|
Plugin boilerplate with modern tools to kickstart your WordPress project This includes common and modern tools to facilitate plugin development and testing with an organized, object-oriented structure and kick-start a build-workflow for your WordPress plugins. |
- The Boilerplate is based on the Plugin API , Coding Standards, and Documentation Standards.
- Includes Composer, Requirements micropackage to test environment requirements for your plugin, Codeception to do unit/acceptance testing, PHPCodeSniffer with WordPress Coding Standards to validate your code, TravisCI configuration for automatic testing & continuous integration, object-oriented code structure for better overview, an automatic class loader that automatically instantiate classes based on type of request.
- This can be combined with the Webpack 5 workflow for front-end development using the npx quickstart script that includes the Webpack v5 bundler, BabelJS v7, BrowserSync v2, PostCSS v8, PurgeCSS v3, Autoprefixer, Eslint, Stylelint, SCSS processor, WPPot, and more.
Should be run inside your plugins folder (wp-content/plugins).
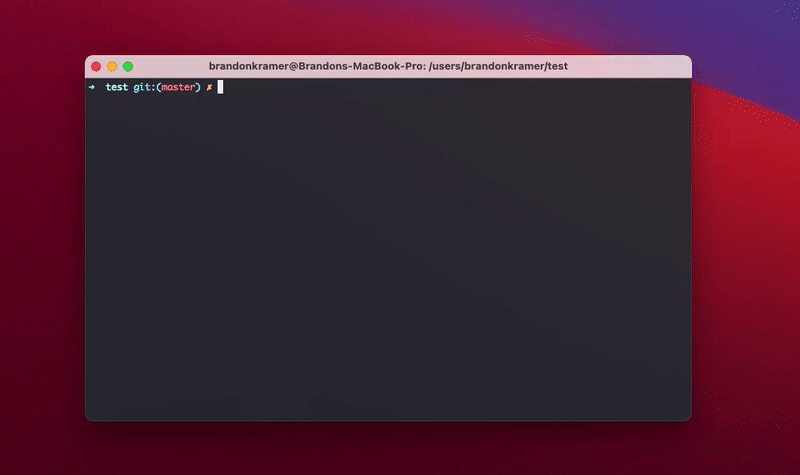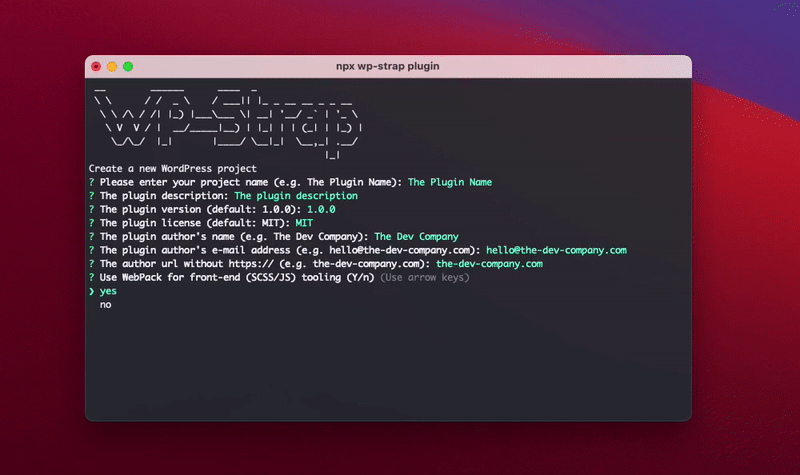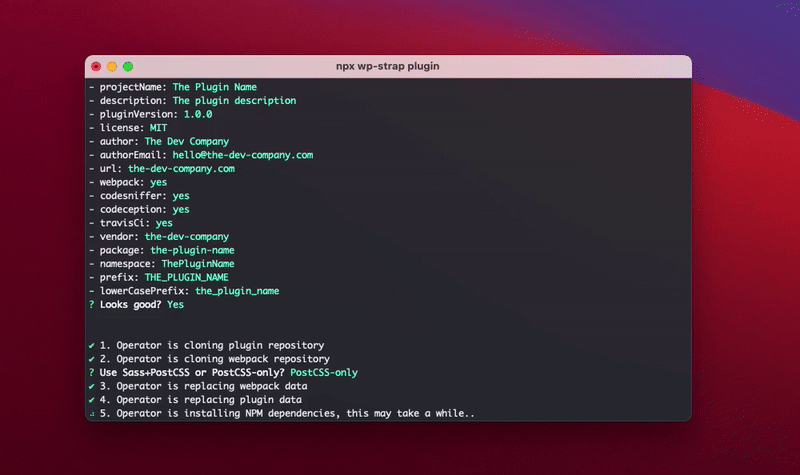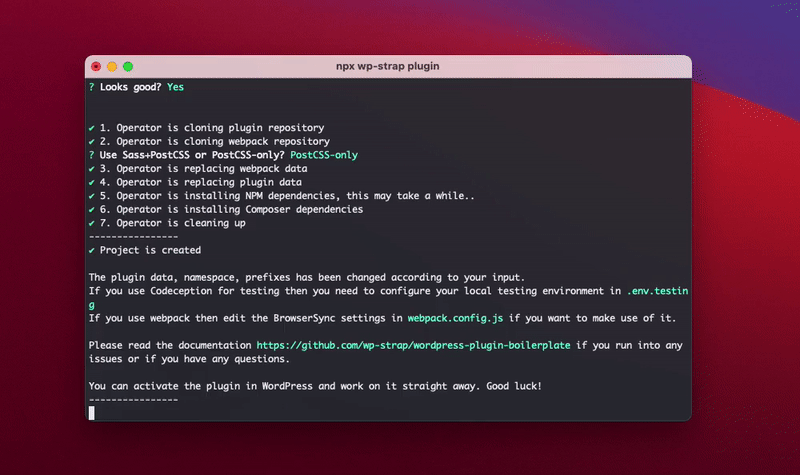
npx wp-strap pluginYou can also use the npx script with predefined answers to get a quicker start
npx wp-strap plugin "projectName:Your plugin name" "description:Test the plugin" "pluginVersion:1.0.0" license:MIT "author:The Dev Company" authorEmail:hello@the-dev-company.com url:the-dev-company.com webpack:Y codesniffer:Y codeception:Y travisCi:Y css:Sass+PostCSSIt will take a couple of minutes to install after your terminal input; it will clone the git repo's, search and replace
all the plugin data, do a composer install, and when it's combined with the Webpack workflow then it wil also do
a npm install
Read more about the configuration & build scripts
Composer (Namespaces + PSR4 autoloader + Dependency manager)
