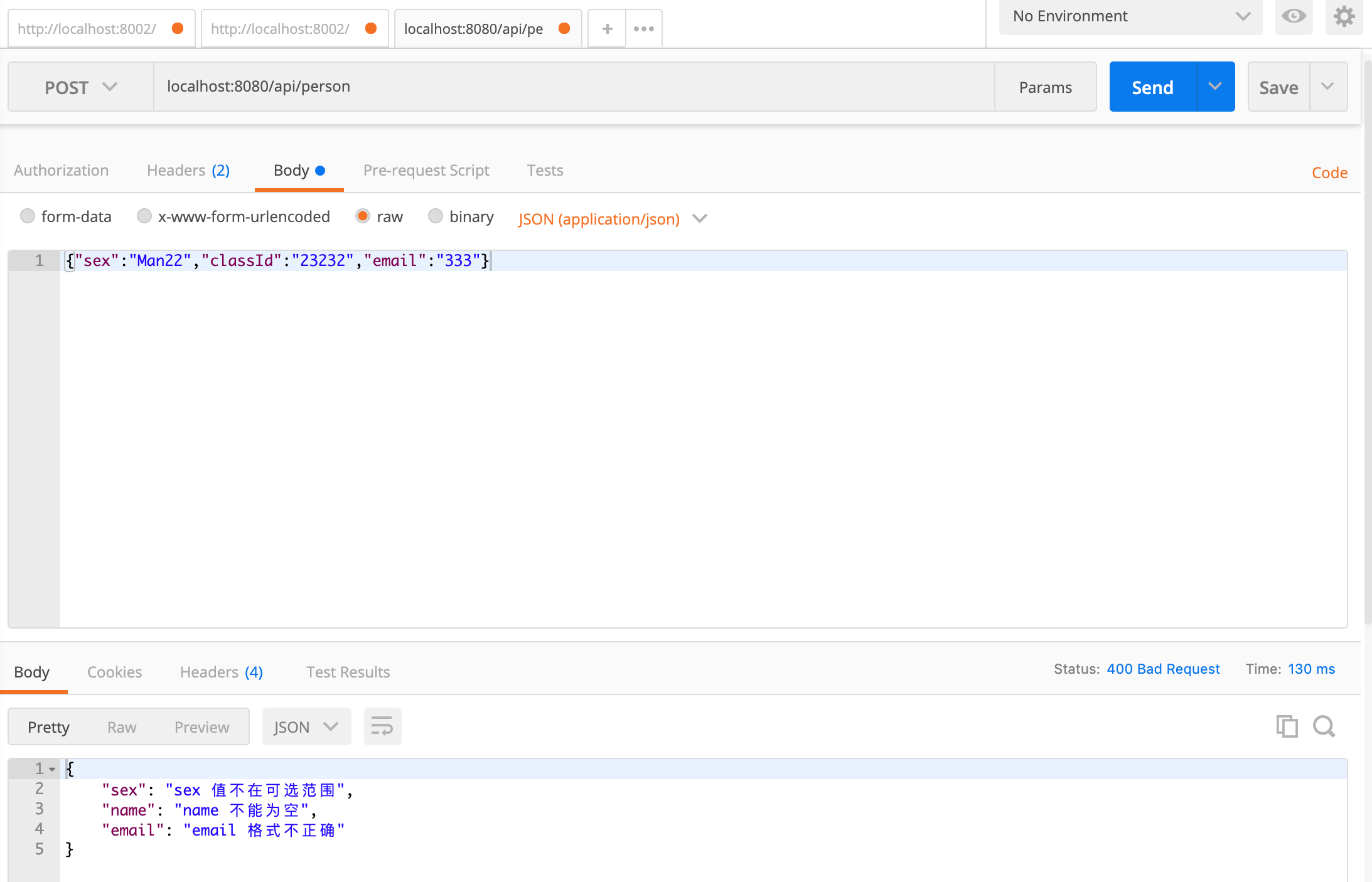
}使用 Postman 验证结果如下:
Controller:
一定一定不要忘记在类上加上 Validated 注解了,这个参数可以告诉 Spring 去校验方法参数。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
@Validated
public class PersonController {
@GetMapping("/person/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Integer> getPersonByID(@Valid @PathVariable("id") @Max(value = 5,message = "超过 id 的范围了") Integer id) {
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(id);
}
@PutMapping("/person")
public ResponseEntity<String> getPersonByName(@Valid @RequestParam("name") @Size(max = 6,message = "超过 name 的范围了") String name) {
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(name);
}
}ExceptionHandler:
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
ResponseEntity<String> handleConstraintViolationException(ConstraintViolationException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).body(e.getMessage());
}通过测试验证:
@Test
public void should_check_param_value() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/api/person/6")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
.andExpect(status().isBadRequest())
.andExpect(content().string("getPersonByID.id: 超过 id 的范围了"));
}
@Test
public void should_check_param_value2() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(put("/api/person")
.param("name","snailclimbsnailclimb")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8))
.andExpect(status().isBadRequest())
.andExpect(content().string("getPersonByName.name: 超过 name 的范围了"));
}我们还可以验证任何Spring组件的输入,而不是验证控制器级别的输入,我们可以使用@Validated和@Valid注释的组合来实现这一需求。
一定一定不要忘记在类上加上 Validated 注解了,这个参数可以告诉 Spring 去校验方法参数。
@Service
@Validated
public class PersonService {
public void validatePerson(@Valid Person person){
// do something
}
}通过测试验证:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class PersonServiceTest {
@Autowired
private PersonService service;
@Test(expected = ConstraintViolationException.class)
public void should_throw_exception_when_person_is_not_valid() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setSex("Man22");
person.setClassId("82938390");
person.setEmail("SnailClimb");
service.validatePerson(person);
}
}某些场景下可能会需要我们手动校验并获得校验结果。
@Test
public void check_person_manually() {
ValidatorFactory factory = Validation.buildDefaultValidatorFactory();
Validator validator = factory.getValidator();
Person person = new Person();
person.setSex("Man22");
person.setClassId("82938390");
person.setEmail("SnailClimb");
Set<ConstraintViolation<Person>> violations = validator.validate(person);
//output:
//email 格式不正确
//name 不能为空
//sex 值不在可选范围
for (ConstraintViolation<Person> constraintViolation : violations) {
System.out.println(constraintViolation.getMessage());
}
}上面我们是通过 Validator 工厂类获得的 Validator 示例,当然你也可以通过 @Autowired 直接注入的方式。但是在非 Spring Component 类中使用这种方式的话,只能通过工厂类来获得 Validator。
@Autowired
Validator validate如果自带的校验注解无法满足你的需求的话,你还可以自定义实现注解。
比如我们现在多了这样一个需求:Person类多了一个 region 字段,region 字段只能是China、China-Taiwan、China-HongKong这三个中的一个。
第一步你需要创建一个注解:
@Target({FIELD})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
@Constraint(validatedBy = RegionValidator.class)
@Documented
public @interface Region {
