In this section we’re going to install and configure:
- MariaDB database server.
- PowerDNS service
Step 1: Install and Configure MariaDB Database Server We need to install database server which will be used by PowerDNS to store zone files. Note that you also have an option to use text files like BIND. Our database server of choice is MariaDB.
For installation of MariaDB on Ubuntu / Debian Linux Server:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install mariadb-server -y
Once the database server is installed and running, proceed to create the PowerDNS Database and User Account in MariaDB.
$ sudo mysql -u root -p
CREATE DATABASE powerdns;
Next is to create powerdns database user and assign privileges: On Mariadb:
GRANT ALL ON powerdns.* TO 'powerdns'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Str0ngPasswOrd';
On MySQL:
CREATE USER 'powerdns'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Str0ngPasswOrd';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON powerdns.* TO 'powerdns'@'localhost';
Flush the privileges to update the user settings:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Switch to powerdns database to create tables:
USE powerdns;
Create the required tables: Or using the PowerDNS Schema up-to-date: https://doc.powerdns.com/authoritative/backends/generic-mysql.html
CREATE TABLE domains (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
master VARCHAR(128) DEFAULT NULL,
last_check INT DEFAULT NULL,
type VARCHAR(8) NOT NULL,
notified_serial INT UNSIGNED DEFAULT NULL,
account VARCHAR(40) CHARACTER SET 'utf8' DEFAULT NULL,
options VARCHAR(64000) DEFAULT NULL,
catalog VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARACTER SET 'latin1';
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX name_index ON domains(name);
CREATE INDEX catalog_idx ON domains(catalog);
CREATE TABLE records (
id BIGINT AUTO_INCREMENT,
domain_id INT DEFAULT NULL,
name VARCHAR(255) DEFAULT NULL,
type VARCHAR(10) DEFAULT NULL,
content VARCHAR(64000) DEFAULT NULL,
ttl INT DEFAULT NULL,
prio INT DEFAULT NULL,
disabled TINYINT(1) DEFAULT 0,
ordername VARCHAR(255) BINARY DEFAULT NULL,
auth TINYINT(1) DEFAULT 1,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARACTER SET 'latin1';
CREATE INDEX nametype_index ON records(name,type);
CREATE INDEX domain_id ON records(domain_id);
CREATE INDEX ordername ON records (ordername);
CREATE TABLE supermasters (
ip VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
nameserver VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
account VARCHAR(40) CHARACTER SET 'utf8' NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (ip, nameserver)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARACTER SET 'latin1';
CREATE TABLE comments (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
domain_id INT NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
type VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
modified_at INT NOT NULL,
account VARCHAR(40) CHARACTER SET 'utf8' DEFAULT NULL,
comment TEXT CHARACTER SET 'utf8' NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARACTER SET 'latin1';
CREATE INDEX comments_name_type_idx ON comments (name, type);
CREATE INDEX comments_order_idx ON comments (domain_id, modified_at);
CREATE TABLE domainmetadata (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
domain_id INT NOT NULL,
kind VARCHAR(32),
content TEXT,
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARACTER SET 'latin1';
CREATE INDEX domainmetadata_idx ON domainmetadata (domain_id, kind);
CREATE TABLE cryptokeys (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
domain_id INT NOT NULL,
flags INT NOT NULL,
active BOOL,
published BOOL DEFAULT 1,
content TEXT,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARACTER SET 'latin1';
CREATE INDEX domainidindex ON cryptokeys(domain_id);
CREATE TABLE tsigkeys (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(255),
algorithm VARCHAR(50),
secret VARCHAR(255),
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) Engine=InnoDB CHARACTER SET 'latin1';
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX namealgoindex ON tsigkeys(name, algorithm);
You can confirm that your tables are created:
MariaDB [powerdns]> show tables;
+--------------------+
| Tables_in_powerdns |
+--------------------+
| comments |
| cryptokeys |
| domainmetadata |
| domains |
| records |
| supermasters |
| tsigkeys |
+--------------------+
7 rows in set (0.000 sec)
Now we have a database and an empty table. PowerDNS should now be able to launch with it.
