This project is archived. Development is now happening in https://github.com/jupyterlab/jupyterlab.
If you use JupyterLab 3.x:
The debugger extension is shipped by default with JupyterLab 3.x and doesn't need to be installed manually.
Be sure to install a kernel that supports debugging, such as xeus-python:
conda install -c conda-forge xeus-pythonRefer to the documentation for more details: https://jupyterlab.readthedocs.io/en/latest/user/debugger.html
Please open new issues and pull requests on the JupyterLab repo: https://github.com/jupyterlab/jupyterlab
If you use JupyterLab 2.x:
Follow the instructions below.
A JupyterLab debugger UI extension. This extension is under active development.
- JupyterLab 2.0+
- xeus-python 0.8.0+
- notebook 6+
A kernel with support for debugging is required to be able to use the debugger.
It is generally recommended to create a new conda environment to install the dependencies:
conda create -n jupyterlab-debugger -c conda-forge xeus-python=0.8.6 notebook=6 jupyterlab=2 ptvsd nodejs
conda activate jupyterlab-debuggerThen, run the following command to install the extension:
jupyter labextension install @jupyterlab/debuggerFor now xeus-python is the only Jupyter kernel that supports debugging. xeus-python can be selected from the JupyterLab launcher:
Alternatively, it is also possible to switch to the xpython kernel using the kernel selection dialog:
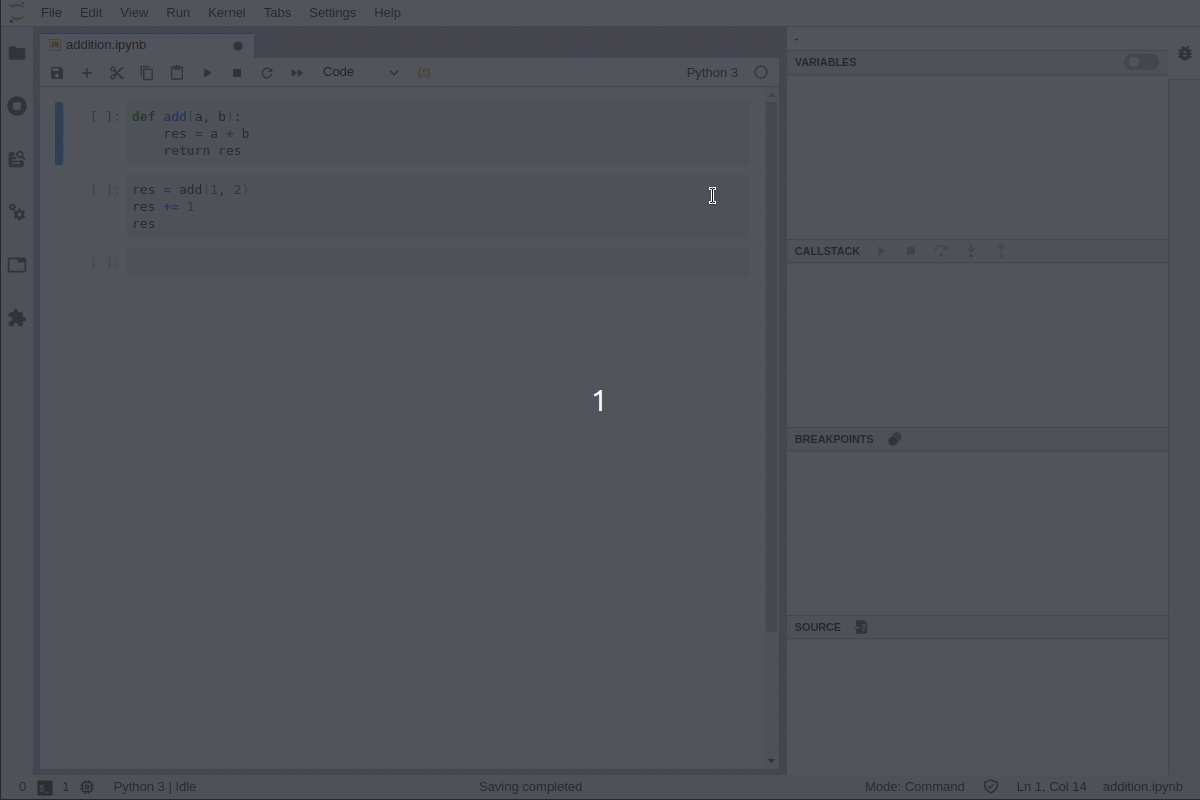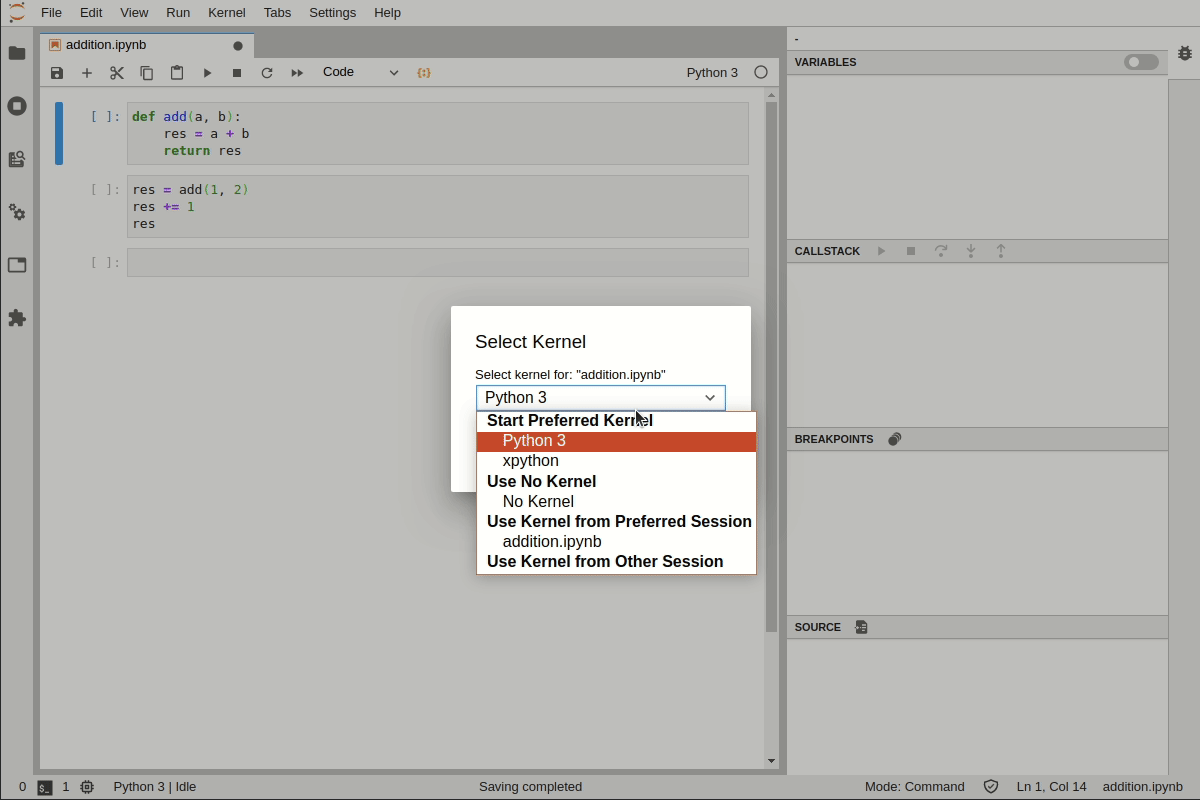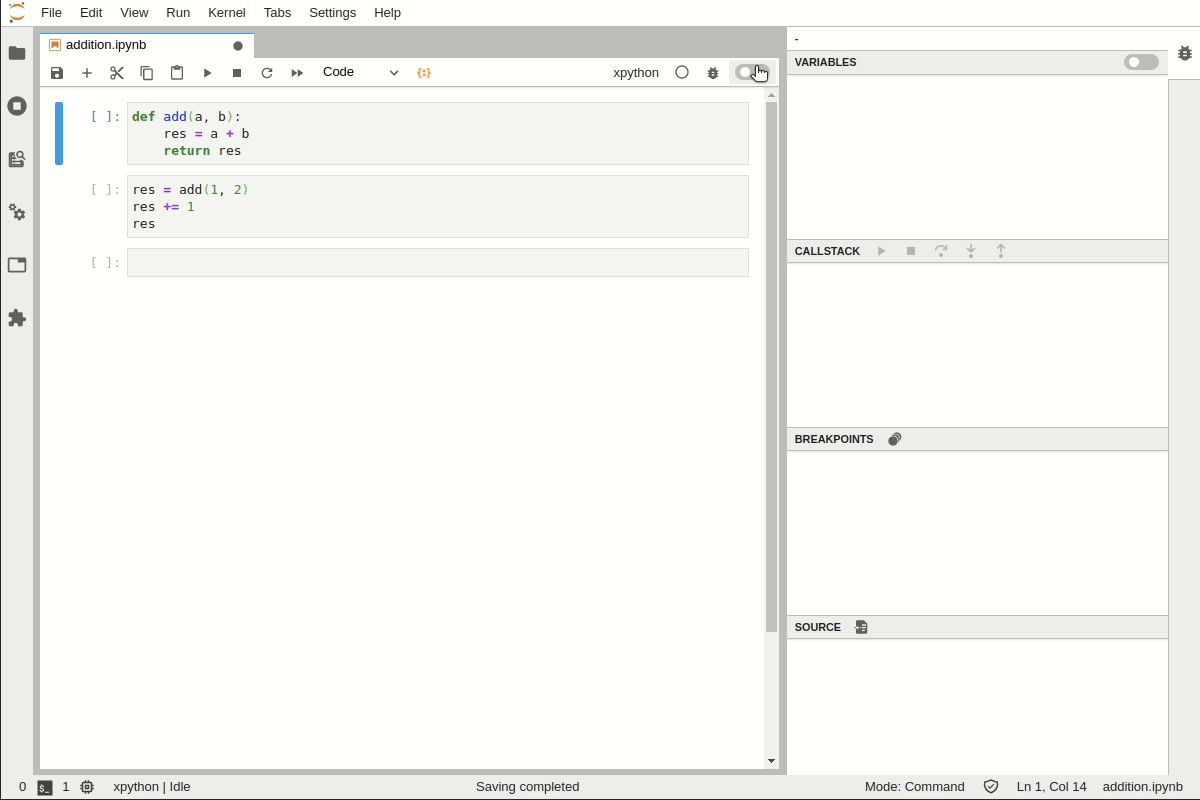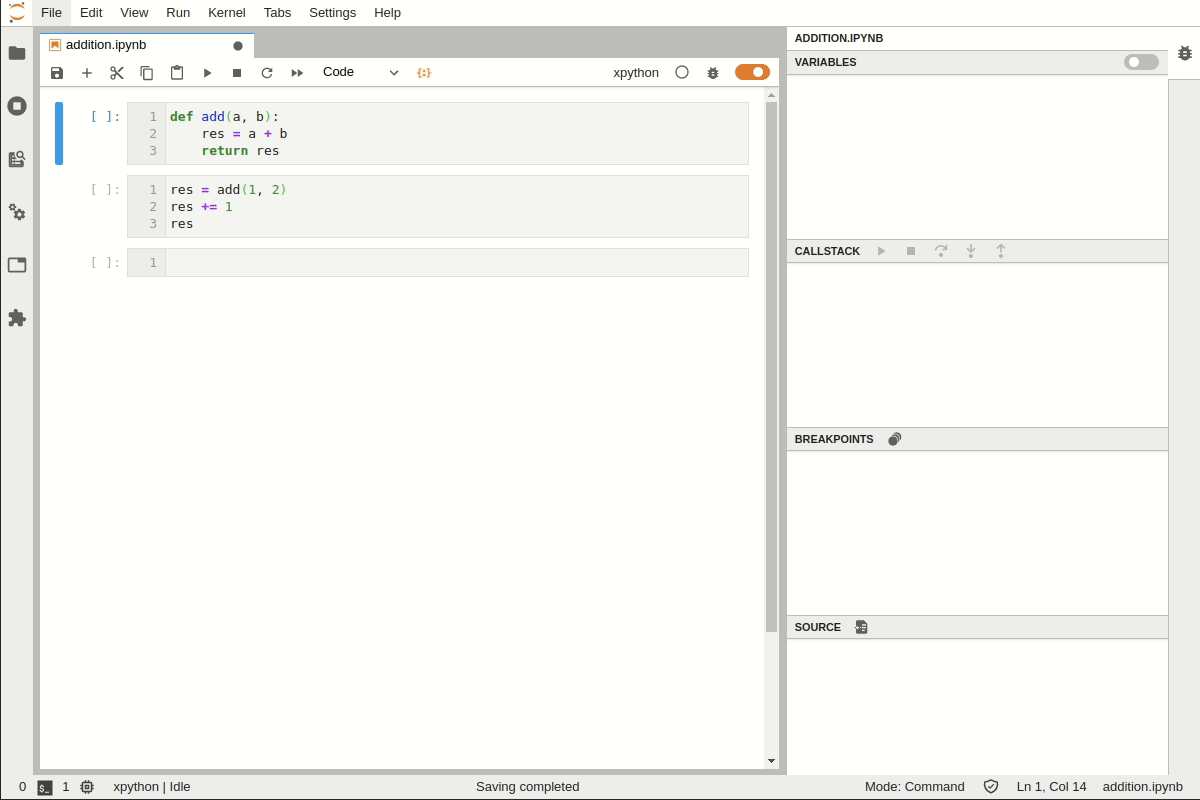
Enable the debugger, set breakpoints and step into the code:
# Create a new conda environment
conda create -n jupyterlab-debugger -c conda-forge nodejs xeus-python=0.8.6 ptvsd jupyterlab=2
# Activate the conda environment
conda activate jupyterlab-debugger
# Install dependencies
jlpm
# Build TypeScript source
jlpm build
# Link your development version of the extension with JupyterLab
jupyter labextension link .
# Rebuild TypeScript source after making changes
jlpm build
# Rebuild JupyterLab after making any changes
jupyter lab build
# Start JupyterLab with the kernel logs enabled and watch mode enabled
XEUS_LOG=1 jupyter lab --no-browser --watchTo run the tests:
# [Optional] to enable the logs for xeus-python
export XEUS_LOG=1
jlpm run testTo run tests for a specific test suite name:
jlpm run test --testNamePattern=<regex>To run tests for a specific test module name:
jlpm run test --testPathPattern=<regex>The kernelspy extension for JupyterLab can be used to inspect the debug messages sent between the debugger UI and the kernel.
