- OTP Authentication in Flutter using Firebase
- Google Firebase Provide Phone Authentication using SMS. The basic plan of firebase includes 10k of free SMS for month. We will learn Firebase Phone Authentication in Flutter in this article. We will start from firebase programmatically setup to actual integration in flutter. So let’s start...
-
First and basic step to create new application in flutter. If you are a beginner in flutter then you can check my blog Create a first app in Flutter. I have created app named as “flutter_otp_auth”
-
Now, You need to setup a project in Google Firebase. Follow below steps for that. Please follow the step very carefully.
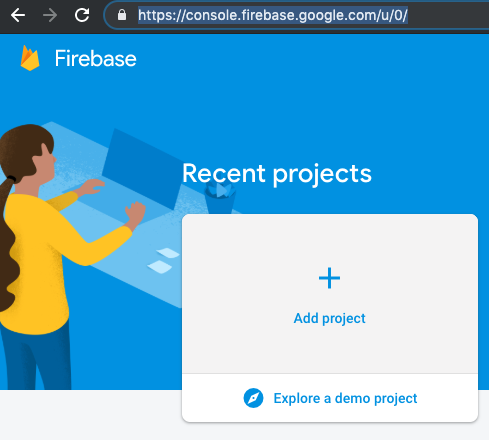
- Goto https://console.firebase.google.com/ and add new project. I will share screenshot how it looks so you will get a better idea.
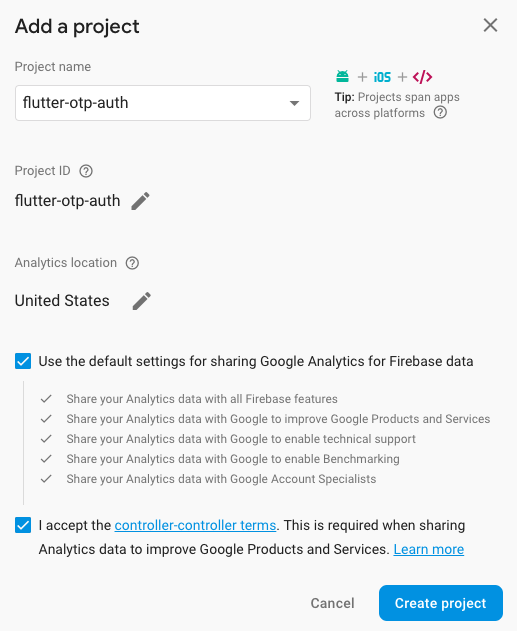
- Click on Add Project to add new project in Google Firebase. Then you will find below form
-
Give a project name and accept the terms and condition and click on the Create Project. It will take some time to create a new project and redirect you to project overview page.
-
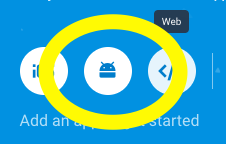
Now, you need to add android app in this project [Please check below screenshot]. You can add new android project from clicking on android icon. You can also add ios project if you want to create ios application for the same.
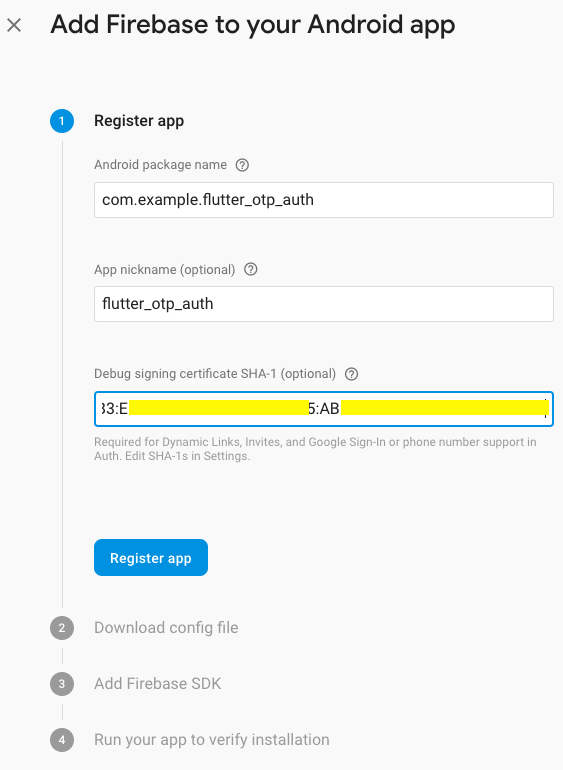
- In Project Overview add android app for that click on the android icon. It will open new form please check below screenshot.
-
Android package name you will find in the AndroidManifest.xml file in the Android => App => main folder of your project.
