原始内容链接:
- 原始文档:https://www.yuque.com/lart/linux/fp6cla
- 博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/p_lart/article/details/107768318#t1
在日常工作中会涉及到 docker 的使用. 经过多番探究, 大致搞明白了使用的基本流程. 这里对于关键部分做一个简要总结和链接的跳转.
另外, 也期望通过本文的对于重要指令及其用途的梳理归类, 从而帮助大家更好更容易的使用 docker.
关于 Docker 官方性说明网上有很多, 官方文档也很详细, 这里不细说. 只是想说在我目前的体验中可以感受到的一点是, Docker 可以打包一个完整的运行环境. 这对于重现代码的使用环境来说非常有用. 使用者不需要再重新配置环境, 只需要直接拉取提供的镜像, 或者是直接载入打包好的镜像, 就可以基于该镜像创建容器运行代码了.
所以我们需要搞清楚的是这样几点:
- 什么是镜像 (image) 和容器 (container)
- 如何获取镜像
- 从网络
docker pulldocker run
- 从他人处
docker load
- 从网络
- 如何使用镜像
- 查看已有镜像
- 基于镜像创建容器
- 查看镜像信息
- 删除镜像
- 如何使用容器
- 进入容器
- 已退出的容器
- 后台分离模式运行的容器
- 进入启动的容器
- 退出容器
- 删除容器
- 停止正在运行的容器
- 从本机与容器中互相拷贝数据
- 进入容器
- 如何生成镜像
docker builddocker commit
- 如何分享镜像
- 上传到在线存储库
- 本地导出分享
- 清理无用数据
- 可视化管理
- 有用的设置
接下来从这几个方面依次介绍.
首先说明我的实验环境:
$ sudo docker --version
Docker version 19.03.6, build 369ce74a3c官方说法:https://docs.docker.com/get-started/#images-and-containers
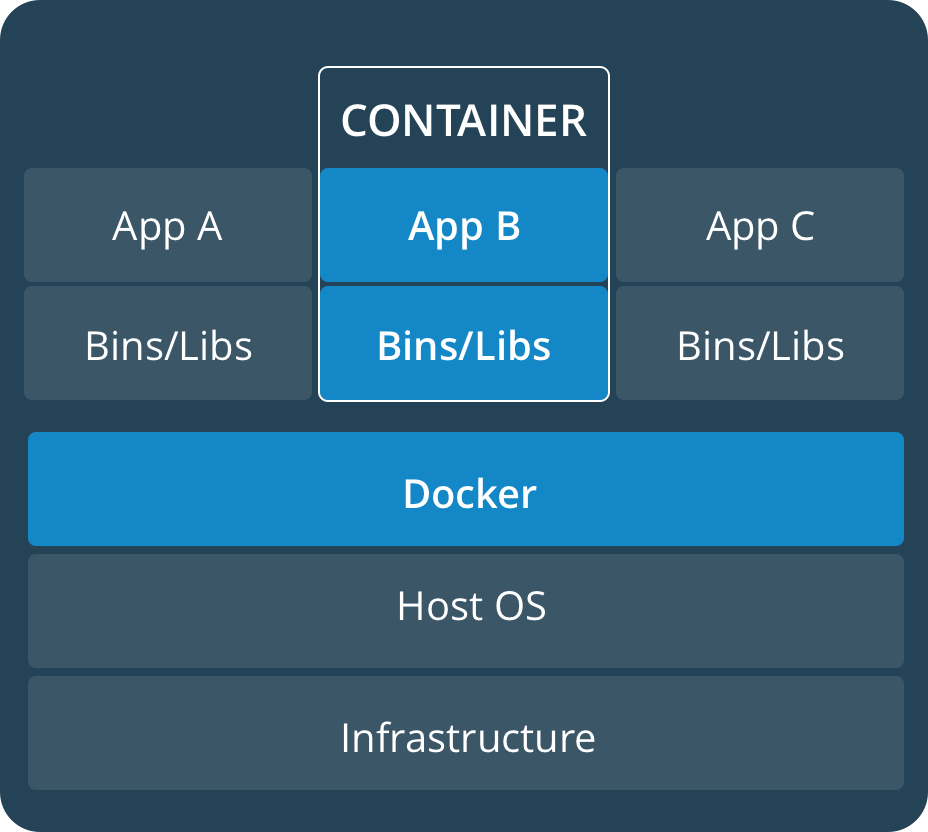
Fundamentally, a container is nothing but a running process, with some added encapsulation features applied to it in order to keep it isolated from the host and from other containers. One of the most important aspects of container isolation is that each container interacts with its own private filesystem; this filesystem is provided by a Docker image. An image includes everything needed to run an application - the code or binary, runtimes, dependencies, and any other filesystem objects required.
