Read paper here
aKmerBroomis a tool to decontaminate ancient oral samples from a FASTA/FASTQ file. It does so in the following steps:
- Build an
ancient_kmers.bloomfilter from an ancient kmers text file (if such a Bloom filter does not yet exist). - For a set of input reads:
- Save those reads which have 2 consecutive kmer matches against
ancient_kmers.bloom - Kmerize the saved reads to generate a new set of ancient kmers, called "anchor kmers"
- Save those reads which have 2 consecutive kmer matches against
- For the same set of input reads, identify matches against anchor kmers and classify each read with >50% matches as an ancient read.
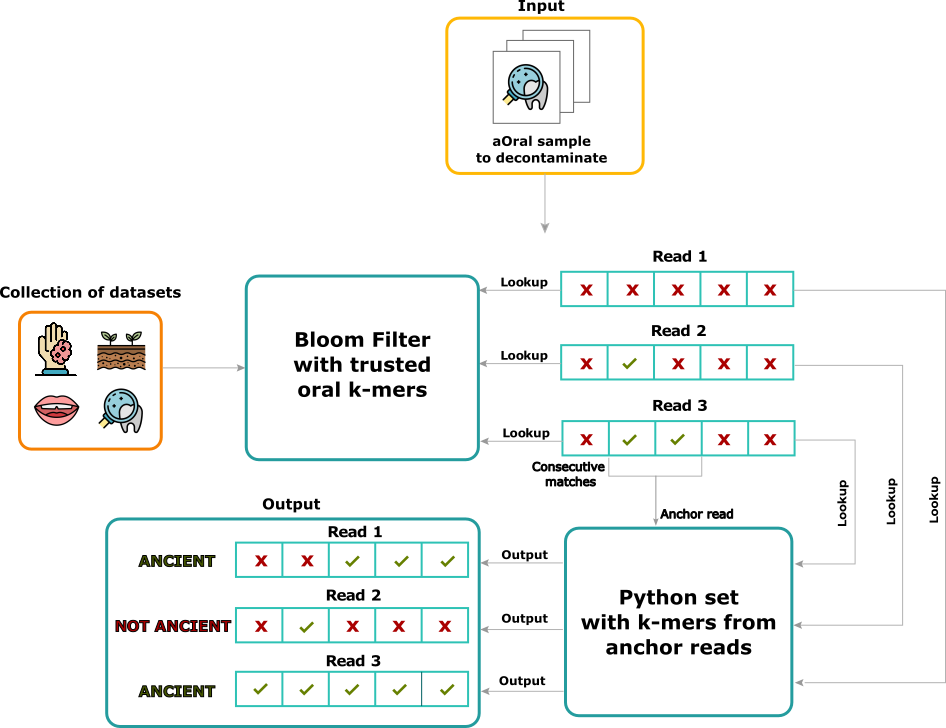 aKmerBroom pipeline: First, an offline step is performed: a collection of samples representative from diverse sources is used to create a trusted set of oral kmers. The trusted collection indexes kmers that appear exclusively in modern and ancient oral samples, but not other samples from contaminant sources (see panel on the left called Collection of datasets). Then this set of oral kmers is used to decontaminate an input set of reads. The algorithm proceeds by looking up each read kmer inside the Bloom Filter of trusted oral kmers, and marking positions of matches. Reads having at least two consecutive matches to the Bloom Filter get passed to the construction of a set containing all kmers from such reads. Finally, the same input reads are scanned again using the aforementioned set, and reads having a proportion of kmer matches over a certain threshold are reported to be of ancient oral origin.
aKmerBroom pipeline: First, an offline step is performed: a collection of samples representative from diverse sources is used to create a trusted set of oral kmers. The trusted collection indexes kmers that appear exclusively in modern and ancient oral samples, but not other samples from contaminant sources (see panel on the left called Collection of datasets). Then this set of oral kmers is used to decontaminate an input set of reads. The algorithm proceeds by looking up each read kmer inside the Bloom Filter of trusted oral kmers, and marking positions of matches. Reads having at least two consecutive matches to the Bloom Filter get passed to the construction of a set containing all kmers from such reads. Finally, the same input reads are scanned again using the aforementioned set, and reads having a proportion of kmer matches over a certain threshold are reported to be of ancient oral origin.
# Use the ancient kmers bloom filter provided
python akmerbroom.py --ancient_bloom
or
# Use an ancient kmers text file
python akmerbroom.py --ancient_kmers_set
The data/ folder should contain the following input files:
ancient_kmers.bloom : a bloom filter with ancient kmers
unknown_reads.fastq : a file with reads which we want to classify as ancient or not
[optional] ancient_kmers : a text file where each row is a known ancient kmer
[optional] n_consec_matches : Number of consecutive matches in the Bloom Filter that should be used to classify a read as anchor read
The output/ folder should contain the following output files:
annotated_reads.fastq # intermediate output
annotated_reads_with_anchor_kmers.fastq # final output
The final output file has the following 4 fields in each record header:
SeqId, ReadLen, isConsecutiveMatchFound, AnchorProportion
By default, reads with AnchorProportion >= 0.5 (ie. 50%) are chosen as ancient reads.
pip install biopython
pip install cython
pip install pybloomfiltermmap3
The tests/ folder contains a test dataset consisting of aOral data @SRR13355797 mixed with non aOral data @ERR671934.
To run a test, use the following steps:
First, link the test dataset in the input data/ folder:
cd data/
ln -sf ../tests/unknown_reads.fastq .
Next, download the Bloom Filter into the data/ folder from the following link
ancient_bloom.
Note that it could take a few minutes (file size = 3Gb).
This can be done from the command line using the wget utility.
cd data/ # if you are not already in the data/ directory
wget https://zenodo.org/record/7587160/files/ancient_kmers.bloom -O ancient_kmers.bloom
NOTE: This Bloom Filter was pre-constructed to reduce the running time and facilitate things for users, and it should be used to decontaminate ancient oral samples only. The way it was constructed was detailed on the manuscript for aKmerBroom, but it basically consists of clean k-mers that are of oral origin.
Finally, run aKmerBroom
cd ../ # if you are not already in the main directory
python akmerbroom.py --ancient_bloom
The ancient reads file will be written to output/annotated_reads_with_anchor_kmers.fastq.