-
App nickname is optional
-
For SHA-1 generation goto https://developers.google.com/android/guides/client-auth
-
In step 2 download google-service.json and put in android => App folder of your project
-
In step 3 you can see you need to configure some
-
dependencies Project-level build.gradle (/build.gradle): means build.gradle file in Android folder directly
buildscript { dependencies { // Add this line classpath 'com.google.gms:google-services:4.2.0' } }App-level build.gradle (//build.gradle): means build.gradle file in Android = > App folder // Add to the bottom of the file
apply plugin: 'com.google.gms.google-services’Note: Don’t need to add implementation 'com.google.firebase:firebase-core:16.0.9' in dependencies
-
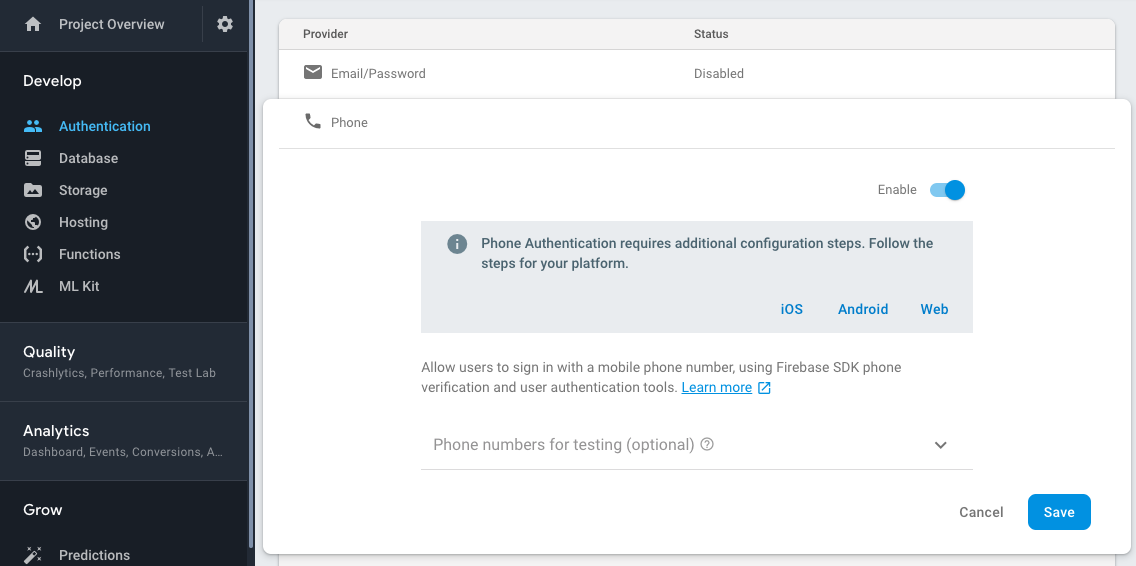
Now, you need to enable Phone # method in firebase. For that you need to go to the Authentication tab and then Signin method tab. From there enable Phone # method. Please check the screenshot.
- Hurrey :) your android app has been created.
-
Get back to the project and Open pubspec.yaml file in the root of the project. Pubspec.yaml is used to define all the dependencies and assets of the project.
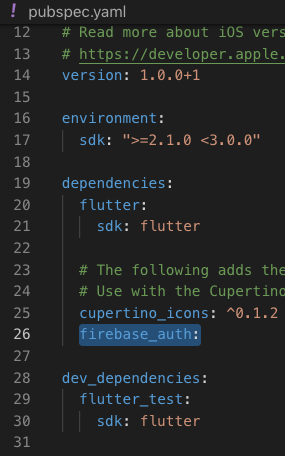
- Add below dependencies and save the file
firebase_auth:-
Please check below screenshot you will get more idea where to add the dependency
-
Run flutter packages get in terminal OR If you are using Visual Studio Code then after saving file it will automatically runs the flutter packages get command.