Step 2: Install PowerDNS on Ubuntu 20.04|18.04 / Debian 10|9 Ubuntu 20.04|18.04 comes with systemd-resolve which you need to disable since it binds to port 53 which will conflict with PowerDNS ports.
Run the following commands to disable the resolved service:
sudo systemctl disable systemd-resolved
sudo systemctl stop systemd-resolved
Also, remove the symlinked resolv.conf file
$ ls -lh /etc/resolv.conf
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 39 Jul 24 15:50 /etc/resolv.conf -> ../run/systemd/resolve/stub-resolv.conf
$ sudo rm /etc/resolv.conf
Then create new resolv.conf file.
echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" | sudo tee /etc/resolv.conf
Note that you can install PowerDNS from the official apt repository or from PowerDNS repository. To install from apt repository, run:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install pdns-server pdns-backend-mysql
Add official PowerDNS repository for Ubuntu 20.04|18.04.
- Ubuntu 20.04
echo "deb [arch=amd64] http://repo.powerdns.com/ubuntu focal-auth-master main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pdns.list
- Ubuntu 18.04
echo "deb [arch=amd64] http://repo.powerdns.com/ubuntu bionic-auth-master main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pdns.list
- Import GPG key:
curl https://repo.powerdns.com/CBC8B383-pub.asc | sudo apt-key add -
- Update package list and install PowerDNS package (pdns-server) and MySQL backend (pdns-backend-mysql).
sudo apt update
sudo apt install pdns-server pdns-backend-mysql
Install packages on Debian 10/9 Add APT repository
- Debian 10
echo "deb [arch=amd64] http://repo.powerdns.com/debian buster-auth-master main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pdns.list
- Debian 9:
echo "deb [arch=amd64] http://repo.powerdns.com/debian stretch-auth-master main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/pdns.list
- Import gpg key:
sudo apt install wget apt-transport-https gnupg2
curl https://repo.powerdns.com/CBC8B383-pub.asc | sudo apt-key add -
- Then install PowerDNS packages on Debian 10 / Debian 9:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install pdns-server pdns-backend-mysql
- When asked whether to configure the PowerDNS database with dbconfig-common, answer No
Configure PowerDNS to use MySQL backend: Here is my MySQL configuration for PowerDNS:
$ sudo vim /etc/powerdns/pdns.d/pdns.local.gmysql.conf
# MySQL Configuration
# Launch gmysql backend
launch+=gmysql
# gmysql parameters
gmysql-host=localhost
gmysql-port=3306
gmysql-dbname=powerdns
gmysql-user=powerdns
gmysql-password=Str0ngPasswOrd
gmysql-dnssec=yes
# gmysql-socket=
Restart and enable the pdns service
sudo systemctl restart pdns
sudo systemctl enable pdns
You can now test PowerDNS to confirm that the service is online:
$ sudo apt install net-tools -y
$ sudo netstat -tap | grep pdns
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:domain 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 6211/pdns_server
tcp6 0 0 [::]:domain [::]:* LISTEN 6211/pdns_server
Check if PowerDNS service is responding correctly:
$ dig @127.0.0.1
; <<>> DiG 9.16.1-Ubuntu <<>> @127.0.0.1
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: REFUSED, id: 14054
;; flags: qr rd; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1
;; WARNING: recursion requested but not available
;; OPT PSEUDOSECTION:
; EDNS: version: 0, flags:; udp: 1232
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;. IN NS
;; Query time: 0 msec
;; SERVER: 127.0.0.1#53(127.0.0.1)
;; WHEN: Wed Apr 28 11:04:57 UTC 2021
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 28
PowerDNS-Admin is a PowerDNS web interface with the following advanced features:
- Multiple domain management
- Domain template
- User management
- User access management based on domain
- User activity logging
- Local DB / LDAP / Active Directory user authentication
- Support SAML authentication
- Google OAuth authentication
- Github OAuth authentication
- Support Two-factor authentication (TOTP)
- Dashboard and pdns service statistics
- DynDNS 2 protocol support
- Edit IPv6 PTRs using IPv6 addresses directly (no more editing of literal addresses!)