从根本上说, 容器只不过是一个正在运行的进程, 它还应用了一些附加的封装功能, 以使其与主机和其他容器保持隔离. 容器隔离的最重要方面之一是每个容器都与自己的私有文件系统进行交互; 该文件系统由Docker 镜像提供.镜像包含运行应用程序所需的所有内容——代码或二进制文件、运行时、依赖项以及所需的任何其他文件系统对象.
实际上在实际使用中, 我们使用镜像创建容器, 非常像使用一个新的系统镜像 (这里的镜像包含了运行程序的所有内容) 来安装系统 (创建容器). 只是这里更加接近于虚拟机. 对系统本身没有影响.
我觉的这句话说的很好: 镜像用来创建容器, 是容器的只读模板.
但是容器和虚拟机还不一样, 这里引用官方文档的表述:
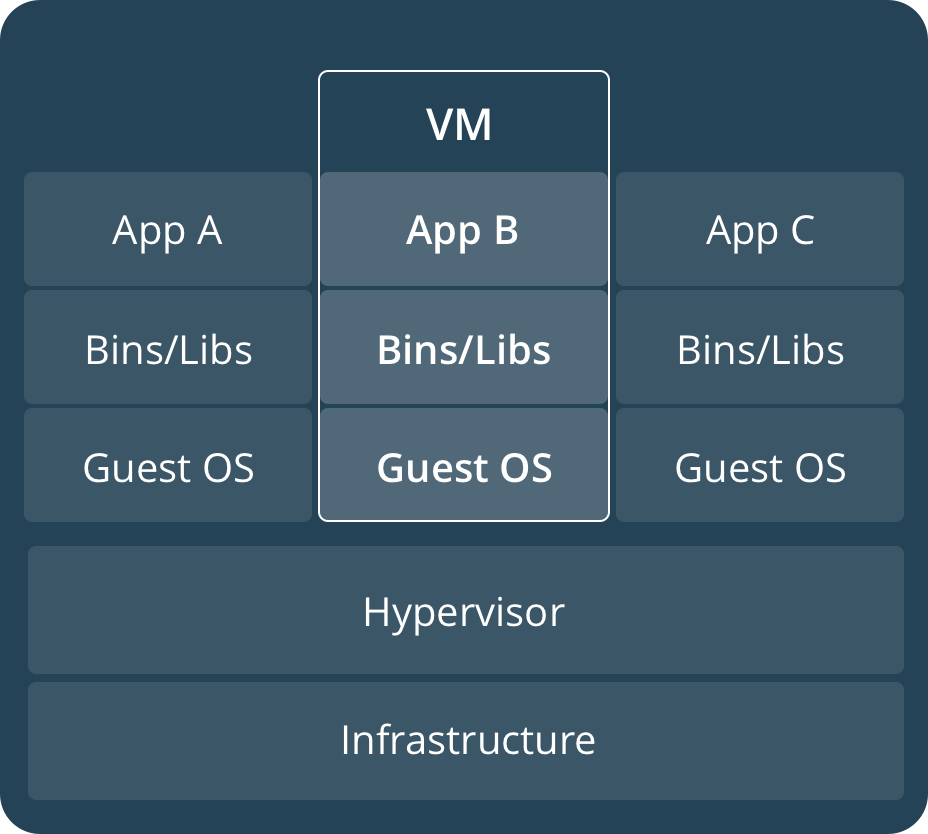
A container runs natively on Linux and shares the kernel of the host machine with other containers. It runs a discrete process, taking no more memory than any other executable, making it lightweight. By contrast, a virtual machine (VM) runs a full-blown "guest" operating system with virtual access to host resources through a hypervisor. In general, VMs incur a lot of overhead beyond what is being consumed by your application logic.
容器在 Linux 上本地运行, 并与其他容器共享主机的内核. 它运行一个独立的进程, 占用的内存不超过任何其他可执行文件, 这也使其更加轻量级. 相比之下, 虚拟机 (VM) 运行成熟的 " 访客 " 操作系统, 并通过管理程序虚拟访问主机资源. 通常, 虚拟机会产生超出应用程序逻辑消耗的开销.
所以归根到底一句话, docker 的容器更加轻便省资源.
文档中给出的容器与虚拟机的结构差异
从前面的描述中我们可以了解到, 使用 docker 的基础是, 我们得有初始的镜像来作为一切的开始. 主要获取镜像的方式有两种, 一种是使用他人打包好, 并通过网络 (主要是 docker 官方的 docker hub 和一些类似的镜像托管网站) 进行分享的镜像, 另一种则是在本地将镜像保存为本地文件, 直接使用生成的文件进行共享. 后者在网络首先环境下更加方便.
这里主要可以借助于两条指令. 一个是 docker pull , 另一个是 docker run .
docker pull [OPTIONS] NAME[: TAG|@DIGEST]
顾名思义, 就是从仓库中拉取 (pull) 指定的镜像到本机.
看它的配置项, 对于可选项我们暂不需要管, 我们重点关注后面的 NAME 和紧跟的两个互斥的配置项.
对应于这里的三种构造指令的方式, 文档中给出了几种不同的拉取方式:
- NAME
docker pull ubuntu- 如果不指定标签, Docker Engine 会使用
:latest作为默认标签拉取镜像.
- NAME: TAG
docker pull ubuntu:14.04- 使用标签时, 可以再次
docker pull这个镜像, 以确保具有该镜像的最新版本. - 例如,
docker pull ubuntu:14.04将会拉取 Ubuntu 14.04 镜像的最新版本.
- NAME@DIGEST
docker pull ubuntu@sha256:45b23dee08af5e43a7fea6c4cf9c25ccf269ee113168c19722f87876677c5cb2- 这个为我们提供了一种指定特定版本镜像的方法.
- 为了保证后期我们仅仅使用这个版本的镜像, 我们可以重新通过指定 DIGEST(通过查看镜像托管网站里的镜像信息或者是之前的
pull输出里的 DIGEST 信息) 的方式pull该版本镜像.
更多详见:
- https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/pull/#pull-an-image-by-digest-immutable-identifier
- 通过 API 获取镜像仓库里镜像的标签:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a5af4f558b0a
docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
docker run 命令首先在指定的映像上创建一个可写的容器层, 然后使用指定的命令启动它.
这个实际上会自动从官方仓库中下载本地没有的镜像. 更多是使用会在后面创建容器的部分介绍.
$ sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
$ sudo docker run hello-world
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
0e03bdcc26d7: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:49a1c8800c94df04e9658809b006fd8a686cab8028d33cfba2cc049724254202
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/
$ sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
hello-world latest bf756fb1ae65 7 months ago 13.3kB关于如何保存镜像在后面介绍, 其涉及到的指令为 [docker save](https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/save/) , 这里主要讲如何加载已经导出的镜像文件.
docker load [OPTIONS] Load an image or repository from a tar archive (even if compressed with gzip, bzip2, or xz) from a file or STDIN. It restores both images and tags.
从 tar 归档文件 (即使使用 gzip、bzip2 或 xz 压缩后的), 从一个文件或者 STDIN 中, 加载镜像或仓库. 它可以恢复镜像和标签.
例子可见:https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/load/#examples
单纯的使用镜像实际上就是围绕指令 docker run 来的.
首先我们通过使用 docker images 来查看本机中已经保存的镜像信息列表.
$ sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE通过运行 docker run 获取镜像并创建容器.
docker run [OPTIONS] IMAGE [COMMAND] [ARG...]
run 包含很多的参数和配置项, 这里放一个我用过的最长的 (这里用到了 nvidia-docker:https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker#usage):
sudo docker run --rm -it --gpus all --name test -v /home/mydataroot:/tcdata:ro nvidia/cuda:10.0-base /bin/bash
这条指令做的就是:
- 启动 Docker 容器时, 必须首先确定是要在后台以 " 分离 " 模式还是在默认前台模式下运行容器:
-d, 这里没有指定-d则是使用默认前台模式运行. 两种模式下, 部分参数配置不同, 这部分细节可以参考文档:https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/run/#detached-vs-foreground - 使用镜像
nvidia/cuda:10.0-base创建容器, 并对容器起一个别名test. - 对于该容器, 开启 gpu 支持, 并且所有 GPU 都可用, 但是前提你得装好 nvidia-docker.
--rm表示退出容器的时候自动移除容器, 在测试环境等场景下很方便, 不用再手动删除已经创建的容器了.-t和-i: 这两个参数的作用是, 为该 docker 创建一个伪终端, 这样就可以进入到容器的交互模式.- 后面的
/bin/bash的作用是表示载入容器后运行bash.**docker 中必须要保持一个进程的运行, 要不然整个容器启动后就会马上 kill itself, 这样当你使用 **docker ps** 查看启动的容器时, 就会发现你刚刚创建的那个容器并不在已启动的容器队列中.**这个/bin/bash就表示启动容器后启动bash. -v表示将本地的文件夹以只读 (:ro, 读写可以写为:rw, 如果不加, 则默认的方式是读写) 的方式挂载到容器中的/tcdata目录中. 可以使用多个-v来挂载多个目录, 例如对于深度学习场景, 可以分别挂载代码目录和数据目录, 这样使得我们也可以在外部修改代码, 容器只用来作为运行的环境, 非常方便.-e或--env可以用来在创建时指定容器内环境的一些额外的环境变量, 例如在容器中使用 nnUNet 时, 需要制定三个基本的环境变量, 则可以借助该配置项进行设置:-e nnUNet_raw_data_base="/data/" -e nnUNet_preprocessed="/data/nnUNetProcessed" -e RESULTS_FOLDER="/workspace/nnUnet/outputs".-p [宿主机端口]:[容器内端口]有时需要从外部访问内部容器的网络服务,需要借助这一项来实现端口映射。
$ sudo docker run -it ubuntu bash
Unable to find image 'ubuntu:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/ubuntu
3ff22d22a855: Pull complete
e7cb79d19722: Pull complete
323d0d660b6a: Pull complete
b7f616834fd0: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:5d1d5407f353843ecf8b16524bc5565aa332e9e6a1297c73a92d3e754b8a636d
Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:latest
root@966d5fa519a5:/# # 此时进入了基于ubuntu:latest创建的容器中。值得注意的是,docker run 有一个设置项为 --shm-size 有时候很重要,其用于设置容器中的目录 /dev/shm,即共享内存。在跑深度学习模型时,PyTorch 的 DataLoader 会涉及到这块内存空间的使用,直接使用默认值可能会报错误 RuntimeError: DataLoader worker (pid 11788) is killed by signal: Bus error. It is possible that dataloader's workers are out of shared memory. Please try to raise your shared memory limit. 所以运行容器的时候,最好手动指定一下 -–shm-size(例如 --shm-size=32g),其单位是字节,docker 容器中默认是 64M,很多软件无法正常工作。这个 /dev/shm 是 linux 下一个非常有用的目录,这个目录(共享内存目录)在内存里而不是硬盘上。更详细内容可见 Docker入门_--shm-size_xinming_365的博客-CSDN博客 和 shm值太小导致docker容器中程序无法运行。
退出容器后, docker ps 查看本机的镜像信息列表和容器信息列表.
root@d9e6e9b9323a:/# exit
exit
$ sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
ubuntu latest 1e4467b07108 9 days ago 73.9M
$ sudo docker ps # 查看正在运行的容器信息
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
$ sudo docker ps -a # 查看所有容器信息
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
966d5fa519a5 ubuntu "bash" 38 seconds ago Exited (0) 9 seconds ago relaxed_kirch当我们想要删除指定的镜像的时候, 我们可以使用 sudo docker rmi 来进行处理.
docker rmi [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...]
后面可以跟多个镜像. 这里支持三种方式:
- 使用 IMAGE ID:
docker rmi fd484f19954f - 使用 TAG:
docker rmi test:latest - 使用 DIGEST:
docker rmi localhost:5000/test/busybox@sha256:cbbf2f9a99b47fc460d422812b6a5adff7dfee951d8fa2e4a98caa0382cfbdbf
从前面可以了解到, 我们可以通过使用 docker run 创建前台运行的容器, 创建好了容器我们会面临如何使用的问题.
进入容器的方法都是一致的, 但是这里会面临两种情况, 一种是已经退出的容器, 另一种是运行在后台的分离模式下的容器.
$ sudo docker run -it --gpus all --name testv3 -v /home/lart/Downloads/:/data nvidia/cuda:10.0-base bash
root@efd722f0321f:/# exit
exit
$ sudo docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
efd722f0321f nvidia/cuda:10.0-base "bash" 19 seconds ago Exited (0) 3 seconds ago testv3可以看到, 我这里存在一个已经退出的容器. 我们想要进入退出的容器首先需要启动已经退出的容器:
$ sudo docker start testv3
testv3
$ sudo docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
efd722f0321f nvidia/cuda:10.0-base "bash" 31 seconds ago Up 1 second testv3关于重启容器, 使用 docker restart 也是可以的. 为了验证, 我们先使用 docker stop 停止指定容器. 再进行测试.
$ sudo docker stop testv3
testv3
$ sudo docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
efd722f0321f nvidia/cuda:10.0-base "bash" 2 minutes ago Exited (0) 4 seconds ago testv3
$ sudo docker restart testv3 # restart 不仅可以重启关掉的容器,也可以重启运行中的容器
testv3
$ sudo docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
efd722f0321f nvidia/cuda:10.0-base "bash" 2 minutes ago Up 1 second testv3对于创建分离模式的容器我们可以使用 docker run -d .
另外前面提到的 start 或者 restart 启动的容器会自动以分离模式运行.
对于已经启动的容器, 我们可以使用 attach 或者 exec 进入该容器, 但是更推荐后者 (https://www.cnblogs.com/niuben/p/11230144.html).
$ sudo docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
efd722f0321f nvidia/cuda:10.0-base "bash" 16 minutes ago Exited (0) 2 minutes ago testv3
$ sudo docker start testv3
testv3
$ sudo docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
efd722f0321f nvidia/cuda:10.0-base "bash" 16 minutes ago Up 2 seconds testv3
$ sudo docker exec -it testv3 bash
root@efd722f0321f:/# exit
exit
$ sudo docker ps -a # 可以看到exec退出后不会把容器关闭
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
efd722f0321f nvidia/cuda:10.0-base "bash" 17 minutes ago Up 36 seconds testv3
$ sudo docker attach testv3
root@efd722f0321f:/# exit
exit
$ sudo docker ps -a # 可以看到attach退出后会把容器关闭
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
efd722f0321f nvidia/cuda:10.0-base "bash" 18 minutes ago Exited (0) 2 seconds ago testv3$ exitdocker rm [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [CONTAINER...]
基于指令 docker rm 移除一个或者多个容器.
我们可以根据容器的 ID 或者名字来删除对应的运行中的或者是已经停止的容器. 更多的例子可见 https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/rm/#examples.
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/Michel4Liu/article/details/80889977
docker stop: 此方式常常被翻译为优雅的停止容器.docker stop 容器ID或容器名-t: 关闭容器的限时, 如果超时未能关闭则用kill强制关闭, 默认值 10s, 这个时间用于容器的自己保存状态,docker stop -t=60 容器ID或容器名
docker kill: 直接关闭容器docker kill 容器ID或容器名
docker cp [OPTIONS] CONTAINER: SRC_PATH DEST_PATH|- docker cp [OPTIONS] SRC_PATH|- CONTAINER: DEST_PATH
- The docker cp utility copies the contents of SRC_PATH to the DEST_PATH. You can copy from the container's file system to the local machine or the reverse, from the local filesystem to the container.
- If
-is specified for either the SRC_PATH or DEST_PATH, you can also stream a tar archive from STDIN or to STDOUT.- The CONTAINER can be a running or stopped container.
- The SRC_PATH or DEST_PATH can be a file or directory.
docker cp : 用于容器与主机之间的数据拷贝.
由于容器内的数据与容器外的数据并不共享, 所以如果我们想要向其中拷贝一些数据, 可以通过这个指令来进行复制. 当然, 另一个比较直接的想法就是通过挂载的目录进行文件共享与复制.
这一过程有两种思路,一种是直接 attach 到现有容器中,另一种则是利用 ssh 连接到容器里。后者的实践和常规的远程方式基本一致,而且配置也不用修改 docker(前者可能需要 docker 运行在超级用户下),仅仅需要为我们的容器中配置好 ssh 即可。
基于 ssh 的本地连接方式可以参考文章 VSCode连接远程服务器里的docker容器。
核心步骤如下:
# 先启动容器并进入,这里主要要通过参数 -p 来配置容器内外的端口映射关系。
# 容器内ssh默认使用22端口。外部宿主机使用6789。
sudo docker run -it -p 6789:22 image_name #(可以继续跟其他参数)
# 更新包的信息,并安装ssh服务端程序。
apt-get update
apt-get install openssh-server
# 设置容器内系统密码,之后登录会用到。
passwd
# 修改ssh配置文件
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# 注释掉 PermitRootLogin prohibit-password 这一行 添加这一行 PermitRootLogin yes
# 保存退出后重启ssh服务。
service ssh restart
# 本地ssh即可链接本机的容器
ssh -p 6789 root@0.0.0.0
# 如果要远程访问,则可以使用如下形式
# ssh -p 6789 root@host_ip主要包含两种方式, 一种是基于构建文件 Dockerfile 和 docker build 的自动构建, 一种是基于 docker commit 提交对于现有容器的修改之后生成镜像.
docker build [OPTIONS] PATH | URL | -
- The docker build command builds Docker images from a Dockerfile and a "context". A build's context is the set of files located in the specified PATH or URL.
- The build process can refer to any of the files in the context. For example, your build can use a COPY instruction to reference a file in the context.
更多细节可见 https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/build/.
这里用到了 Dockerfile, 这些参考资料不错:
- 你必须知道的 Dockerfile:https://www.cnblogs.com/edisonchou/p/dockerfile_inside_introduction.html
对于已有的 Dockerfile 文件, 我们可以使用如下指令生成镜像:
$ docker build -t vieux/apache:2.0 .
# 使用'.'目录下的Dockerfile文件。注意结尾的路径`.`,这里给打包的镜像指定了TAG
$ docker build -t whenry/fedora-jboss:latest -t whenry/fedora-jboss:v2.1 .
# 也可以指定多个TAG
$ docker build -f dockerfiles/Dockerfile.debug -t myapp_debug .
# 也可以不使用'.'目录下的Dockerfile文件,而是使用-f指定文件打包完之后, 我们就可以在 docker images 中看到新增的镜像了.
docker commit [OPTIONS] CONTAINER [REPOSITORY[: TAG]]
- It can be useful to commit a container's file changes or settings into a new image. This allows you to debug a container by running an interactive shell, or to export a working dataset to another server.
- Generally, it is better to use Dockerfiles to manage your images in a documented and maintainable way. Read more about valid image names and tags.
- The commit operation will not include any data contained in volumes mounted inside the container.
- By default, the container being committed and its processes will be paused while the image is committed. This reduces the likelihood of encountering data corruption during the process of creating the commit. If this behavior is undesired, set the --pause option to false.
一般使用指定容器的 ID 就可以进行提交了.
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
c3f279d17e0a ubuntu:12.04 /bin/bash 7 days ago Up 25 hours desperate_dubinsky
197387f1b436 ubuntu:12.04 /bin/bash 7 days ago Up 25 hours focused_hamilton
$ docker commit c3f279d17e0a svendowideit/testimage:version3
f5283438590d
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG ID CREATED SIZE
svendowideit/testimage version3 f5283438590d 16 seconds ago 335.7 MB在使用这一命令时有一点需要注意,就是commit 建立的镜像中,会把你的创建容器时附加的命令行指令(“正如前面使用的**bash**”)当做新的**CMD**指令存到镜像的设置里。所以如果你希望能够延续创建容器的原始镜像的 CMD 设置,那么有这样三种策略:
- 建议在对于新 commit 的镜像重新使用这些命令行参数创建一个新的容器来重新构建一个镜像。
- 在停掉 docker 服务之后,直接需改镜像的配置文件。
- 【推荐】利用
docker commit的-c配置项,可以对应修改多条 Dockerfile 的设置。例如:docker commit --change='CMD ["apachectl", "-DFOREGROUND"]' -c "EXPOSE 80" c3f279d17e0a svendowideit/testimage:version4
- 上传到 Docker Hub:https://docs.docker.com/get-started/part3/
- 上传到阿里云:https://blog.csdn.net/xiayto/article/details/104133417/
这里基于指令 docker save .
docker save [OPTIONS] IMAGE [IMAGE...] Produces a tarred repository to the standard output stream. Contains all parent layers, and all tags + versions, or specified
repo:tag, for each argument provided.
具体的例子可见:https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/save/#examples
$ sudo docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
153999a1dfb2 hello-world "/hello" 2 hours ago Exited (0) 2 hours ago naughty_euler
$ sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
hello-world latest bf756fb1ae65 7 months ago 13.3kB
$ sudo docker save -o hello-world-latest.tar hello-world:latest
$ ls
hello-world-latest.tar
$ sudo docker rmi hello-world:latest
Error response from daemon: conflict: unable to remove repository reference "hello-world:latest" (must force) - container 153999a1dfb2 is using its referenced image bf756fb1ae65
$ sudo docker rmi -f hello-world:latest # 强制删除镜像
Untagged: hello-world:latest
Untagged: hello-world@sha256:49a1c8800c94df04e9658809b006fd8a686cab8028d33cfba2cc049724254202
Deleted: sha256:bf756fb1ae65adf866bd8c456593cd24beb6a0a061dedf42b26a993176745f6b
$ sudo docker ps -a # 可见,强制删除镜像后,原始关联的容器并不会被删除
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
153999a1dfb2 bf756fb1ae65 "/hello" 5 hours ago Exited (0) 5 hours ago naughty_euler
$ sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
$ sudo docker load -i hello-world-latest.tar
Loaded image: hello-world:latest
$ sudo docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
hello-world latest bf756fb1ae65 7 months ago 13.3kB
$ sudo docker ps -a # 可见,当重新加载对应的镜像时,这里的IMAGE名字又对应了回来
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
153999a1dfb2 hello-world "/hello" 5 hours ago Exited (0) 5 hours ago naughty_euler这里也有个例子:
- docker 打包本地镜像, 并到其他机器进行恢复:https://blog.csdn.net/zf3419/article/details/88533274
相关的内容并没有一个统一的一级选项来负责, 都是二级选项.
- 最全面的删除:
docker system prune这一指令会询问你是否执行 _Remove all unused containers, networks, images (both dangling and unreferenced), and optionally, volumes. _ 注意, 这个命令会把你暂时关闭的容器, 以及暂时没有用到的 Docker 镜像都删掉.- 添加参数
--all或者-a来 Remove all unused images not just dangling ones. - 添加参数
--volumes来 Remove all volumes not used by at least one container.
- 添加参数
- 对于 volumes 的删除:
docker volume pruneRemove all unused local volumes. Unused local volumes are those which are not referenced by any containers. - 对于容器的删除:
docker container pruneRemove all stopped containers. - 对于镜像的删除:
docker image pruneRemove all dangling images. If-ais specified, will also remove all images not referenced by any container.
实际上这些指令是一次性删除一类目标, 属于范围性操作. 而 docker 提供的那些 rm 类指令, 则更加属于针对性的操作. 但是这些针对性操作由于其本身是可以接收多个需要处理的目标的, 所以也可以利用迂回的方式进行处理:
- 容器:
docker rm $(docker ps -aq): 删除所有停止的容器.docker container rm和docker rm等价docker container ls和docker ps等价
- 镜像:
docker rmi $(docker images -f dangling=true -aq): 删除所有挂起的镜像docker image rm和docker rmi等价docker image ls和docker images等价
- 数据卷 Volume:
docker volume rm $(docker volume ls -q): 删除不再使用的数据卷.
- build cache:
- Docker 18.09 引入了 BuildKit , 提升了构建过程的性能、安全、存储管理等能力.
docker builder prune: 删除 build cache.
命令虽直接, 但是却也增加了记忆负担, 这里列举了 5个好用的Docker图形化管理工具 中提到的五款工具:
- Portainer, 开源, Web 应用.
- DockStation, 免费的, 桌面应用.
- Docker Desktop, Docker 自己的客户端.
- Lazydocker, 开源, TUI(终端界面), 按照作者的话来说:LazyDocker 更多地有关管理现有容器/服务, 而 Docui 则更多地有关创建和配置它们. 这也是目前我在使用的工具, 比较简单, 安装非常容易, 单文件程序, 直接执行即可, 终端里, 按键都有提示.
- Docui, 开源, TUI.
安装 docker 时通常是默认安装的系统盘目录 /var/lib/docker。
- 推荐(基于软连接,迁移更彻底),可见 docker安装目录迁移的两种常用方法_docker_脚本之家:
- 先将
/var/lib/docker整个目录拷贝到需要迁移的目录中去:- 停掉 docker 服务:
systemctl stop docker - 将该目录拷贝到要迁移的目录中去(例如
/home/docker/lib/):rsync -r -avz /var/lib/docker /home/docker/lib/。
- 停掉 docker 服务:
- 如果原目录仍然存在,则可以先改名,再使用软链接将新目录中的
docker链接过来:
- 先将
mv /var/lib/docker /var/lib/docker-old
ln -s /home/docker/lib/docker /var/lib/- 重启 docker:
systemctl start docker或者systemctl restart docker - 验证镜像和容器可以正常运行,即可删除
/var/lib/docker-old目录(注意:在未确定镜像和容器正常运行前,千万别删除/var/lib/docker-old目录) - 修改下载的镜像的存储目录 (https://stackoverflow.com/questions/24309526/how-to-change-the-docker-image-installation-directory): 在
/etc/docker/daemon.json中添加"data-root": "/home/lart/DockerData/docker/"来指定存储位置 (注意, 最好在一开始就弄, 不然或许还存在需要搬迁之前文件的问题), 之后重启服务.
- docker 命令行的基本指令都在这里:https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/docker/
- 官方给了一些指导性的文档:https://docs.docker.com/develop/
- 常用镜像:
- NIVIDIA 提供的自家工具的容器资源:https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/containers
- Docker 官方提供的平台:https://hub.docker.com
- 关于 Docker 数据清理的内容主要参考自这里:https://www.jianshu.com/p/ffc697692dd7
- 我的后续的一篇文章:使用 Docker 为无网络环境搭建深度学习环境:https://www.yuque.com/lart/blog/nxomkh