ReceiveMIDI is a multi-platform command-line tool makes it very easy to quickly receive and monitor MIDI messages from MIDI devices on your computer.
All the heavy lifting is done by the wonderful JUCE library.
The project website is https://github.com/gbevin/ReceiveMIDI
Join the Forums: https://forum.uwyn.com
Chat on Discord: https://discord.gg/sKM6pE575y
This tool is mainly intended for quickly monitoring the messages that are sent to your computer from a particular MIDI device. By providing filter commands, it's possible to only focus on particular MIDI messages.
Here's a tutorial video about both SendMIDI and ReceiveMIDI, including some tips and tricks of how to use the command-line on macOS:
If you're looking for a beautiful GUI to effortlessly visualize MIDI activity without having to wade through log files, please take a look at my other tool ShowMIDI: https://github.com/gbevin/ShowMIDI
You can download pre-built ReceiveMIDI binaries from the release section: https://github.com/gbevin/ReceiveMIDI/releases
Since ReceiveMIDI is free and open-source, you can also easily build it yourself. Just take a look into the Builds directory when you download the sources.
If you're using the macOS Homebrew package manager, you can install ReceiveMIDI with:
brew install gbevin/tools/receivemidi
To use it, simply type "receivemidi" or "receivemidi.exe" on the command line and follow it with a series of commands that you want to execute. These commands have purposefully been chosen to be concise and easy to remember, so that it's extremely fast and intuitive to quickly receive or monitor MIDI messages.
These are all the supported commands:
dev name Set the name of the MIDI input port
virt (name) Use virtual MIDI port with optional name (Linux/macOS)
pass name Set name of MIDI output port for MIDI pass-through
list Lists the MIDI input ports
file path Loads commands from the specified program file
dec Interpret the next numbers as decimals by default
hex Interpret the next numbers as hexadecimals by default
ch number Set MIDI channel for the commands (0-16), defaults to 0
ts Output a timestamp for each received MIDI message
nn Output notes as numbers instead of names
omc number Set octave for middle C, defaults to 3
voice Show all Channel Voice messages
note Show all Note messages
on (note) Show Note On, optionally for note (0-127)
off (note) Show Note Off, optionally for note (0-127)
pp (note) Show Poly Pressure, optionally for note (0-127)
cc (number) Show Control Change, optionally for controller (0-127)
cc14 (number) Show 14-bit CC, optionally for controller (0-63)
nrpn (number) Show NRPN, optionally for parameter (0-16383)
nrpnf (number) Show full NRPN (MSB+LSB), optionally for parameter (0-16383)
rpn (number) Show RPN, optionally for parameter (0-16383)
rpnf (number) Show full RPN (MSB+LSB), optionally for parameter (0-16383)
pc (number) Show Program Change, optionally for program (0-127)
cp Show Channel Pressure
pb Show Pitch Bend
sr Show all System Real-Time messages
clock Show Timing Clock
start Show Start
stop Show Stop
cont Show Continue
as Show Active Sensing
rst Show Reset
sc Show all System Common messages
syx Show System Exclusive
syf path Store SysEx into a .syx file
tc Show MIDI Time Code Quarter Frame
spp Show Song Position Pointer
ss Show Song Select
tun Show Tune Request
q Don't show the received messages on standard output
dump Dump the received messages 1:1 on standard output
js code Execute this script for each received MIDI message
jsf path Execute the script in this file for each message
mpp name Configure responder MPE Profile creating virtual MIDI input
manager and output ports with the provided name, available manager
members channel (1-15 or 0 for any) and desired member channel
count (1-15, or 0 for any) (Linux/macOS)
mcr flag Sets MPE Profile channel response feature (0-1)
mpb flag Sets MPE Profile pitch bend feature (0-1)
mcp flag Sets MPE Profile channel pressure feature (0-2)
m3d flag Sets MPE Profile 3rd dimension feature (0-2)
-h or --help Print Help (this message) and exit
--version Print version information and exit
-- Read commands from standard input until it's closed
Alternatively, you can use the following long versions of the commands:
device virtual pass-through decimal hexadecimal channel timestamp
note-numbers octave-middle-c note-on note-off poly-pressure control-change
control-change-14 nrpn-full rpn-full program-change channel-pressure
pitch-bend system-realtime continue active-sensing reset system-common
system-exclusive system-exclusive-file time-code song-position song-select
tune-request quiet javascript javascript-file mpe-profile mpe-channel-reponse
mpe-pitch-bend mpe-channel-pressure mpe-3rd-dimension
By default, numbers are interpreted in the decimal system, this can be changed to hexadecimal by sending the "hex" command. Additionally, by suffixing a number with "M" or "H", it will be interpreted as a decimal or hexadecimal respectively.
The MIDI device name doesn't have to be an exact match. If ReceiveMIDI can't find the exact name that was specified, it will pick the first MIDI output port that contains the provided text, irrespective of case.
Where notes can be provided as arguments, they can also be written as note names, by default from C-2 to G8 which corresponds to note numbers 0 to 127. By setting the octave for middle C, the note name range can be changed. Sharps can be added by using the "#" symbol after the note letter, and flats by using the letter "b".
For details on how to use the "javascript" and "javascript-file" commands, please refer to the JAVASCRIPT.md documentation file.
