This project aims to detect forest fires and smoke in images using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) implemented with TensorFlow and Keras. The dataset contains images categorized as fire, smoke, and non-fire.
Forest fires pose a significant threat to the environment, wildlife, and human lives. Early detection of fires and smoke is crucial for mitigating their impact. This project utilizes deep learning techniques to classify images into three categories: fire, smoke, and non-fire.
The dataset is downloaded from Kaggle and consists of images categorized into three classes:
- Fire
- Smoke
- Non-Fire
- 32398 - Training images belonging to 3 classes.
- 10500 - Testing images belonging to 3 classes.
To get started with this project, clone the repository and install the necessary dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/ABHINAV2087/Forest-Fire-and-Smoke-Detection.git
cd forest-fire-smoke-detection
The following libraries are required to run the project:
- TensorFlow
- Keras
- Kaggle API
- OpenCV
- Matplotlib
- Scikit-learn
- NumPy
- PIL (Python Imaging Library)
You can install the required libraries using the following command:
pip install tensorflow keras kaggle opencv-python matplotlib scikit-learn numpy pillowTo download the dataset from Kaggle, you need to set up the Kaggle API. Follow these steps:
- Install the Kaggle API:
pip install kaggle- Place your kaggle.json file in the ~/.kaggle/ directory:
!mkdir -p ~/.kaggle
!cp kaggle.json ~/.kaggle/
!chmod 600 ~/.kaggle/kaggle.json- After downloading, extract the dataset:
from zipfile import ZipFile
datasets = 'forest-fire-smoke-and-non-fire-image-dataset.zip'
with ZipFile(datasets, 'r') as zip:
zip.extractall()
print('The dataset is extracted')To prepare the image data for training and testing the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model, we use the ImageDataGenerator class from Keras.
This class allows us to augment our images in real-time while the model is being trained, which helps improve the model's generalization ability.
The images are rescaled, and data augmentation techniques such as shear, zoom, and horizontal flip are applied.
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
training_data_gen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1./255,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True
)
training_set = training_data_gen.flow_from_directory(
'/content/FOREST_FIRE_SMOKE_AND_NON_FIRE_DATASET/train',
target_size=(64, 64),
batch_size=32,
class_mode='categorical'
)
testing_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255, horizontal_flip=True)
testing_set = testing_datagen.flow_from_directory(
'/content/FOREST_FIRE_SMOKE_AND_NON_FIRE_DATASET/test',
target_size=(64, 64),
batch_size=32,
class_mode='categorical'
)A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is built using TensorFlow and Keras with the following architecture:
- Convolutional layers with ReLU activation
- Max Pooling layers
- Flatten layer
- Fully connected (Dense) layers
- Output layer with Softmax activation
import tensorflow as tf
cnn = tf.keras.models.Sequential()
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu', input_shape=[64, 64, 3]))
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu'))
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2))
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu'))
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=16, kernel_size=3, activation='relu'))
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=3, strides=2))
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten())
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=100, activation='relu'))
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=100, activation='relu'))
cnn.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=3, activation='softmax'))The model is compiled with the Adam optimizer and categorical cross-entropy loss function. It is trained for 25 epochs with the training and testing sets.
cnn.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
cnn.fit(x=training_set, validation_data=testing_set, epochs=25)
cnn.summary()The model's accuracy is evaluated on both the training and testing sets.
scores = cnn.evaluate(training_set)
print(f'Training Accuracy: {scores[1] * 100}%')
scores = cnn.evaluate(testing_set)
print(f'Testing Accuracy: {scores[1] * 100}%')A confusion matrix is plotted to visualize the model's performance on the test set.
