-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 375
API_Python_Base
The MemProcFS process and module API for Python consists of two primary objects:
-
Vmm- the core MemProcFS virtual memory manager object. -
VmmPdb- an object for the Microsoft symbol server PDB debug symbols. -
memprocfs.CONSTANTS- MemProcFS constants.
MemProcFS is initialized by creating a Vmm object. Only one Vmm object may exist within a Python process at a given time at this moment.
The core MemProcFS virtual memory manager.
-
memprocfs.Vmm([str1, ..., strN])- constructor: create a new vmm object with a parameter list. -
memprocfs.Vmm()- constructor: grab a reference to an already initialized vmm object. -
virtualmachine.Vmm()- constructor: analyze a virtual machine.
vmm.vfs # VmmVfs: see methods below. ex: vmm.vfs -> Vfs
vmm.maps # VmmMaps: see methods below. ex: vmm.maps -> Maps
vmm.memory # VmmMaps: see methods below. ex: vmm.memory -> PhysicalMemory
vmm.kernel.build # int: the kernel build number.
vmm.kernel.pdb # VmmPdb: the kernel debug symbols. ex: vmm.kernel.pdb -> Pdb:nt
vmm.kernel.process # VmmProcess: the kernel process. ex: vmm.kernel.process -> Process:4# Close the VMM MemProcFS handle - which should not be accessed after the close.
# New VMM MemProcFS handles may be created after a close().
vmm.close() # -> None
# example:
# vmm.close() -> None
# Retrieve a VMM numeric config value denoted by config id.
# -- config_id = memprocfs.OPT_*.
# -- return
vmm.get_config(int: config_id) # -> int
# example:
# vmm.get_config(memprocfs.OPT_WIN_VERSION_MAJOR) -> 10
# Set a VMM numeric config value denoted by config id.
# -- config_id = memprocfs.OPT_*.
# -- config_value
vmm.set_config(int: config_id, int: config_value) # -> None
# example:
# vmm.set_config(memprocfs.OPT_CORE_PRINTF_ENABLE, 1)
# Retrieve a process by process id PID or name.
# -- pid
# -- return
vmm.process(int: pid) # -> VmmProcess
# example:
# vmm.process(4) -> Process:4
# Retrieve a process by process id PID or name.
# -- name
# -- return
vmm.process(str: name) # -> VmmProcess
# example:
# vmm.process('explorer.exe') -> Process:4280
# List all processes.
# --return
vmm.process_list() # -> list:VmmProcess
# example:
# vmm.process_list() ->
# [Process:4, Process:1776, Process:10136, Process:9584, Process:1720, Process:6592, ...]
# List all registry hives.
# -- return
vmm.reg_hive_list() # -> list:VmmRegHive
# example:
# vmm.reg_hive_list() ->
# [RegHive:ekyb3d8bbwe\ActivationStore.dat, ..., RegHive:SYSTEM]
# Retrieve a registry key by its path/name.
# -- path
# -- return
vmm.reg_key(str: path) # -> VmmRegKey
# example:
# vmm.reg_key('HKLM\\SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run') -> RegKey:Run
# Retrieve a registry value by its path/name.
# -- path
# -- return
vmm.reg_value(str: path) # -> VmmRegValue
# example:
# vmm.reg_value('HKLM\\SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run\\SecurityHealth') ->
# RegValue:SecurityHealth
# Read physical memory.
# -- address_physical
# -- bytes_to_read
# -- flags = optional read flags memprocfs.FLAG_*.
# -- return
vmm.memory.read(int: address_physical, int: size_to_read, opt int: flags) # -> bytes