- Namespace support to group all of your code under a custom name. That way, your classes, functions, and so on don’t clash with other people’s code running on the site at the same time
- PSR-4 Autoloader to autoload files and directories in connection with namespaces
- Includes a dependency manager to easily load in 3rd party libraries from packagist, locked onto specific versions
Object-oriented & classes autoloader
- Includes a OOP-style structure for building a high-quality PHP development
- Classes are being auto-instantiated by extending the PSR-4 Autoloader from Composer and based on type of request and folder structure for which you can add the types of request here. So you can add your own new class files by naming them correctly and putting the files in the most appropriate location and work in it straight away without having to include them or instantiate them manually. Composer's Autoloader and the Bootstrap class will auto include your file and instantiate the class.
- The structure follows the the Plugin API , Coding Standards, and Documentation Standards
PHPCodeSniffer + WordPress Coding Standards + Automattic's phpcs-neutron-ruleset
- PHP CodeSniffer is built in with predefined configuration for proper linting. PHP_CodeSniffer is an essential development tool that ensures your code remains clean and consistent.
- PHPCS is extended with the WordPress Coding Standards & PHPCompatibilityWP for PHP_CodeSniffer which is a collection of PHP_CodeSniffer rules (sniffs) to validate code developed for WordPress. It ensures code quality and adherence to coding conventions, especially the official WordPress Coding Standards.
- PHPCS is also extented with Automattic's phpcs-neutron-ruleset which is a set of modern (PHP >7) linting guidelines for WordPress development.
Codeception (unit/acceptance testing)
- Codeception is built in which combines all testing levels (acceptance, functional, integration, unit) with WordPress defined functions, constants, classes and methods in any test.
- With a flexible set of included modules, tests are easy to write, easy to use, and easy to maintain.