Install Python 3 development package
sudo apt install -y python3-dev git libsasl2-dev libldap2-dev python3-venv libmariadb-dev pkg-config build-essential curl libpq-dev
Install required packages for building python libraries from requirements.txt file
sudo apt install -y default-libmysqlclient-dev libsasl2-dev libldap2-dev libssl-dev libxml2-dev libxslt1-dev libxmlsec1-dev libffi-dev pkg-config apt-transport-https virtualenv build-essential
Install Node.js
curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_14.x | bash -
apt install -y nodejs
Install yarn to build asset files:
sudo curl -sS https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | apt-key add -
echo "deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.list
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install -y yarn
git clone https://github.com/PowerDNS-Admin/PowerDNS-Admin.git /opt/web/powerdns-admin
cd /opt/web/powerdns-admin
virtualenv -p python3 flask
Output:
Already using interpreter /usr/bin/python3
Using base prefix '/usr'
New python executable in /opt/web/powerdns-admin/flask/bin/python3
Also creating executable in /opt/web/powerdns-admin/flask/bin/python
Installing setuptools, pkg_resources, pip, wheel...done.
Activate your python3 environment and install libraries:
source ./flask/bin/activate
pip install -r requirements.txt
Before running PowerDNS-Admin, we need to configure database connectivity.
vim ./powerdnsadmin/default_config.py
These are the required config:
- DB connection information
- PNDS API service endpoint and API key
- Port Number used
- Bind Address
- Comment out SQLite SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI line and uncomment MySQL one:
### DATABASE CONFIG
SQLA_DB_USER = 'powerdns'
SQLA_DB_PASSWORD = 'Str0ngPasswOrd'
SQLA_DB_HOST = '127.0.0.1'
SQLA_DB_NAME = 'powerdns'
SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS = True
### DATABASE - MySQL
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI = 'mysql://'+SQLA_DB_USER+':'+SQLA_DB_PASSWORD+'@'+SQLA_DB_HOST+'/'+SQLA_DB_NAME
Once you your configuration is ready. Create the database schema by running commands:
(flask) $ export FLASK_APP=powerdnsadmin/__init__.py
(flask)$ flask db upgrade
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Context impl MySQLImpl.
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Will assume non-transactional DDL.
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade -> 787bdba9e147, Init DB
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 787bdba9e147 -> 59729e468045, Add view column to setting table
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 59729e468045 -> 1274ed462010, Change setting.value data type
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 1274ed462010 -> 4a666113c7bb, Adding Operator Role
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 4a666113c7bb -> 31a4ed468b18, Remove all setting in the DB
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 31a4ed468b18 -> 654298797277, Upgrade DB Schema
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 654298797277 -> 0fb6d23a4863, Remove user avatar
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 0fb6d23a4863 -> 856bb94b7040, Add comment column in domain template record table
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 856bb94b7040 -> b0fea72a3f20, Update domain serial columns type
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade b0fea72a3f20 -> 3f76448bb6de, Add user.confirmed column
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Running upgrade 3f76448bb6de -> 0d3d93f1c2e0, Add domain_id to history table
Then run db migrate:
(flask)$ flask db migrate -m "Init DB"
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Context impl MySQLImpl.
INFO [alembic.runtime.migration] Will assume non-transactional DDL.