# example:
# print(vmm.hex( vmm.memory.read(0x1000, 0x20) )) ->
# 0000 e8 40 f3 df 00 00 00 00 2b 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 .@......+.......
# 0010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
# Read physical memory (multiple ranges).
# -- list of physical ranges
# -- flags = optional read flags memprocfs.FLAG_*.
# -- return
vmm.memory.read(list: physical_ranges, opt int: flags) # -> bytes
# example:
# vmm.memory.read( [[0x1000, 0x20], [0x3000, 0x10]] ) -> [b'..', b'..']
# Read a single native data type from memory.
# Valid types: i8, u8, i16, u16, f32, i32, u32, f64, i64, u64.
# -- address_physical
# -- bytes_to_read
# -- flags = optional read flags memprocfs.FLAG_*.
# -- return
vmm.memory.read_type(int: address_physical, str: type_to_read, opt int: flags) # -> type
# example:
# vmm.memory.read_type(0x930000, 'u16') -> 23117
# Read multiple native data type from memory.
# Valid types: i8, u8, i16, u16, f32, i32, u32, f64, i64, u64.
# -- list_of_types
# -- flags = optional read flags memprocfs.FLAG_*.
# -- return
vmm.memory.read_type(list: list_of_types, str: type_to_read, opt int: flags) # -> [type1, .., typeN]
# example:
# vmm.memory.read_type([[0x7FF750930000, 'u64'], [0x7FF750930000, 'f32']]) -> [12894362189, 1.325670526335053e-38]
# Read multiple 0x1000 bytes-sized chunks scattered among listed
# 0x1000 byte aligned addresses.
# -- address_list = list of 0x1000-aligned physical addresses.
# -- return
vmm.memory.read_scatter([int: address_physical1, ...], opt int: flags) # -> list:dict
# example:
# vmm.memory.read_scatter([0x1000, 0x2000]) ->
# [{'addr': 4096, 'pa': 4096, 'data': b'\xe8@\xf3\xdf\x00\x00\x00\x00+\x00...', 'size': 4096},
# {'addr': 8192, 'pa': 8192, 'data': b'c\x18\x10\x00\x00\x00...', 'size': 4096}]Please see VmmScatterMemory for information about how to use the VmmScatterObject returned by function vmm.memory.scatter_initialize(opt int: flags) which is documented below.
# Initialize a Scatter Physical Memory Read object which is used to simplify efficient memory reads.
# This is accomplished by using the simplified native MemProcFS VMMDLL_Scatter_* functionality.
# -- flags = flags as specified by memprocfs.FLAG_*.
# -- return
vmm.memory.scatter_initialize(opt int: flags) # -> VmmScatterMemory
# example:
# vmm.memory.scatter_initialize(memprocfs.FLAG_NOCACHE) -> VmmScatterMemory
# Write data (if supported) to physical memory.
# -- address_physical
# -- data
vmm.memory.write(int: address_physical, bytes: data) # -> None
# example:
# process.memory.write(0x1000, b'0000')
# Create a hexascii 'dump-style' string from bytes.
# -- data
# -- initial_offset = optional initial offset of data.
# -- return
vmm.hex(bytes: data, opt int: initial_offset) # -> str
# example:
# print(vmm.hex( vmm.read(0x1000, 0x20) )) ->
# 0000 e8 40 f3 df 00 00 00 00 2b 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 .@......+.......
# 0010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 10 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
# Search physical memory
# See API documentation for search/yara.
# -- addr_min = opt int: min physical address to search.
# -- addr_max = opt int: max physical address to search.
# -- flags = opt int: optional read flags memprocfs.FLAG_*.
# -- return = VmmSearch object.
vmm.search(opt int: addr_min, opt int: addr_max, opt int: flags) # -> VmmSearch
# example:
# vmm.search(0, 0x200000000, memprocfs.FLAG_NOCACHE) -> VmmSearch:Physical
# Yara search physical memory
# See API documentation for search/yara.
# -- rules = list str: yara rule(s) to use to search. str or list of str.
# -- addr_min = opt int: min physical address to search.
# -- addr_max = opt int: max physical address to search.
# -- results = opt int: max search results (max = 0x10000).
# -- flags = opt int: optional read flags memprocfs.FLAG_*.
# -- return = VmmYara object.
vmm.search_yara(list str: rules, opt int: min, opt int: max, opt int: results, opt int: flags) # -> VmmYara