Plugin requirements
- Requirements micropackage is built in that allows you to test environment requirements to run your plugin. It can test: PHP version, PHP Extensions, WordPress version, Active plugins, Current theme, DocHooks support
- Easily to configure using a simple array
- If the plugin doesn't pass the test then it will disable the plugin automatically for the user in WordPress and show a notification in the back-end
TravisCI
- Ready to use TravisCI configuration for automatic testing & continuous integration which currently only validates the plugin code with PHPCodeSniffer during automated testing when being deployed, but can also be extended to test unit/acceptance cases from Codeception
Prettified errors & Classes debug array
- Includes a function called
Errors::wpDieto show a prettified WP_DEBUG error with the plugin information and file source- Includes a function called
Errors::pluginDieto kill the plugin and show a prettified admin notification with the plugin information and file source- Includes a function if set true to debug the bootstrap's class loader and see which classes are loaded, if they load on the requested page, in which order and to check the execution time of the code run in each class
For front-end tooling the webpack workflow is being cloned. Read more about this workflow here: https://github.com/wp-strap/wordpress-webpack-workflow
Styling (CSS)
- Minification in production mode handled by Webpack
- PostCSS for handy tools during post CSS transformation using Webpack's PostCSS-loader
- Auto-prefixing using PostCSS's autoprefixer to parse CSS and add vendor prefixes to CSS rules using values from Can I Use. It is recommended by Google and used in Twitter and Alibaba.
- PurgeCSS which scans your php (template) files to remove unused selectors from your css when in production mode, resulting in smaller css files.
- Sourcemaps generation for debugging purposes with various styles of source mapping handled by WebPack
- Stylelint that helps you avoid errors and enforce conventions in your styles. It includes a linting tool for Sass.
Styling when using PostCSS-only
- Includes postcss-import to consume local files, node modules or web_modules with the @import statement
- Includes postcss-import-ext-glob that extends postcss-import path resolver to allow glob usage as a path
- Includes postcss-nested to unwrap nested rules like how Sass does it.
- Includes postcss-nested-ancestors that introduces ^& selector which let you reference any parent ancestor selector with an easy and customizable interface
- Includes postcss-advanced-variables that lets you use Sass-like variables, conditionals, and iterators in CSS.
Styling when using Sass+PostCSS
- Sass to CSS conversion using Webpack's sass-loader
- Includes Sass magic importer to do lot of fancy things with Sass @import statements
JavaScript
- BabelJS Webpack loader to use next generation Javascript with a BabelJS Configuration file
- Minification in production mode
- Code Splitting, being able to structure JavaScript code into modules & bundles
- Sourcemaps generation for debugging purposes with various styles of source mapping handled by WebPack
- ESLint find and fix problems in your JavaScript code with a linting configuration including configurations and custom rules for WordPress development.
- Prettier for automatic JavaScript / TypeScript code formatting
Images
- ImageMinimizerWebpackPlugin + CopyWebpackPlugin to optimize (compress) all images using
- File types:
.png,.jpg,.jpeg,.gif,.svg
Translation
- WP-Pot scans all the files and generates
.potfile automatically for i18n and l10n
BrowserSync, Watcher & WebpackBar
- Watch Mode, watches for changes in files to recompile
- File types:
.css,.html,.php,.js- BrowserSync, synchronising browsers, URLs, interactions and code changes across devices and automatically refreshes all the browsers on all devices on changes
- WebPackBar so you can get a real progress bar while development which also includes a profiler
Configuration
- All configuration files
.prettierrc.js,.eslintrc.js,.stylelintrc.js,babel.config.js,postcss.config.jsare organised in a single folder- The Webpack configuration is divided into 2 environmental config files for the development and production build/environment
You can add your own new class files by naming them correctly and putting the files in the most appropriate location, see other files for examples. Composer's Autoloader and the Bootstrap class will auto include your file and instantiate the class. The idea of this organisation is to be more conscious of structuring your code.
