源码API:support-v4-23.4.0
因为 App 的内存限制,出现OOM的错误,导致我们不得不关注一些底层数据结构以及去分析 App 的内存使用情况。
HashMap在扩容时采取的做法是:将当前的数据结构所占空间 * 2,而这对稀缺的资源来说,可是非常大的消耗。
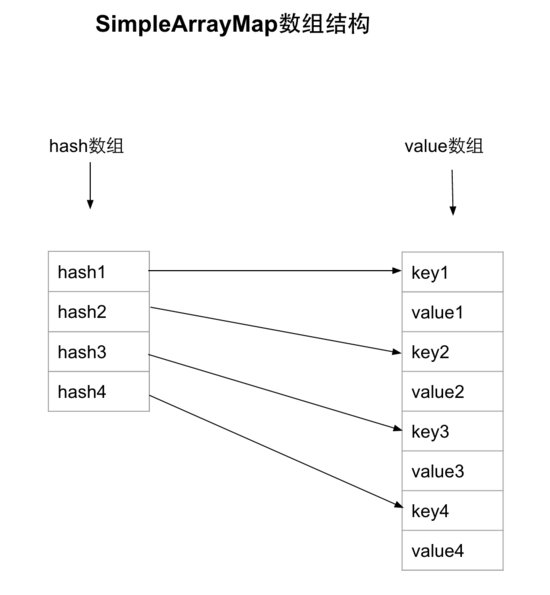
- SimpleArrayMap —— 采用了两个数组来进行
hash值与key、value值得保存,另外,数组大小超过8时,并需要进行扩容时,只增大当前数组大小的一半,并对大小为4和8的数组进行缓存。 - ArrayMap —— 继承了
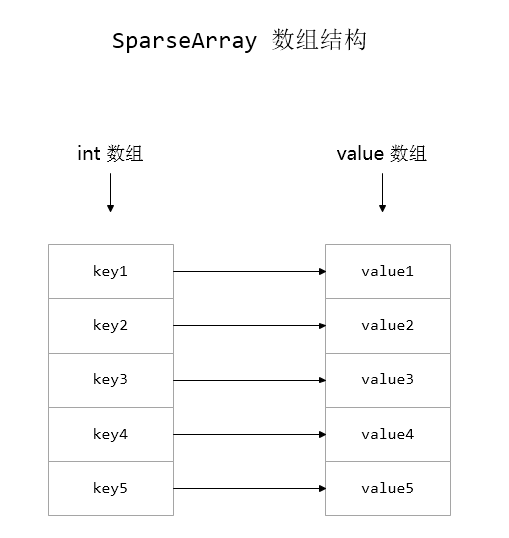
SimpleArrayMap,又实现了Map的接口;主要的操作,则是通过引入MapCollections类,使用Map中的Entry结构,这样在ArrayMap中就可以通过Iterator来进行数据的的迭代操作。 - SparseArray —— 采用了两个数组来进行
key、value值得保存,只能存储key为int类型的数据,免了对 key 的自动装箱(int转为Integer类型)
这三个类存取的数量不能过多,过多时,二分查找效率会很低。过多就是用 HashMap。
使用了两个数组,一个是 Hash 数组,另一个是大小2的 Object 数组。Object 数组中使用 key+value 间隔存取的方式;另外 Hash 数组,则是对应的 Key 的 Hash 值数组,并且这是一个有序的 int 数组,这样在进行 Key 的查找时,使用二分查找则是最有效率的方式了。
int[] mHashes; // hash 数据
Object[] mArray; // key+value 数组
int mSize; public SimpleArrayMap() {
// 默认为两个空数组
mHashes = ContainerHelpers.EMPTY_INTS;
mArray = ContainerHelpers.EMPTY_OBJECTS;
// 大小为 0
mSize = 0;
} public V put(K key, V value) {
final int hash;
int index;
if (key == null) {
// key 为 null 的情况,
hash = 0;
index = indexOfNull();
} else {
hash = key.hashCode();
// 根据 key 的 hash 值进行查找
index = indexOf(key, hash);
}
if (index >= 0) {
// 数组中存在相同的 key,则更新并返回旧的值
index = (index<<1) + 1;
final V old = (V)mArray[index];
mArray[index] = value;
return old;
}
index = ~index;
// 判断容量是否足够
if (mSize >= mHashes.length) {
// 第一次是 mSize=0,增加为 BASE_SIZE=4
// 第二次是 mSize=4,增加为 BASE_SIZE*2=8
// 第三次是 mSize=8,增加为 mSize+(mSize>>1)=12
// 第四次是 mSize=8,增加为 mSize+(mSize>>1)=18
// ....