Here are a few examples to get you started:
List all the available MIDI output ports on your system
receivemidi list
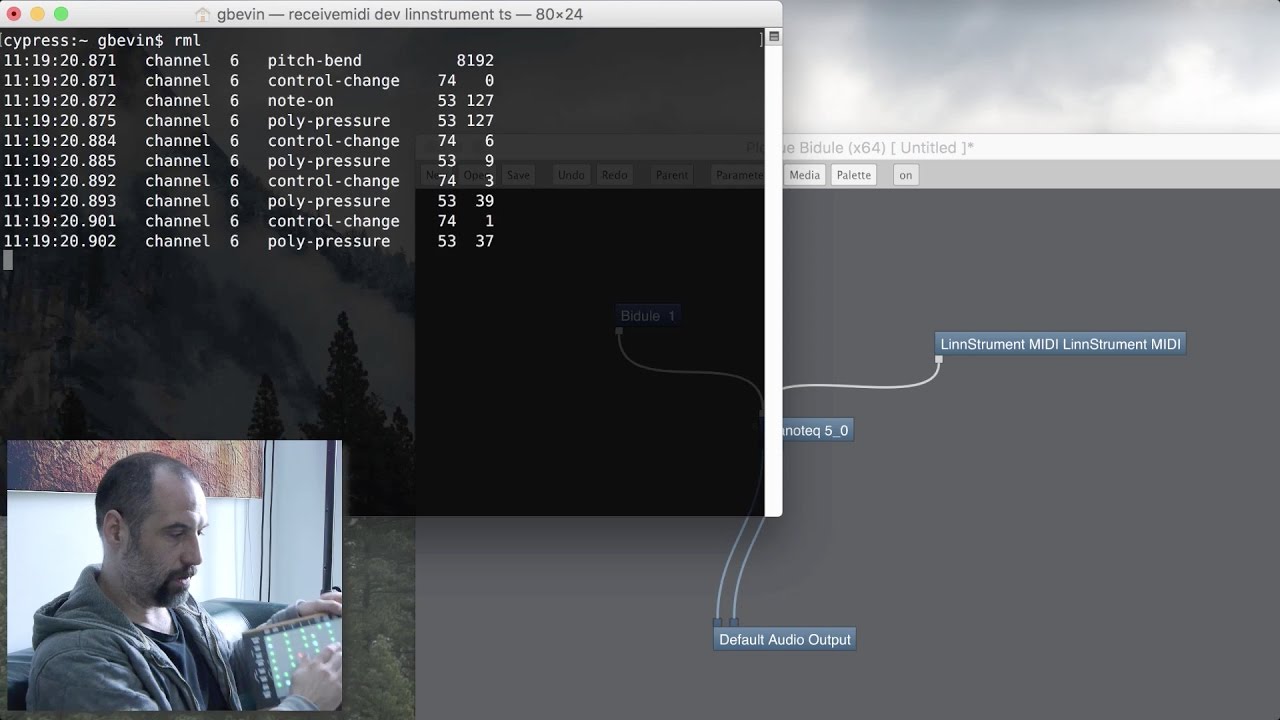
Receive all the MIDI messages coming from LinnStrument:
receivemidi dev "LinnStrument MIDI"
Receive only notes coming from LinnStrument:
receivemidi dev "LinnStrument MIDI" note
Receive all voice messages coming from LinnStrument, and also MIDI clock start and stop, all displayed with a timestamp:
receivemidi dev "LinnStrument MIDI" ts voice start stop
Receive all messages from LinnStrument and pipe them to the SendMIDI tool in order to forward them to Bidule:
receivemidi dev linnstrument | sendmidi dev "Bidule 1" --
Receive all messages from LinnStrument.
Through the JavaScript feature, each note on will execute the test.sh command with the note number as argument.
receivemidi dev linnstrument
js "if (MIDI.isNoteOn()) Util.command('/path/to/test.sh ' + MIDI.noteNumber());"
Receive all messages from LinnStrument and don't print them out. Through the JavaScript feature, each note on message will send an OSC message to 127.0.0.1:12800.
receivemidi dev linnstrument quiet
javascript "if (MIDI.isNoteOn()) OSC.connect('127.0.0.1', 12800).send('/note-on', MIDI.noteNumber());"
The text file that can be read through the "file" command can contain a list of commands and options, just like when you would have written them manually on the console (without the "sendmidi" executable). You can insert new lines instead of spaces and any line that starts with a hash (#) character is a comment.
For instance, this is a text file for one of the examples above:
dev "LinnStrument MIDI"
# timestamp the output
ts
# show all voice messages
voice
# show MIDI clock start and stop
start stop
To build ReceiveMIDI on Linux you need a minimal set of packages installed beforehand, on Ubuntu this can be done with:
sudo apt install build-essential pkg-config libasound2-dev
After that, go to the LinuxMakeFile directory
cd Builds/LinuxMakeFile
and build the binary by typing make
make
The resulting binary will be in the Build/LinuxMakeFile/build directory and can be moved anywhere appropriate on your system, for instance into /usr/local/bin:
sudo mv build/receivemidi /usr/local/bin
The output of the ReceiveMIDI tool is compatible with the SendMIDI tool, allowing you to store MIDI message sequences and play them back later. By using Unix-style pipes on the command-line, it's even possible to chain the receivemidi and sendmidi commands in order to forward MIDI messages.
If you changed the octave for middle C or are outputting hexadecimal numbers instead of the default decimal numbers, make sure that you set up SendMIDI with the same parameters.
SendMIDI can be downloaded from https://github.com/gbevin/SendMIDI