│ ## First level files
├──the-plugin-name.php # Main entry file for the plugin
├──composer.json # Composer dependencies & scripts
├──phpcs.xml.dist # PHPCodeSniffer configuration
├──codeception.dist.yml # Codeception testing configuration
├──.env.testing # Codeception testing environment configuration
├──.travis.yml # TravisCI configuration for automatic testing & continuous integration
├──package.json # (incl. when using webpack) Node.js dependencies & scripts (NPM functions)
├──webpack.config.js # (incl. when using webpack) Holds all the base Webpack configurations
│
│ ## Folders
├──src # Holds all the plugin php classes
│ ├── Bootstrap.php # Bootstraps the plugin and auto-instantiate classes
│ ├── App # Holds the plugin application-specific functionality
│ │ ├── Frontend # All public-facing hooks/functionality
│ │ ├── Backend # All admin-specific hooks/functionality
│ │ ├── General # Hooks/functionality shared between the back-end and frontend
│ │ ├── Cli # Code for cli commands
│ │ ├── Cron # Code for cron events
│ │ ├── Rest # Code for rest api functionalities
│ ├── Config # Plugin configuration code
│ │ ├── Classes.php # Defines the folders and order of classes to init
│ │ ├── I18n.php # Internationalization and localization definitions
│ │ ├── Plugin.php # Plugin data which are used through the plugin
│ │ ├── Requirements.php # Defines the requirements that are needed to run this plugin.
│ │ ├── Setup.php # Plugin setup hooks (activation, deactivation, uninstall)
│ ├── Common # Utilities & helpers shared in the whole plugin
│ │ ├── Abstracts # Here you can add abstract classes to extend your php classes
│ │ │ ├── Base.php # A base class which all classes extends to load in default methods, currently the plugin data is only being injected
│ │ ├── Traits # Here you can add handy traits to extend your php classes
│ │ │ ├── Requester.php # The requester trait to determine what we request; used to determine which classes we instantiate in the Bootstrap class
│ │ │ ├── Singleton.php # The singleton skeleton trait to instantiate the class only once
│ │ ├── Utils # Here you can add helper/utiliy functions, eg: array functions
│ │ │ ├── Errors.php # Utility class for the prettified errors and to write debug logs as string or array
│ │ ├── Functions.php # Main function class for external/global functions, eg: "plugin_name()->your_function"
│ ├── Integrations # Includes the integration with libraries, api's or other plugins
│ ├── Compatibility # 3rd party compatibility code
├──tests # Codeception test files
├──templates # Folder to include all the template files
│ ├── test-template.php # Example template file
├──languages # WordPress default language map in Plugins & Themes
│ ├── the-plugin-name.pot # Boilerplate POT File that gets overwritten by WP-Pot
├──webpack # (incl. when using webpack) Holds all the sub-config files for webpack
│ ├── .prettierrc.js # Configuration for Prettier
│ ├── .eslintrc.js # Configuration for Eslint
│ ├── .stylelintrc.js # Configuration for Stylelint
│ ├── babel.config.js # Configuration for BabelJS
│ ├── postcss.config.js # Configuration for PostCSS
│ ├── config.base.js # Base config for Webpack's development & production mode
│ ├── config.development.js # Configuration for Webpack in development mode
│ └── config.production.js # Configuration for Webpack in production mode
└──assets
├── src # (incl. when using webpack) Holds all the source files
│ ├── images # Uncompressed images
│ ├── scss/pcss # Holds the Sass/PostCSS files
│ │ ├─ frontend.scss/pcss # For front-end styling
│ │ └─ backend.scss/pcss # For back-end / wp-admin styling
│ └── js # Holds the JS files
│ ├─ frontend.js # For front-end scripting
│ └─ backend.js # For back-end / wp-admin scripting
│
└── public
├── images # Optimized (compressed) images
├── css # Compiled CSS files with be generated here
└── js # Compiled JS files with be generated here- When using codeception; configure the environments settings in
.env.testing, other configurations can be found incodeception.dist.yml - When using Webpack; edit the BrowserSync settings in
webpack.config.jswhich applies to your local/server environment- You can also disable BrowserSync, Eslint & Stylelint in
webpack.config.js - You may want to configure the files in
/webpack/andwebpack.config.jsto better suite your needs
- You can also disable BrowserSync, Eslint & Stylelint in
- You can activate the plugin in WordPress and work on it straight away.