-
Now, we are done with all dependency setup at project side as well…. :)
-
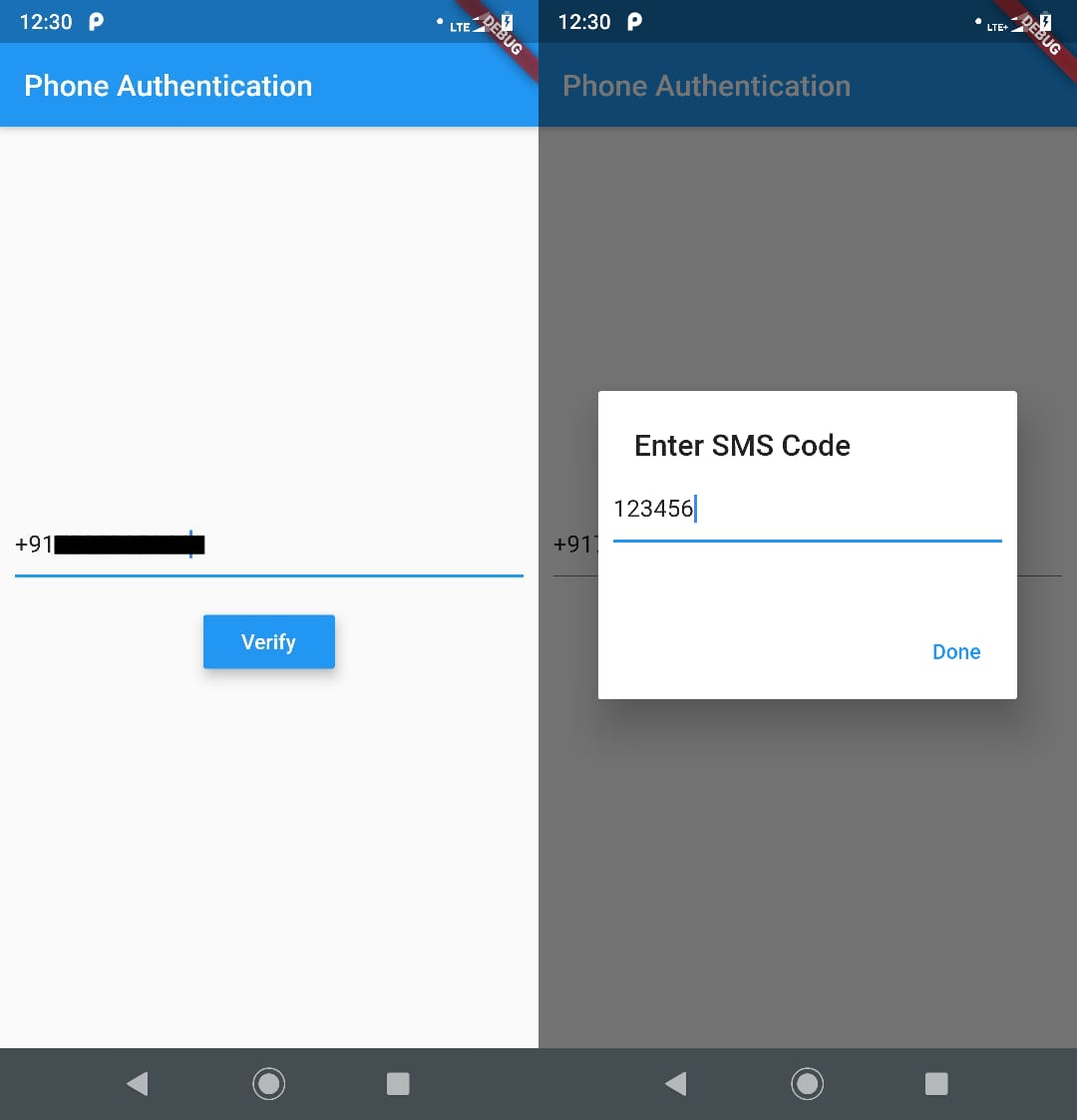
Now, we need to programmatically handle OTP Login in google firebase. For that we create 2 pages main.dart(default) and homepage.dart. I have attached a link of git repo in the bottom of the article, you can take reference from there. Here I will just important methods for send and verify OTP. Below is the source code for main.dart file
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; import 'package:firebase_auth/firebase_auth.dart'; import 'package:flutter/services.dart'; import 'homepage.dart'; void main() => runApp(MyApp()); class MyApp extends StatelessWidget { @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return MaterialApp( title: 'Phone Authentication', routes: <String, WidgetBuilder>{ '/homepage': (BuildContext context) => MyHome(), '/#page': (BuildContext context) => MyApp(), }, theme: ThemeData( primarySwatch: Colors.blue, ), home: MyAppPage(title: 'Phone Authentication'), ); } } class MyAppPage extends StatefulWidget { MyAppPage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key); final String title; @override _MyAppPageState createState() => _MyAppPageState(); } class _MyAppPageState extends State<MyAppPage> { String phoneNo; String smsOTP; String verificationId; String errorMessage = ''; FirebaseAuth _auth = FirebaseAuth.instance; Future<void> verifyPhone() async { final PhoneCodeSent smsOTPSent = (String verId, [int forceCodeResend]) { this.verificationId = verId; smsOTPDialog(context).then((value) { print('#'); }); }; try { await _auth.verifyPhoneNumber( phoneNumber: this.phoneNo, // PHONE NUMBER TO SEND OTP codeAutoRetrievalTimeout: (String verId) { //Starts the phone number verification process for the given phone number. //Either sends an SMS with a 6 digit code to the phone number specified, or sign's the user in and [verificationCompleted] is called. this.verificationId = verId; }, codeSent: smsOTPSent, // WHEN CODE SENT THEN WE OPEN DIALOG TO ENTER OTP. timeout: const Duration(seconds: 20), verificationCompleted: (AuthCredential phoneAuthCredential) { print(phoneAuthCredential); }, verificationFailed: (AuthException exceptio) { print('${exceptio.message}'); }); } catch (e) { handleError(e); } } Future<bool> smsOTPDialog(BuildContext context) { return showDialog( context: context, barrierDismissible: false, builder: (BuildContext context) { return new AlertDialog( title: Text('Enter SMS Code'), content: Container( height: 85, child: Column(children: [ TextField( onChanged: (value) { this.smsOTP = value; }, ), (errorMessage != '' ? Text( errorMessage, style: TextStyle(color: Colors.red), ) : Container()) ]), ), contentPadding: EdgeInsets.all(10), actions: <Widget>[ FlatButton( child: Text('Done'), onPressed: () { _auth.currentUser().then((user) { if (user != null) { Navigator.of(context).pop(); Navigator.of(context).pushReplacementNamed('/homepage'); } else { signIn(); } }); }, ) ], ); }); } signIn() async { try { final AuthCredential credential = PhoneAuthProvider.getCredential( verificationId: verificationId, smsCode: smsOTP, ); final FirebaseUser user = await _auth.signInWithCredential(credential); final FirebaseUser currentUser = await _auth.currentUser(); assert(user.uid == currentUser.uid); Navigator.of(context).pop(); Navigator.of(context).pushReplacementNamed('/homepage'); } catch (e) { handleError(e); } } handleError(PlatformException error) { print(error); switch (error.code) { case 'ERROR_INVALID_VERIFICATION_CODE': FocusScope.of(context).requestFocus(new FocusNode()); setState(() { errorMessage = 'Invalid Code'; }); Navigator.of(context).pop(); smsOTPDialog(context).then((value) { print('#'); }); break; default: setState(() { errorMessage = error.message; }); break; } } @override Widget build(BuildContext context) { return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar( title: Text(widget.title), ), body: Center( child: Column( mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center, children: <Widget>[ Padding( padding: EdgeInsets.all(10), child: TextField( decoration: InputDecoration( hintText: 'Enter Phone Number Eg. +910000000000'), onChanged: (value) { this.phoneNo = value; }, ), ), (errorMessage != '' ? Text( errorMessage, style: TextStyle(color: Colors.red), ) : Container()), SizedBox( height: 10, ), RaisedButton( onPressed: () { verifyPhone(); }, child: Text('Verify'), textColor: Colors.white, elevation: 7, color: Colors.blue, ) ], ), ), ); } } -
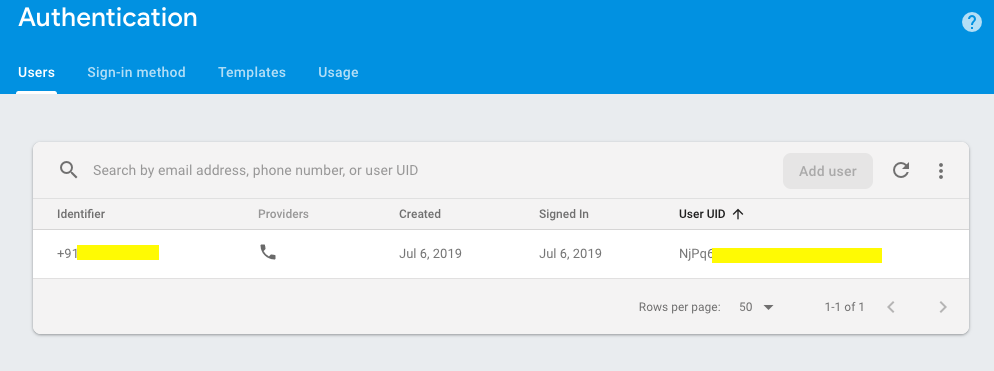
When you successfully verify OPT you can check that google firebase store the user detail in server. Please check the screenshot.
# Error: import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
# Solution :
Put android.useAndroidX=true
android.enableJetifier=true
In android/gradle.properties file
- PLEASE CHECK OUT GIT REPO FOR FULL SOURCE CODE. YOU NEED TO ADD YOUR google-services.json FILE IN ANDROID => APP FOLDER.
https://github.com/myvsparth/flutter_otp_auth
- OTP verification becomes one of the musts required authentication techniques where security is very important. Google firebase provide OTP Phone authentication free starter plan and flutter provide easy to setup technique for this.
Related to Tags: Flutter, Dart, Firebase Auth, OTP Authentication
For help getting started with Flutter, view online documentation, which offers tutorials, samples, guidance on mobile development, and a full API reference.