# example:
# vmm.search_yara('c:/temp/rules.yar', 0, 0x200000000, 1000, memprocfs.FLAG_NOCACHE) -> VmmYara:Physical
# Retrieve the physical memory map of the system.
# -- return
vmm.maps.memmap() # -> list:list:int
# example:
# vmm.maps.memmap() ->
# [[4096, 651264], [1048576, 3738521600], [3739574272, 17301504], [3757285376, 548864],
# [3757965312, 65536], [4294967296, 2684354560]]
# Retrieve networking connection info.
# -- return
vmm.maps.net() # -> list:dict
# example:
# vmm.maps.net() ->
# [{'ver': 6, 'pid': 4, 'pooltag': 1415802956, 'state': 1, 'va': 18446644053909865472, 'time': 132162320706122210,
# 'time-str': '2019-10-22 15:34:30 UTC', 'src-ip': '::', 'src-port': 445, 'dst-ip': '::', 'dst-port': 0},
# ...]
# Retrieve user information.
# -- return
vmm.maps.user() # -> list:dict
# example:
# vmm.maps.user() ->
# [{'va-reghive': 18446663847596163072, 'sid': 'S-1-5-21-3317879871-105768242-2947499445-1001', 'name': 'User'},
# ...]
# Retrieve kernel device information.
# -- return
vmm.maps.kdevice() # -> list:dict
# example:
# vmm.maps.kdevice() ->
# [{'va': 18446697356379880928, 'depth': 0, 'type': 0, 'type_name': 'FILE_DEVICE_BUS_EXTENDER', 'va_driver_object': 18446697356459971328, 'va_attached_device': 0, 'va_file_system_device': 0, 'volume_info_str': ''},
# ...]
# Retrieve kernel driver information.
# -- return
vmm.maps.kdriver() # -> list:dict
# example:
# vmm.maps.kdriver() ->
# [{'va': 18446697356381322544, 'name': 'RAW', 'path': '\\FileSystem\\RAW', 'service_key_name': '', 'major_function': [18446735291007860560, ...]},
# ...]
# Retrieve kernel named objects information.
# -- return
vmm.maps.kobject() # -> list:dict
# example:
# vmm.maps.kobject() ->
# [{'va': 18446714959288364592, 'va_parent': 0, 'name': '\\', 'type': 'Directory', 'va_child': [18446697356386645024, ...]},
# ...]
# Retrieve services information.
# -- return = dict keyed by service ordinal.
vmm.maps.service() # -> dict:dict
# example:
# vmm.maps.service() ->
# {1: {'ordinal': 1, 'va-obj': 2187256236608, 'pid': 0, 'dwStartType': 3, 'dwServiceType': 1,
# 'dwCurrentState': 1, 'dwControlsAccepted': 0, 'dwWin32ExitCode': 1077,
# 'dwServiceSpecificExitCode': 0, 'dwCheckPoint': 0, 'dwWaitHint': 0, 'name': '1394ohci',
# 'name-display': '1394ohci', 'path': '', 'user-tp': '', 'user-acct': '',
# 'path-image': '\\SystemRoot\\System32\\drivers\\1394ohci.sys'},
# ...
# N: {...}}
# Retrieve info about select page frame numbers (PFNs).
# -- pfns_to_query = list of PFNs to query.
# -- return = dict keyed by pfn.
vmm.maps.pfn(list<int>: pfns_to_query) # -> dict:dict
# example:
# vmm.maps.pfn([1, 2]) ->
# {1: {'pfn': 1, 'pid': 0, 'va': 18446735127292674048, 'va-pte': 18446640152387256320, 'tp': 'Active', 'tpex': '-'},
# 2: {'pfn': 2, 'pid': 0, 'va': 0, 'va-pte': 18446639966764083528, 'tp': 'Bad', 'tpex': 'Unused'}}
# Retrieve all kernel pool allocations.
# Pool allocations are sorted by pool tag and virtual address.
# -- return
vmm.maps.pool() # -> dict
# example:
# vmm.maps.pool() ->
# { 'va': {18446690201385311152: {'va': 18446690201385311152, 'cb': 384, 'alloc': True, 'tpPool': 1, 'tpSS': 1, 'dwTag': 1701603654, 'tag': 'File'},
# ... }
# { 'tag': {'File': {18446690201385311152: {'va': 18446690201385311152, 'cb': 384, 'alloc': True, 'tpPool': 1, 'tpSS': 1, 'dwTag': 1701603654, 'tag': 'File'},