- Testing with Codeception works out of the box
- Create test files with
composer generate:wpunitorcomposer generate:acceptance - Write your test methods and run
composer run:wpunitorcomposer run:acceptance - Extensive documentation can be found here https://codeception.com/for/wordpress
- Run PHPCodeSniffer with
composer phpcsto validate your plugin code - Configure PHPCodeSniffer in
phpcs.xm.dist - Documentation can be found here:
- Set your plugin requirements in
src/Config/Requirements.phpusing a simple array - It can test: PHP version, PHP Extensions, WordPress version, Active plugins, Current theme, DocHooks support
- If the plugin doesn't pass the test then it will be disabled automatically in WordPress and show a notification in the back-end
- Documentation can be found here: https://github.com/micropackage/requirements
- Configure TravisCI in
.travis.yml - Currently it only validates the plugin code with PHPCodeSniffer during automated testing when being deployed
- A great article can be found here: https://stevegrunwell.com/blog/travis-ci-wordpress-plugins/
When using webpack then you can use the following for the front-end build process. Read here more for more information about this workflow.
To work on the project locally (with Eslint, Stylelint & Prettier active), run:
yarn devOr run with watcher & browserSync
yarn dev:watchThis will open a browser, watch all files (php, scss, js, etc) and reload the browser when you press save.
To create an optimized production build (purged with PurgeCSS & fully minified CSS & JS files), run:
yarn prodOr run with watcher & browserSync
yarn prod:watch# To scan for text-domain functions and generate WP POT translation file
yarn translate
# To find problems in your JavaScript code
yarn eslint
# To find fix problems in your JavaScript code
yarn eslint:fix
# To find problems in your sass/css code
yarn stylelint
# To find fix problems in your sass/css code
yarn stylelint:fix
# To make sure files in assets/src/js are formatted
yarn prettier
# To fix and format the js files in assets/src/js
yarn prettier:fix| Depedency | Description | Version |
|---|---|---|
| Plugin Requirements | ||
| micropackage/requirements | Allows you to test environment requirements to run your plugin. | 1.0 |
| PHPCodeSniffer | ||
| dealerdirect/phpcodesniffer-composer-installer | Allows for easy installation of PHP_CodeSniffer coding standards (rulesets) | 0.7.1 |
| wp-coding-standards/wpcs | Collection of PHP_CodeSniffer rules (sniffs) to validate code developed for WordPress | * |
| automattic/phpcs-neutron-ruleset | Set of modern (PHP >7) linting guidelines for WordPress development | 3.3 |
| phpcompatibility/phpcompatibility-wp | Analyse the codebase of a WordPress-based project for PHP cross-version compatibility | 2.1 |
| Codeception | ||
| lucatume/function-mocker | A Patchwork powered function mocker to mock function for testing | 1.0 |
| lucatume/wp-browser | Provides easy acceptance, functional, integration and unit testing for WordPress plugins, themes and whole sites using Codeception | 3.0 |
| Codeception/lib-innerbrowser | Parent library for all Codeception framework modules and PhpBrowser. | 1.0 |
| codeception/module-asserts | A Codeception module containing various assertions | 1.0 |
| codeception/module-phpbrowser | Use to perform web acceptance tests with non-javascript browser | 1.0 |
| codeception/module-webdriver | Run tests in real browsers using the W3C WebDriver protocol. | 1.0 |
| codeception/module-db | A database module for Codeception. | 1.0 |
| codeception/module-filesystem | A Codeception module for testing local filesystem. | 1.0 |
| codeception/module-cli | A Codeception module for testing basic shell commands and shell output. | 1.0 |
| codeception/module-rest | A REST module for Codeception | 1.2 |
| codeception/util-universalframework | Mock framework module used in internal Codeception tests | 1.0 |
| codeception/codeception-progress-reporter | Reporter for codeception with a progress bar | 4.0.2 |
https://github.com/wp-strap/wordpress-webpack-workflow#packagejson-dependencies
Documenting this project's progress...
- refactor: (webpack/frontend) Migrated from NPM to Yarn for speed,
installwent from 183.281s to 65.76s-90.02s.
- feat: Added
POTFile with all the translation strings - refactor: Moved classes array to own config file
- feat: Added
npxCLI build script + docs
- refactor: Rename plugin (meta) data to replace-able names
- feat: Added
PHP_CodeSnifferwithWordPress-Coding-Standardsincluding configuration file - feat(
.travis.yml): added TravisCI configuration file - feat: Added bootstrap classes debugger method
- feat:
README.mdfile