To install it:
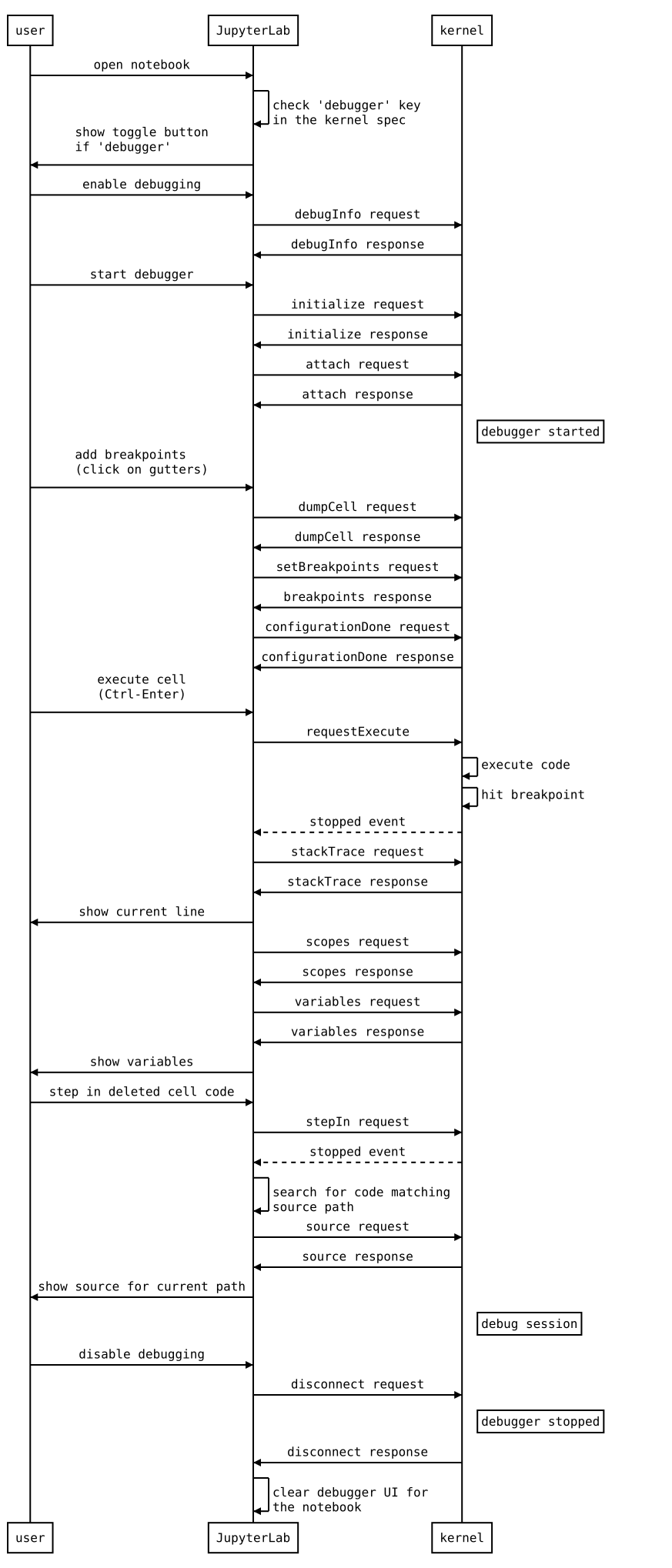
jupyter labextension install jupyterlab-kernelspyThe following diagram illustrates the types of messages sent between the JupyterLab extension and the kernel.