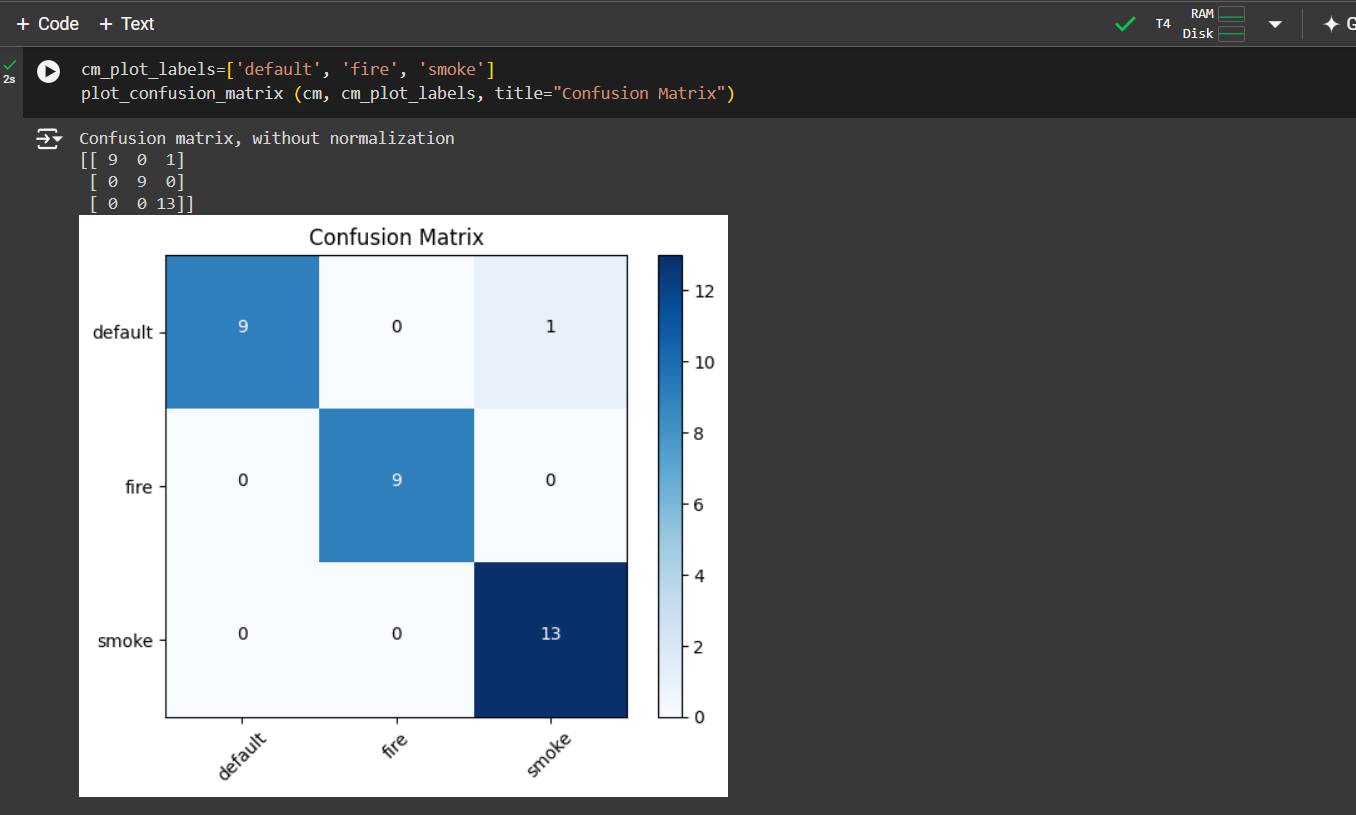
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import itertools
import numpy as np
cm = confusion_matrix(testing_set[0][1].argmax(axis=1), rounded_predictions.argmax(axis=1))
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes, normalize=False, title='Confusion matrix', cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
if normalize:
cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
print("Normalized confusion matrix")
else:
print('Confusion matrix, without normalization')
print(cm)
thresh = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i, cm[i, j], horizontalalignment='center', color='white' if cm[i, j] > thresh else 'black')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
cm_plot_labels = ['default', 'fire', 'smoke']
plot_confusion_matrix(cm, cm_plot_labels, title='Confusion Matrix')The model is used to predict new images from the test set.
from keras.preprocessing import image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
def predict_image(img_path):
im = cv2.imread(img_path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)
plt.imshow(im)
plt.show()
test_image = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(64, 64))
test_image = image.img_to_array(test_image)
test_image = np.expand_dims(test_image, axis=0)
result = cnn.predict(test_image)
if result[0][0] == 1:
print("Nothing Detected!")
elif result[0][1] == 1:
print("Fire Detected!")
elif result[0][2] == 1:
print("Smoke Detected")
predict_image('/content/FOREST_FIRE_SMOKE_AND_NON_FIRE_DATASET/test/non fire/NF_1180.jpg')
predict_image('/content/data/data/img_data/test/default/img_114.jpg')The trained model is saved and can be reloaded for future use.
cnn.save('fire_smoke_detection_model.h5')
from keras.models import load_model
new_model = load_model('fire_smoke_detection_model.h5')This project demonstrates the application of a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for detecting forest fires and smoke in images. The model can effectively classify images into fire, smoke, and non-fire categories.
Possible future improvements include:
- Increasing the dataset size for better generalization.
- Experimenting with different CNN architectures and hyperparameters.
- Implementing real-time fire and smoke detection using video streams.