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed index 'namealgoindex' on 'tsigkeys'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed table 'tsigkeys'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed index 'domainidindex' on 'cryptokeys'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed table 'cryptokeys'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed index 'nametype_index' on 'records'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed table 'records'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed index 'domainmetadata_idx' on 'domainmetadata'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed table 'domainmetadata'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed table 'supermasters'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed index 'comments_name_type_idx' on 'comments'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed index 'comments_order_idx' on 'comments'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed table 'comments'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed index 'name_index' on 'domains'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected removed table 'domains'
INFO [alembic.autogenerate.compare] Detected added index 'ix_history_created_on' on '['created_on']'
Generating /opt/web/powerdns-admin/migrations/versions/b84731e09a35_init_db.py ... done
Generate asset files with yarn:
(flask)$ yarn install --pure-lockfile
yarn install v1.22.5
[1/4] Resolving packages...
[2/4] Fetching packages...
[3/4] Linking dependencies...
[4/4] Building fresh packages...
Done in 14.84s.
(flask)$ flask assets build
Building bundle: generated/#.js
[INFO] Building bundle: generated/#.js
Building bundle: generated/#.css
[INFO] Building bundle: generated/#.css
Building bundle: generated/main.js
[INFO] Building bundle: generated/main.js
Building bundle: generated/main.css
[INFO] Building bundle: generated/main.css
Test that your PowerDNS-Admin runs fine:
(flask)$ ./run.py
[INFO] * Running on http://127.0.0.1:9191/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
[INFO] * Restarting with stat
[WARNING] * Debugger is active!
[INFO] * Debugger PIN: 466-405-858
git clone https://github.com/PowerDNS-Admin/PowerDNS-Admin.git /opt/web/powerdns-admin
cd /opt/web/powerdns-admin
python3 -mvenv ./venv
Activate your python3 environment and install libraries:
source ./venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
Running PowerDNS-Admin Create PowerDNS-Admin config file and make the changes necessary for your use case. Make sure to change SECRET_KEY to a long random string that you generated yourself (see Flask docs), do not use the pre-defined one. E.g.:
cp /opt/web/powerdns-admin/configs/development.py /opt/web/powerdns-admin/configs/production.py
vim /opt/web/powerdns-admin/configs/production.py
export FLASK_CONF=../configs/production.py
Do the DB migration
export FLASK_APP=powerdnsadmin/__init__.py
flask db upgrade
Then generate asset files
yarn install --pure-lockfile
flask assets build
Now you can run PowerDNS-Admin by command
./run.py
This is good for testing, but for production usage, you should use gunicorn or uwsgi. See Running PowerDNS Admin with Systemd, Gunicorn and Nginx for instructions.
Create a service unit file like below:
$ sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/powerdns-admin.service
[Unit]
Description=PowerDNS-Admin
Requires=powerdns-admin.socket
After=network.target
[Service]
PIDFile=/run/powerdns-admin/pid
User=pdns
Group=pdns
WorkingDirectory=/opt/web/powerdns-admin
ExecStart=/opt/web/powerdns-admin/flask/bin/gunicorn --pid /run/powerdns-admin/pid --bind unix:/run/powerdns-admin/socket 'powerdnsadmin:create_app()'
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s TERM $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Create socket file
$ sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/powerdns-admin.socket
[Unit]
Description=PowerDNS-Admin socket
[Socket]
ListenStream=/run/powerdns-admin/socket
[Install]
WantedBy=sockets.target
Create environment file
$ sudo vim /etc/tmpfiles.d/powerdns-admin.conf
d /run/powerdns-admin 0755 pdns pdns -
Powerdns-Admin service and set it to start on boot:
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart powerdns-admin
sudo systemctl enable powerdns-admin
Set permissions of the
sudo chown -R pdns:pdns /run/powerdns-admin
sudo chown -R pdns:pdns /opt/web/powerdns-admin
sudo systemctl restart powerdns-admin
Confirm that status is running state:
$ systemctl status powerdns-admin
● powerdns-admin.service - PowerDNS-Admin
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/powerdns-admin.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2021-04-28 12:51:22 UTC; 9s ago
TriggeredBy: ● powerdns-admin.socket
Main PID: 19574 (gunicorn)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 4683)
Memory: 63.3M
CGroup: /system.slice/powerdns-admin.service
├─19574 /opt/web/powerdns-admin/flask/bin/python /opt/web/powerdns-admin/flask/bin/gunicorn --pid /run/powerdns-admin/pid --bind unix:/run/powerdns->
└─19582 /opt/web/powerdns-admin/flask/bin/python /opt/web/powerdns-admin/flask/bin/gunicorn --pid /run/powerdns-admin/pid --bind unix:/run/powerdns->
Apr 28 12:51:22 ubuntu systemd[1]: Started PowerDNS-Admin.