- Dump cell and state restoration: #52
- Protocol Overview: https://microsoft.github.io/debug-adapter-protocol/overview
- Specification: https://microsoft.github.io/debug-adapter-protocol/specification
Generated using: https://bramp.github.io/js-sequence-diagrams/
Diagram source
user->JupyterLab: open notebookJupyterLab->JupyterLab: check 'debugger' key\nin the kernel spec
JupyterLab->user: show toggle button\nif 'debugger'
user->JupyterLab: enable debugging
JupyterLab->kernel: debugInfo request
kernel->JupyterLab: debugInfo response
user->JupyterLab: start debugger
JupyterLab->kernel: initialize request
kernel->JupyterLab: initialize response
JupyterLab->kernel: attach request
kernel->JupyterLab: attach response
Note right of kernel: debugger started
user->JupyterLab: add breakpoints\n(click on gutters)
JupyterLab->kernel: dumpCell request
kernel->JupyterLab: dumpCell response
JupyterLab->kernel: setBreakpoints request
kernel->JupyterLab: breakpoints response
JupyterLab->kernel: configurationDone request
kernel->JupyterLab: configurationDone response
user->JupyterLab: execute cell\n(Ctrl-Enter)
JupyterLab->kernel: requestExecute
kernel->kernel: execute code
kernel->kernel: hit breakpoint
kernel-->JupyterLab: stopped event
JupyterLab->kernel: stackTrace request
kernel->JupyterLab: stackTrace response
JupyterLab->user: show current line
JupyterLab->kernel: scopes request
kernel->JupyterLab: scopes response
JupyterLab->kernel: variables request
kernel->JupyterLab: variables response
JupyterLab->user: show variables
user->JupyterLab: step in deleted cell code
JupyterLab->kernel: stepIn request
kernel-->JupyterLab: stopped event
JupyterLab->JupyterLab: search for code matching\nsource path
JupyterLab->kernel: source request
kernel->JupyterLab: source response
JupyterLab->user: show source for current path
Note right of kernel: debug session
user->JupyterLab: disable debugging
JupyterLab->kernel: disconnect request
Note right of kernel: debugger stopped
kernel->JupyterLab: disconnect response
JupyterLab->JupyterLab: clear debugger UI for\nthe notebook
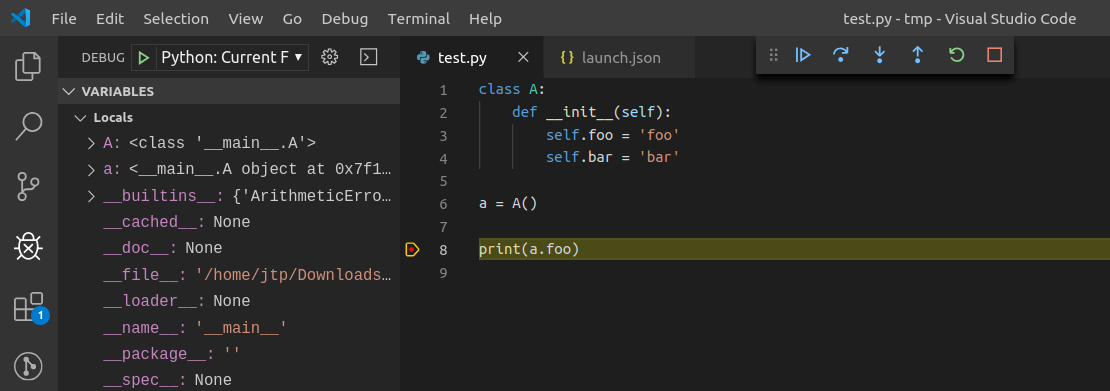
Inspecting the debug messages in VS Code can be useful to understand when debug requests are made (for example triggered by a UI action), and to compare the behavior of the JupyterLab debugger with the Python debugger in VS Code.
The first step is to create a test file and a debug configuration:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Python: Current File",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${file}",
"console": "integratedTerminal",
"env": { "DEBUGPY_LOG_DIR": "/path/to/logs/folder" }
}
]
}The content of the log file look like this:
...
D00000.032: IDE --> {
"command": "initialize",
"arguments": {
"clientID": "vscode",
"clientName": "Visual Studio Code",
"adapterID": "python",
"pathFormat": "path",
"linesStartAt1": true,
"columnsStartAt1": true,
"supportsVariableType": true,
"supportsVariablePaging": true,
"supportsRunInTerminalRequest": true,
"locale": "en-us"
},
"type": "request",
"seq": 1
}
...
With:
IDE= VS CodePYD= pydev debugger- Messages follow the DAP: https://microsoft.github.io/debug-adapter-protocol/specification