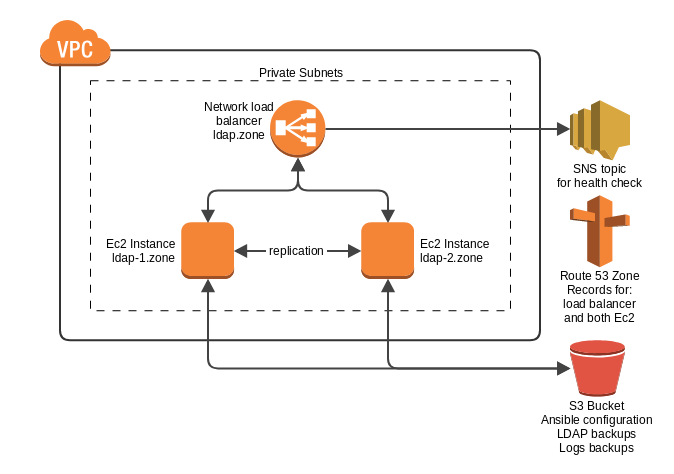
This repository is for deploying a multi master 389ds ldap setup with two Ec2 instances behind a network load balancer.
- First create an S3 bucket to hold the config files.
- Then populate a variable file based off
example-vars.yml. - Run ansible.
ansible-playbook ansible-deploy.yml --extra-vars "var_file=dev.yml"
After deploying the cloudformation stack the network load balancer will blindly route traffic to both servers. In order to enable health checks for the network load balancer you must add the IP addresses for it to your security group. You can get a list of network interfaces IP addresses via the CLI and filter by those with the name LDAP.
aws ec2 describe-network-interfaces | jq '[.NetworkInterfaces | .[] | {IP: .PrivateIpAddress, Name: .Description} ]' | grep ldap -B1
Put these addresses in to the network load balancer addresses cloudformation parameter and re-deploy the stack. Alternatively simply update the security group manually via the web console. Future cloudformation updates won't overwrite these changes unless something conflicts with the rules.
The EC2 IAM roles get granted write access to the config bucket under the bak directory. A nightly cron job runs on each host and syncs rotated logs and a dump of the entire database using db2ldif.
The templates in this cloudformation stack should all be templated in a way that you could deploy a new one along side of another and they won't conflict and should be easily discernible from each other. This means that a new stack could be deployed along side a production stack then the LDAP backup ldif could be imported in to the new stack to replace production as a hot swap.
There is intentionally not a route53 record for the NLB. This is intended to be a manual step after deploying so that the route53 record can be independent of the cloudformation stack for the ease of a DNS cutover with the option of rolling back easily when the stack needs replacement.