String message() default "Region 值不在可选范围内";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}第二步你需要实现 ConstraintValidator接口,并重写isValid 方法:
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class RegionValidator implements ConstraintValidator<Region, String> {
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
HashSet<Object> regions = new HashSet<>();
regions.add("China");
regions.add("China-Taiwan");
regions.add("China-HongKong");
return regions.contains(value);
}
}现在你就可以使用这个注解:
@Region
private String region;校验我们的电话号码是否合法,这个可以通过正则表达式来做,相关的正则表达式都可以在网上搜到,你甚至可以搜索到针对特定运营商电话号码段的正则表达式。
PhoneNumber.java
import javax.validation.Constraint;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD;
import static java.lang.annotation.ElementType.PARAMETER;
import static java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = PhoneNumberValidator.class)
@Target({FIELD, PARAMETER})
@Retention(RUNTIME)
public @interface PhoneNumber {
String message() default "Invalid phone number";
Class[] groups() default {};
Class[] payload() default {};
}PhoneNumberValidator.java
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidator;
import javax.validation.ConstraintValidatorContext;
public class PhoneNumberValidator implements ConstraintValidator<PhoneNumber,String> {
@Override
public boolean isValid(String phoneField, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
if (phoneField == null) {
// can be null
return true;
}
return phoneField.matches("^1(3[0-9]|4[57]|5[0-35-9]|8[0-9]|70)\\d{8}$") && phoneField.length() > 8 && phoneField.length() < 14;
}
}搞定,我们现在就可以使用这个注解了。
@PhoneNumber(message = "phoneNumber 格式不正确")
@NotNull(message = "phoneNumber 不能为空")
private String phoneNumber;某些场景下我们需要使用到验证组,这样说可能不太清楚,说简单点就是对对象操作的不同方法有不同的验证规则,示例如下(这个就我目前经历的项目来说使用的比较少,因为本身这个在代码层面理解起来是比较麻烦的,然后写起来也比较麻烦)。
先创建两个接口:
public interface AddPersonGroup {
}
public interface DeletePersonGroup {
}我们可以这样去使用验证组
@NotNull(groups = DeletePersonGroup.class)
@Null(groups = AddPersonGroup.class)
private String group;@Service
@Validated
public class PersonService {
public void validatePerson(@Valid Person person) {
// do something
}
@Validated(AddPersonGroup.class)
public void validatePersonGroupForAdd(@Valid Person person) {
// do something
}
@Validated(DeletePersonGroup.class)
public void validatePersonGroupForDelete(@Valid Person person) {
// do something
}
}通过测试验证:
@Test(expected = ConstraintViolationException.class)
public void should_check_person_with_groups() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setSex("Man22");
person.setClassId("82938390");
person.setEmail("SnailClimb");
person.setGroup("group1");
service.validatePersonGroupForAdd(person);
}
@Test(expected = ConstraintViolationException.class)
public void should_check_person_with_groups2() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setSex("Man22");
person.setClassId("82938390");
person.setEmail("SnailClimb");
service.validatePersonGroupForDelete(person);
}使用验证组这种方式的时候一定要小心,这是一种反模式,还会造成代码逻辑性变差。
在使用 JPA 操作数据的时候会经常碰到 @Column(nullable = false) 这种类型的约束,那么它和 @NotNull 有何区别呢?搞清楚这个还是很重要的!
@NotNull是 JSR 303 Bean验证批注,它与数据库约束本身无关。@Column(nullable = false): 是JPA声明列为非空的方法。
总结来说就是即前者用于验证,而后者则用于指示数据库创建表的时候对表的约束。
- 原理分析