Apr 28 12:51:22 ubuntu gunicorn[19574]: [2021-04-28 12:51:22 +0000] [19574] [INFO] Starting gunicorn 20.0.4
Apr 28 12:51:22 ubuntu gunicorn[19574]: [2021-04-28 12:51:22 +0000] [19574] [INFO] Listening at: unix:/run/powerdns-admin/socket (19574)
Apr 28 12:51:22 ubuntu gunicorn[19574]: [2021-04-28 12:51:22 +0000] [19574] [INFO] Using worker: sync
Apr 28 12:51:22 ubuntu gunicorn[19582]: [2021-04-28 12:51:22 +0000] [19582] [INFO] Booting worker with pid: 19582
Install Nginx using:
sudo apt install nginx
Configure Nginx
sudo vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/powerdns-admin.conf
Add content like below:
server {
listen *:80;
server_name powerdns-admin.example.com www.powerdns-admin.example.com;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
root /opt/web/powerdns-admin;
access_log /var/log/nginx/powerdns-admin.local.access.log combined;
error_log /var/log/nginx/powerdns-admin.local.error.log;
client_max_body_size 10m;
client_body_buffer_size 128k;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_connect_timeout 90;
proxy_send_timeout 90;
proxy_read_timeout 90;
proxy_buffers 32 4k;
proxy_buffer_size 8k;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_headers_hash_bucket_size 64;
location ~ ^/static/ {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
root /opt/web/powerdns-admin/powerdnsadmin;
location ~* \.(jpg|jpeg|png|gif)$ {
expires 365d;
}
location ~* ^.+.(css|js)$ {
expires 7d;
}
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://unix:/run/powerdns-admin/socket;
proxy_read_timeout 120;
proxy_connect_timeout 120;
proxy_redirect off;
}
}
Check nginx syntax then restart nginx service:
$ sudo nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Visit PowerDNS-Admin web interface.
http://powerdns-admin.example.com/
Click “Create an account” button and Register a user. The first user will be in the Administrator role.
When you log in with created username and password, you should get an interface like below:
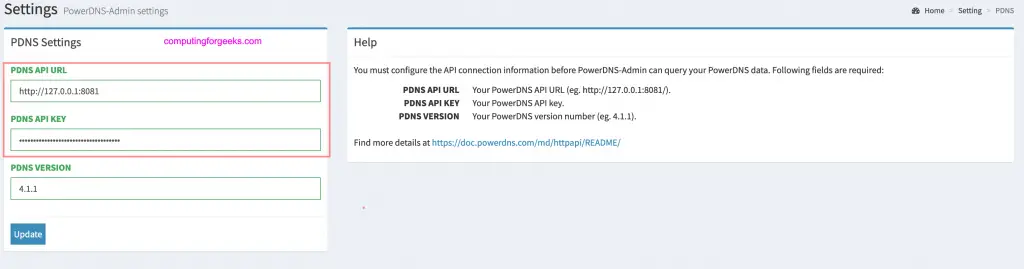
Edit PowerDNS configuration file and enable the built-in API:
$ sudo vim /etc/powerdns/pdns.conf
# Configure like below
webserver-port=8081
api=yes
api-key=f5ee4390-6542-48c9-a2a0-e5d0bd399490 #You can generate one from https://codepen.io/corenominal/pen/rxOmMJ
Restart powerdns service:
sudo systemctl restart powerdns-admin
Provide PowerDNS API connection information before PowerDNS-Admin can query your PowerDNS data. This is done under Settings > PDNS