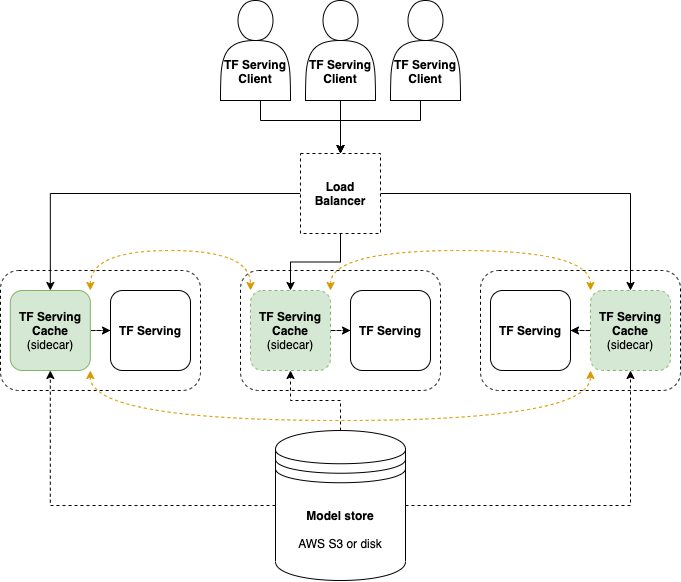
TF Serving load balancer/model cache that dynamically loads and unloads models into TensorFlow Serving services on demand.
An article about the project can be found here.
This is a work-in-progress.
TF Serving is used to serve TensorFlow models in production. Usually, one TF Serving service runs a specific set of models, e.g. an inception model or maybe several custom models. All models are loaded into main memory, which limits the number of models to be served per TF Serving service. This approach works well when the number of models is small, and the cost of running a TF Serving service for model, or for a small set of models, is low.
However, in other situations it is required to serve a large number of models, e.g. when each tenant or user has its own specific model. The load on each model may not be high so the requirements to availability are fairly low, and it can be expensive to serve all models simultaneously with TF Serving due to the total memory requirements being high. For example, consider if 1000 users have a model of size 1gb each, the total memory requirement is 1 terabyte of memory if all models are to be served simultaneously.
TF Serving Cache distributes the models among a number of TensorFlow Serving services, each providing at most N models concurrently. The cache implements the TF Serving predict protocol (both REST and gRPC), and hence it does not require any modification to clients using TensorFlow Serving.
When a model is requested, TF Serving Cache will identify a TF Serving service that will serve the model. If the model is loaded and ready, the request will be forwarded to the TF Serving. Otherwise, the cache will fetch it from an external source (disk or AWS S3) and load it into TF Serving while unloading the least-recently-used model, before it forwards the request to TF Serving.1
In order to identify which TF Serving service that should provide a model, TF Serving Cache employs consistent hashing with a user-defined number of replicas per model. The number of TF Serving services available can be scaled dynamically, and either etcd or Consul are supported for service discovery.
| Variable | Type | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
proxyRestPort |
int | HTTP port for the proxy service | |
proxyGrpcPort |
int | gRPC port for the proxy service | |
cacheRestPort |
int | HTTP port for the cache service | |
cacheGrpcPort |
int | gRPC port for the cache service | |
metrics.path |
string | URL path where metrics are exposed | |
metrics.timeout |
int | Timeout (in second) for gathering metrics from TF Serving | |
metrics.modelLabels |
bool | Whether to expose model names and versions as metric labels | |
modelProvider.type |
string | The model provider service, either diskProvider, s3Provider or azBlobProvider |
|
modelProvider.diskProvider.basePath |
string | The path to the disk model provider | |
modelProvider.s3.bucket |
string | The S3 bucket for the model provider | |
modelProvider.s3.basePath |
string | Prefix for S3 keys | |
modelProvider.azBlob.container |
string | The Azure storage container containing the models | |
modelProvider.azBlob.containerUrl |
string | The Azure storage container url (an alternative to modelProvider.azBlob.container) |
|
modelProvider.azBlob.basePath |
string | The model prefix for Azure blob keys | |
modelProvider.azBlob.accountName |
string | The Azure storage account name | |
modelProvider.azBlob.accountKey |
string | The Azure storage account access key | |
modelCache.hostModelPath |
string | The directory path specifying where the cached models are stored | |
modelCache.size |
int | The size of the cache in bytes | |
serving.servingModelPath |
string | The directory path where models are stored in TF Serving | |
serving.grpcHost |
string | The gRPC host for TF Serving, e.g. localhost:8500 |
|
serving.restHost |
string | The REST host for TF Serving, e.g. http://localhost:8501 |
|
serving.maxConcurrentModels |
int | The number of models to be serving simultaneously | |
serving.grpcConfigTimeout |
int | gRPC config timeout in seconds | |
serving.grpcPredictTimeout |
int | gRPC prediction timeout in seconds | |
serving.grpcMaxMsgSize |
int | Max message size for gRPC requests in bytes | |
serving.metricsPath |
string | metrics.path |
Path to TF Serving metrics |
proxy.replicasPerModel |
int | The number of nodes that should serve each model | |
proxy.grpcTimeout |
int | Timeout for the gRPC proxy | |
serviceDiscovery.type |
string | The service discovery type to use. Either consul, etcd, or k8s |
|
serviceDiscovery.consul.serviceName |
string | The name to identify the TFServingCache service | |
serviceDiscovery.consul.serviceId |
string | The service id to identify the TFServingCache service | |
serviceDiscovery.etcd.serviceName |
string | The service id to identify the TFServingCache service | |
serviceDiscovery.etcd.endpoints |
string list | The endpoints for the etcd service | |
serviceDiscovery.etcd.allowLocalhost |
bool | Whether to allow localhost IPs for nodes | |
serviceDiscovery.etcd.authorization.username |
string | etcd username | |
serviceDiscovery.etcd.authorization.password |
string | etcd password | |
serviceDiscovery.k8s.fieldSelector |
dict | The fieldselector to identify TFServingCache services | |
serviceDiscovery.k8s.portNames.grpcCache |
string | The name of the gRPC port of the cache | |
serviceDiscovery.k8s.portNames.httpCache |
string | The name of the HTTP port of the cache | |
healthProbe.modelName |
string | __TFSERVINGCACHE_PROBE_CHECK__ |
The name of the model to use for health probes |
- REST (proxy):
- Timeouts
- Retries
- Smaller mutex-region in cache
1: This Just-In-Time model loading is inspired by ideas by @mpdn