You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
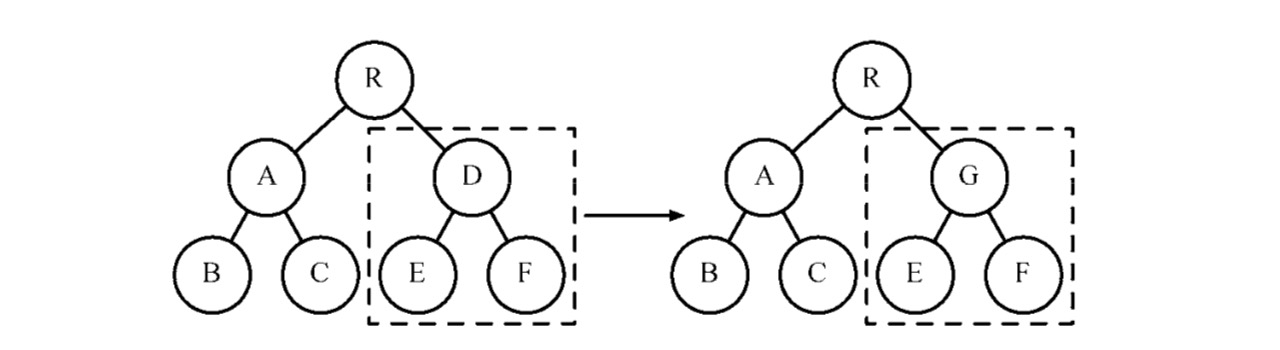
假设我们的 react 组件渲染成功后,在浏览器中显示的真实 DOM 节点是A、B、C、D,我们更新后的虚拟DOM是B、A、E、D。
那我们这里需要做的操作就是,将原来 DOM 中已经存在的A、B、D进行更新,将原来 DOM 中原本存在,而现在不存在的C移除掉,再创建新的E节点。
这样一来,问题就简化了很多,我们只需要收集到需要 create、remove和update 的节点信息就行了。
浅谈react diff实现
这是一篇硬核文,因此不会用生动幽默的语言来讲述,这篇文章大概更像是自己心血来潮的总结吧哈哈哈哈。
有很多文章讲过 react 的 diff 算法,但要么是晦涩难懂的源码分析,让人很难读进去,要么就是流于表面的简单讲解,实际上大家看完后还是一头雾水,因此我将 react-lite(基于 react v15) 中的 diff 算法实现稍微整理了一下,希望能够帮助大家解惑。
对于 react diff,我们已知的有两点,一个是会通过 key 来做比较,另一个是 react 默认是同级节点做diff,不会考虑到跨层级节点的 diff(事实是前端开发中很少有DOM节点跨层级移动的)。
递归更新
首先,抛给我们一个问题,那就是 react 怎么对那么深层次的 DOM 做的 diff?实际上 react 是对 DOM 进行递归来做的,遍历所有子节点,对子节点再做递归,这一过程类似深度优先遍历。
因此,我们这里以其中一层节点来讲解diff是如何做到更新的。
状态收集
假设我们的 react 组件渲染成功后,在浏览器中显示的真实 DOM 节点是A、B、C、D,我们更新后的虚拟DOM是B、A、E、D。
那我们这里需要做的操作就是,将原来 DOM 中已经存在的A、B、D进行更新,将原来 DOM 中原本存在,而现在不存在的C移除掉,再创建新的E节点。
这样一来,问题就简化了很多,我们只需要收集到需要 create、remove和update 的节点信息就行了。
这样,我们便拿到了想要的状态信息。
diff
在得到需要 create、update 和 remove 的节点后,我们这时就可以开始进行渲染了。
node | 状态 | index
:-: | :-: | :-: | :-: | :-:
A | update | 1
B | update| 0
C | remove
D | update | 3
E | create | 2
首先,我们遍历所有需要 remove 的节点,将其从真实DOM中 remove 掉。因此这里需要 remove 掉C节点,最后渲染结果是A、B、D。
其次,我们再遍历需要更新的节点,将其插入到对应的位置中。所以这里最后渲染结果是B、A、D。
最后一步,我们需要创建新的 DOM 节点,并插入到正确的位置中,最后渲染结果为B、A、E、D。
虽然这篇文章写的比较简单,但是一个完整的diff流程就是这样了,可以加深对react的一些理解。当然了,还有一些对 DOM 节点属性之类的比较,这里不做讲解。
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: