Forward modeling of gravitational fields in spherical coordinates.
Developed by Leonardo Uieda in cooperation with Carla Braitenberg.
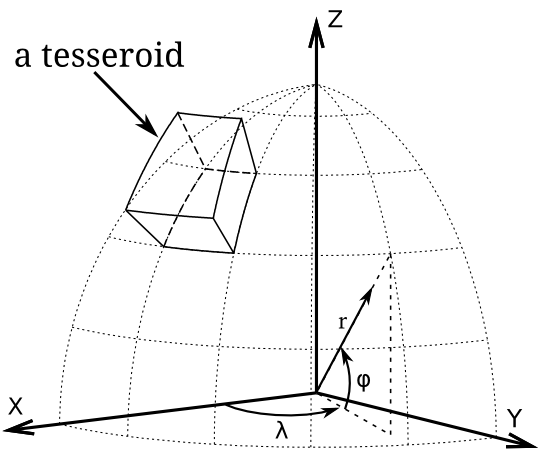
Tesseroids is a collection of command-line tools for modeling the gravitational potential, acceleration, and gradient (Marussi) tensor.
The mass models can be made of right rectangular prisms or tesseroids (spherical prisms). Computation for rectangular prisms can be made in Cartesian or spherical (geocentric) coordinates.
Tesseroids is free software made available under the terms of the BSD 3-clause license. See LICENSE.txt.
Tesseroids is research software made by scientists. If you use it in your research, please cite our Geophysics paper in your publications:
Uieda, L., V. Barbosa, and C. Braitenberg (2016), Tesseroids: Forward-modeling gravitational fields in spherical coordinates, GEOPHYSICS, F41-F48, doi:10.1190/geo2015-0204.1.
You can download a copy of the paper PDF at leouieda.com/papers/paper-tesseroids-2016.html and see all source code used in the paper at the Github repository pinga-lab/paper-tesseroids.
See CITATION.txt or the Citing page of the documentation for more information.
The easiest way to install is to download the latest compiled binary distribution from:
https://github.com/leouieda/tesseroids/releases/latest
We offer binaries for Windows (32 and 64 bit) and GNU/Linux (32 and 64 bit).
Once downloaded, simply unpack the archive in the desired directory.
The executables will be in the bin folder.
For easier access to the programs, consider
adding the bin folder to your PATH environment
variable.
Take a look at the examples in the Cookbook. They contain scripts that run Tesseroids and some Python code to plot the results.
The documentation contains sections on the theory and equations and usage instructions.
Also, all programs accept the -h flag to print the instructions for using
that particular program. For example:
$ tessgrd -h
Usage: tessgrd [PARAMS] [OPTIONS]
Make a regular grid of points.
All units either SI or degrees!
Output:
Printed to standard output (stdout) in the format:
lon1 lat1 height
lon2 lat1 height
... ... ...
lonNLON lat1 height
lon1 lat2 height
... ... ...
... ... ...
lonNLON latNLAT height
* Comments about the provenance of the data are inserted into
the top of the output
Parameters:
-r W/E/S/N: Bounding region of the grid.
-b NLON/NLAT: Number of grid points in the
longitudinal and latitudinal directions.
-z HEIGHT: Height of the grid with respect to the
mean Earth radius.
-h Print instructions.
--version Print version and license information.
Options:
-v Enable verbose printing to stderr.
-lFILENAME Print log messages to file FILENAME.
Part of the Tesseroids package.
Project site: <http://fatiando.org/software/tesseroids>
Report bugs at: <http://code.google.com/p/tesseroids/issues/list>
Write an e-mail to Leonardo Uieda, or tweet, or Google Hangout. Even better, submit a bug report/feature request/question to the Github issue tracker.
If you want to build Tesseroids from source, you'll need:
Tesseroids uses the build tool SCons.
A SConstruct file (Makefile equivalent)
is used to define the compilation rules.
The advantage of SCons over Make is that it automatically detects your system
settings.
You will have to download and install SCons
in order to easily compile Tesseroids.
SCons is available for both GNU/Linux and Windows
so compiling should work the same on both platforms.
SCons requires that you have Python installed. Follow the instructions in the SCons website to install it. Python is usually installed by default on most GNU/Linux systems.
Under Windows you will have to put SCons on
your PATH environment variable
in order to use it from the command line.
It is usually located in the Scripts directory of your Python installation.
On GNU/Linux, SCons will generally use the GCC compiler to compile sources. On Windows it will search for an existing compiler. We recommend that you install GCC on Windows using MinGW.
Download a source distribution and
unpack the archive anywhere you want
(e.g., ~/tesseroids or C:\tesseroids or whatever).
To compile,
open a terminal (or cmd.exe on Windows)
and go to the directory where you unpacked (use the cd command).
Then, type the following and hit Enter:
scons
If everything goes well, the compiled executables will be placed on a bin
folder.
To clean up the build (delete all generated files), run:
scons -c
If you get any strange errors or the code doesn't compile for some reason,
please submit a bug report.
Don't forget to copy the output of running scons.
After the compilation,
a program called tesstest
will be placed in the directory where you unpacked the source.
This program runs the unit tests
for Tesseroids (sources in the test directory).
To run the test suite, simply execute tesstest with no arguments:
tesstest
or on GNU/Linux:
./tesstest
A summary of all tests (pass or fail) will be printed on the screen.
If all tests pass,
the compilation probably went well.
If any test fail,
please submit a bug report
with the output of running tesstest.