final int n = mSize >= (BASE_SIZE*2) ? (mSize+(mSize>>1))
: (mSize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE*2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n);
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + mSize + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, mSize);
}
if (index < mSize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: move " + index + "-" + (mSize-index)
+ " to " + (index+1));
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index, mHashes, index + 1, mSize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, index << 1, mArray, (index + 1) << 1, (mSize - index) << 1);
}
// 添加数据
mHashes[index] = hash;
mArray[index<<1] = key;
mArray[(index<<1)+1] = value;
mSize++;
return null;
}
int indexOf(Object key, int hash) {
final int N = mSize;
// 当 mSize=0,是直接返回
if (N == 0) {
return ~0;
}
// 二分查找
int index = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mHashes, N, hash);
// 没有查到,直接返回
if (index < 0) {
return index;
}
// 查到,判断 key 是否相等(hash 会相等),相等说明存在,直接返回
// 进行数据替换
if (key.equals(mArray[index<<1])) {
return index;
}
// hash 值相同,key 不同,循环查询,向后
int end;
for (end = index + 1; end < N && mHashes[end] == hash; end++) {
if (key.equals(mArray[end << 1])) return end;
}
// hash 值相同,key 不同,循环查询,向前
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0 && mHashes[i] == hash; i--) {
if (key.equals(mArray[i << 1])) return i;
}
// 没,直接返回
return ~end;
} public V get(Object key) {
// 二分查找到 key 的位置
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
// 返回 value
return index >= 0 ? (V)mArray[(index<<1)+1] : null;
} public V remove(Object key) {
// 二分查找到 key 的位置
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
if (index >= 0) {
return removeAt(index);
}
return null;
}static Object[] mBaseCache;
static int mBaseCacheSize;
static Object[] mTwiceBaseCache;
static int mTwiceBaseCacheSize;代码中有两个静态的 Object 数组,这两个静态数组采用链表的方式来缓存所有的数组。即 Object 数组会用来指向 array 数组,而这个 array 的第一个值为指针,指向下一个 array,而第二个值是对应的 hash 数组,其他的值则为空。另外,缓存数组即 baseCache 和 twiceBaseCache,它俩大小容量的限制:最小值为4,最大值为10,而 BaseCache 数组主要存储的是容量为4的数组,twiceBaseCache 主要存储容量为8的数组。
// 缓存
private static void freeArrays(final int[] hashes, final Object[] array, final int size) {
if (hashes.length == (BASE_SIZE*2)) {
synchronized (ArrayMap.class) {
if (mTwiceBaseCacheSize < CACHE_SIZE) {
array[0] = mTwiceBaseCache;
array[1] = hashes;
for (int i=(size<<1)-1; i>=2; i--) {
array[i] = null;
}
mTwiceBaseCache = array;
mTwiceBaseCacheSize++;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Storing 2x cache " + array
+ " now have " + mTwiceBaseCacheSize + " entries");
}
}
} else if (hashes.length == BASE_SIZE) {
synchronized (ArrayMap.class) {
if (mBaseCacheSize < CACHE_SIZE) {
array[0] = mBaseCache;
array[1] = hashes;
for (int i=(size<<1)-1; i>=2; i--) {
array[i] = null;
}
mBaseCache = array;
mBaseCacheSize++;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Storing 1x cache " + array
+ " now have " + mBaseCacheSize + " entries");
}
}
}
}
// 读取
private void allocArrays(final int size) {
if (size == (BASE_SIZE*2)) {
synchronized (ArrayMap.class) {
if (mTwiceBaseCache != null) {
final Object[] array = mTwiceBaseCache;
mArray = array;
mTwiceBaseCache = (Object[])array[0];
mHashes = (int[])array[1];
array[0] = array[1] = null;
mTwiceBaseCacheSize--;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Retrieving 2x cache " + mHashes
+ " now have " + mTwiceBaseCacheSize + " entries");
return;
}
}
} else if (size == BASE_SIZE) {
synchronized (ArrayMap.class) {
if (mBaseCache != null) {
final Object[] array = mBaseCache;
mArray = array;
mBaseCache = (Object[])array[0];
mHashes = (int[])array[1];
array[0] = array[1] = null;
mBaseCacheSize--;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Retrieving 1x cache " + mHashes
+ " now have " + mBaseCacheSize + " entries");
return;
}
}
}
mHashes = new int[size];
mArray = new Object[size<<1];
}继承了 SimpleArrayMap,又实现了Map的接口;主要的操作,则是通过引入 MapCollections 类,使用 Map 中的 Entry 结构,这样在 ArrayMap 中就可以通过 Iterator 来进行数据的的迭代操作。
采用了两个数组来进行 key、value 值得保存,只能存储 key 为 int 类型的数据,免了对 key 的自动装箱(int转为Integer类型)
private int[] mKeys; // key 数组
private Object[] mValues; // values 数组
private int mSize; public SparseArray() {
this(10);
}
public SparseArray(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0) {
mKeys = EmptyArray.INT;
mValues = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
mValues = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedObjectArray(initialCapacity);
mKeys = new int[mValues.length];
}
mSize = 0;
}存取数据有两种方式 put、append
public void put(int key, E value) {
// 二分查找
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
// 查找到,替换
mValues[i] = value;
} else {
i = ~i;
// 空间满足,插入数据
if (i < mSize && mValues[i] == DELETED) {
mKeys[i] = key;
mValues[i] = value;
return;
}
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
gc();
// Search again because indices may have changed.
i = ~ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
// 扩容,赋值
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mValues, mSize, i, value);
mSize++;
}
}
public void append(int key, E value) {
if (mSize != 0 && key <= mKeys[mSize - 1]) {
put(key, value);
return;
}
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
gc();
}
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.append(mKeys, mSize, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.append(mValues, mSize, value);
mSize++;
} public E get(int key) {
return get(key, null);
}
public E get(int key, E valueIfKeyNotFound) {
// 二分查找到位置
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
// 查不到返回默认值,查到直接返回
if (i < 0 || mValues[i] == DELETED) {
return valueIfKeyNotFound;
} else {
return (E) mValues[i];
}
}- keyAt(int index) —— 查看第几个位置的键
- valueAt(int index) —— 查看第几个位置的值
- indexOfKey(int key) —— 查看 key 所在位置,没有的话返回-1:
public void remove(int key) {
delete(key);
}
public void delete(int key) {
// 二分查找到位置
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
// 删除
if (i >= 0) {
if (mValues[i] != DELETED) {
mValues[i] = DELETED;
mGarbage = true;
}
}
}