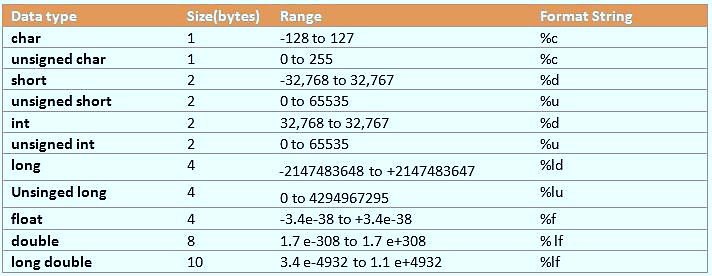
There are several data types, which can be broadly classified as follows
-
char 1 byte, stores characters or small integers.
-
short int (or short) 2 bytes, stores small integers.
-
int 2 or 4 bytes (depending on the system), stores integers.
-
long int (or long) 4 or 8 bytes (depending on the system), stores large integers.
-
long long int (or long long): 8 bytes, stores very large integers (C99 and later).
-
unsigned char 1 byte, stores positive values of characters or small integers.
-
**unsigned short int (or unsigned short): 2 bytes, stores positive values of small integers.
-
unsigned int 2 or 4 bytes (depending on the system), stores positive values of integers.
-
unsigned long int (or unsigned long) 4 or 8 bytes (depending on the system), stores positive values of large integers.
-
unsigned long long int (or unsigned long long) 8 bytes, stores positive values of very large integers (C99 and later).
-
float 4 bytes, stores single-precision floating-point numbers.
-
double 8 bytes, stores double-precision floating-point numbers.
-
long double 8 or 16 bytes (depending on the system), stores extended-precision floating-point numbers.
-
Array A collection of elements of the same data type.
-
Pointer A variable that stores the memory address of another variable.
-
Structure A user-defined data type that groups multiple variables of different data types under one name.
-
Union A user-defined data type that can hold different data types but uses the same memory location.
In C, union and struct are both used to define custom data types that can hold multiple values of different data types. However, they have some key differences in how they store and access data
struct A struct is a user-defined data type that groups different variables of various data types together. Each variable in the struct is called a member, and they all have their own memory space.
union A union is also a user-defined data type that allows different variables to share the same memory space.
-
struct Each member in a struct has its own memory space, and the total memory used by the struct is the sum of the memory sizes of its members.
-
union A union shares memory among its members. The size of a union is equal to the size of its largest member.
-
struct You can access each member of a struct independently using the dot operator (.).
-
union You can only access one member of a union at a time. Since all members share the same memory, changing the value of one member will overwrite the values of other members.
- Enum Used to define a custom data type consisting of a set of named constants called enumerators.
Enums help improve code readability, maintainability, and robustness. They are a powerful tool to create self-documenting and expressive code by giving meaningful names to related integer constants.
- void Represents the absence of a type or an empty return type in functions.