# ...},
# ...}}
# Retrieve only specific kernel pool allocations by pool tag.
# List consisting of string, bytes or integers are allowed.
# Pool allocations are sorted by pool tag and virtual address.
# -- return
vmm.maps.pool(opt list<string|bytes|int> pooltags) # -> dict
# example:
# vmm.maps.pool(['File', b'MmSt']) ->
# { 'va': {18446690201385311152: {'va': 18446690201385311152, 'cb': 384, 'alloc': True, 'tpPool': 1, 'tpSS': 1, 'dwTag': 1701603654, 'tag': 'File'},
# ... }
# { 'tag': {'File': {18446690201385311152: {'va': 18446690201385311152, 'cb': 384, 'alloc': True, 'tpPool': 1, 'tpSS': 1, 'dwTag': 1701603654, 'tag': 'File'},
# ...},
# ...}}Please see VmmVirtualMachine for information about how to use the VmmVirtualMachine returned by function vmm.maps.virtualmachines() which is documented below. Please also note that one of the startup arguments -vm / -vm-basic / -vm-nested must have been supplied at Vmm() initialization for vmm.maps.virtualmachines() to work.
# List available virtual machines. Please note that the VMM must have
# been initialized with the -vm option for virtual machines to parse.
# -- path = virtual file system path starting with '/' or '\\'
# -- return = list of VmmVirtualMachine
vmm.maps.virtualmachines() # -> list:VmmVirtualMachine
# example:
# vmm.maps.virtualmachines() ->
# [VmmVirtualMachine, VmmVirtualMachine, ...]
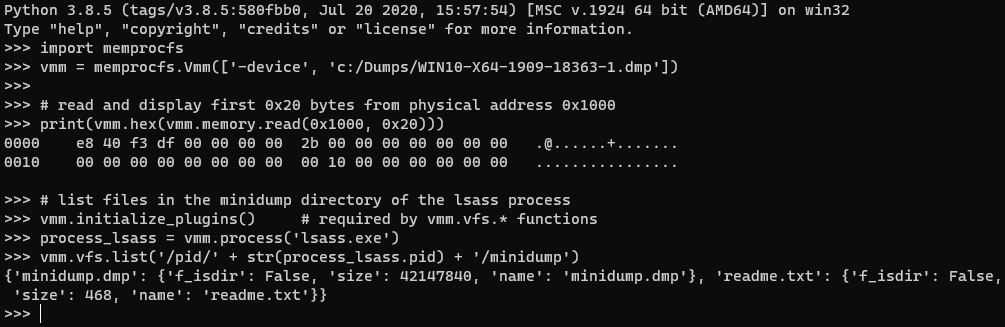
# List a directory in the MemProcFS virtual file system.
# -- path = virtual file system path starting with '/' or '\\'
# -- return = dict keyed by file name
vmm.vfs.list(str: path) # -> dict:dict
# example:
# vmm.vfs.list('/sys/services') ->
# {'services.txt': {'f_isdir': False, 'size': 180576, 'name': 'services.txt'},
# 'by-name': {'f_isdir': True, 'size': 0, 'name': 'by-name'},
# 'by-id': {'f_isdir': True, 'size': 0, 'name': 'by-id'}}
# Read a file in the virtual file system.
# -- filepath
# -- length = optional max length to read, default = 1MB.
# -- offset = optional starting file offset.
# -- return
vmm.vfs.read(str: filepath, opt int: length, opt int: offset) # -> bytes
# example:
# vmm.vfs.read('/sys/version-build.txt') -> b'18363'
# Write to a file in the virtual file system (if supported).
# -- filepath
# -- data
# -- offset = optional starting file offset.
vmm.vfs.write(str: filepath, bytes: data, opt int: offset) # -> None
# example:
# vmm.vfs.write('/.status/config_printf_enable.txt', b'1')Represents debug symbols for a specific module. Debug symbols are loaded from the Microsoft symbol server. Due to some overhead please use some care when selecting which modules to query.

-
module.pdb- symbols related to a specific module (if any). -
vmm.kernel.pdb- the ntoskrnl.exe 'nt' symbols.
pdb.module # str: the pdb symbols module. ex: pdb.module -> 'nt'# Retrieve a symbol address given its name.
# -- symbol_name = the symbol name.
# -- return = the symbol address.
pdb.symbol_address(str: symbol_name) # -> int: address
# example:
# pdb.symbol_address('PsCreateSystemThread') -> 18446735307940213600
# Retrieve a symbol name given its address offset.
# -- symbol_address_or_offset = address or offset to the symbol from module base (exact or nearby).
# -- return = the symbol name and the displacement (distance) to its location.
pdb.symbol_name(int: symbol_address_or_offset ) # -> dict: name info
# example #1:
# pdb.symbol_name(18446735307940213600) ->
# {'symbol': 'PsCreateSystemThread', 'displacement': 0}
# example #2:
# pdb.symbol_name(7254880) ->
# {'symbol': 'PsCreateSystemThread', 'displacement': 0}
# Retrieve the child name offset within a type.
# -- type_name = the name of the type.
# -- child_name = the struct name of the type child.
# -- return = an offset.
pdb.type_child_offset(str: type_name, str: child_name) # -> int: offset
# example:
# pdb.type_child_offset('_EPROCESS', 'Token') -> 864
# Retrieve the size of a type.
# -- type_name = the name of the type.
# -- return = the size of the type.
pdb.type_size(str: type_name) # -> int: type size
# example:
# pdb.type_size('_EPROCESS') -> 2176MemProcFS constants used by various functions. Constants are generally equal to constants in vmmdll.h.
Constants are generally accessed by memprocfs.<CONSTANT_NAME>.
PID_PROCESS_CLONE_WITH_KERNELMEMORY
# MemProcFS flags related to memory read() / write() functionality:
FLAG_NOCACHE # do not use the data cache (force reading from memory acquisition device)
FLAG_ZEROPAD_ON_FAIL # zero pad failed physical memory reads and report success if read within range of physical memory.
FLAG_FORCECACHE_READ # force use of cache - fail non-cached pages - only valid for reads, invalid with VMM_FLAG_NOCACHE/VMM_FLAG_ZEROPAD_ON_FAIL.
FLAG_NOPAGING # do not try to retrieve memory from paged out memory from pagefile/compressed (even if possible)
FLAG_NOPAGING_IO # do not try to retrieve memory from paged out memory if read would incur additional I/O (even if possible).
FLAG_NOCACHEPUT # do not write back to the data cache upon successful read from memory acquisition device.
FLAG_CACHE_RECENT_ONLY # only fetch from the most recent active cache region when reading.
FLAG_NO_PREDICTIVE_READ # do not perform additional predictive page reads (default on smaller requests).
# NTSTATUS values. (Used/Returned by Write file plugin callbacks).
STATUS_SUCCESS
STATUS_UNSUCCESSFUL
STATUS_END_OF_FILE
STATUS_FILE_INVALID
# SYSTEM values:
SYSTEM_UNKNOWN_X64
SYSTEM_WINDOWS_X64
SYSTEM_UNKNOWN_X86
SYSTEM_WINDOWS_X86
# MEMORYMODEL values:
MEMORYMODEL_NA
MEMORYMODEL_X86
MEMORYMODEL_X86PAE
MEMORYMODEL_X64
# NOTIFY EVENT values - received by the notify callback function for specific
# events occuring in the native plugin manager / VMM / MemProcFS.
PLUGIN_NOTIFY_VERBOSITYCHANGE
PLUGIN_NOTIFY_REFRESH_FAST # refresh fast event - at partial process refresh.
PLUGIN_NOTIFY_REFRESH_MEDIUM # refresh medium event - at full process refresh.
PLUGIN_NOTIFY_REFRESH_SLOW # refresh slow event - at registry refresh.
PLUGIN_NOTIFY_FORENSIC_INIT
PLUGIN_NOTIFY_FORENSIC_INIT_COMPLETE
# WINDOWS REGISTRY contants below:
WINREG_NONE
WINREG_SZ
WINREG_EXPAND_SZ
WINREG_BINARY
WINREG_DWORD
WINREG_DWORD_BIG_ENDIAN
WINREG_LINK
WINREG_MULTI_SZ
WINREG_RESOURCE_LIST
WINREG_FULL_RESOURCE_DESCRIPTOR
WINREG_RESOURCE_REQUIREMENTS_LIST
WINREG_QWORD
# CONFIG GET/SET OPTION VALUES BELOW:
# used together with vmm.get_config() / vmm.set_config()
OPT_CORE_PRINTF_ENABLE # RW
OPT_CORE_VERBOSE # RW
OPT_CORE_VERBOSE_EXTRA # RW
OPT_CORE_VERBOSE_EXTRA_TLP # RW
OPT_CORE_MAX_NATIVE_ADDRESS # R
OPT_CORE_LEECHCORE_HANDLE # R - underlying leechcore handle (do not close).
OPT_CORE_SYSTEM # R
OPT_CORE_MEMORYMODEL # R
OPT_CONFIG_IS_REFRESH_ENABLED # R - 1/0
OPT_CONFIG_TICK_PERIOD # RW - base tick period in ms
OPT_CONFIG_READCACHE_TICKS # RW - memory cache validity period (in ticks)
OPT_CONFIG_TLBCACHE_TICKS # RW - page table (tlb) cache validity period (in ticks)
OPT_CONFIG_PROCCACHE_TICKS_PARTIAL # RW - process refresh (partial) period (in ticks)
OPT_CONFIG_PROCCACHE_TICKS_TOTAL # RW - process refresh (full) period (in ticks)
OPT_CONFIG_VMM_VERSION_MAJOR # R
OPT_CONFIG_VMM_VERSION_MINOR # R
OPT_CONFIG_VMM_VERSION_REVISION # R
OPT_CONFIG_STATISTICS_FUNCTIONCALL # RW - enable function call statistics (.status/statistics_fncall file)
OPT_CONFIG_IS_PAGING_ENABLED # RW - 1/0
OPT_CONFIG_DEBUG # W
OPT_CONFIG_YARA_RULES # R
OPT_WIN_VERSION_MAJOR # R
OPT_WIN_VERSION_MINOR # R
OPT_WIN_VERSION_BUILD # R
OPT_WIN_SYSTEM_UNIQUE_ID # R
OPT_FORENSIC_MODE # RW - enable/retrieve forensic mode type [0-4].
OPT_REFRESH_ALL # W - refresh all caches
OPT_REFRESH_FREQ_MEM # W - refresh memory cache (excl. TLB) [fully]
OPT_REFRESH_FREQ_MEM_PARTIAL # W - refresh memory cache (excl. TLB) [partial 33%/call]
OPT_REFRESH_FREQ_TLB # W - refresh page table (TLB) cache [fully]
OPT_REFRESH_FREQ_TLB_PARTIAL # W - refresh page table (TLB) cache [partial 33%/call]
OPT_REFRESH_FREQ_FAST # W - refresh fast frequency - incl. partial process refresh
OPT_REFRESH_FREQ_MEDIUM # W - refresh medium frequency - incl. full process refresh
OPT_REFRESH_FREQ_SLOW # W - refresh slow frequency.
OPT_PROCESS_DTB # W - force set process directory table base. [LO-DWORD: Process PID]Sponsor PCILeech and MemProcFS:
PCILeech and MemProcFS is free and open source!
I put a lot of time and energy into PCILeech and MemProcFS and related research to make this happen. Some aspects of the projects relate to hardware and I put quite some money into my projects and related research. If you think PCILeech and/or MemProcFS are awesome tools and/or if you had a use for them it's now possible to contribute by becoming a sponsor!
If you like what I've created with PCIleech and MemProcFS with regards to DMA, Memory Analysis and Memory Forensics and would like to give something back to support future development please consider becoming a sponsor at: https://github.com/sponsors/ufrisk
Thank You 💖